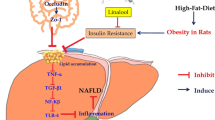
The study employed a rat model to examine the effects of taurine (Tau) on prevention and therapy of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In model rats maintained on a high-fat diet (HFD), the serum levels of ALT, AST, triglycerides, cholesterol, and LDL were higher than the corresponding levels in normal control and NP groups (p<0.05). In Tau-prevention and Tau-treatment groups, the serum levels of AST and triglycerides were lower than in HFD rats (p<0.05). In HFD rats, diffuse fatty degeneration and infiltration with inflammatory cells was observed in the liver; in the ileal mucosa, the villi were fractured or absent, the epithelium was exfoliated and infiltrated with inflammatory cells. The levels of TGF-β, IL-9, and their mRNA in the liver and ileal mucosa of HFD rats were significantly higher than in normal control and NP groups (p<0.05). In Tau-prevention and Tau-treatment groups, these levels were significantly lower than in HFD rats (p<0.05). Thus, TGF-β and IL-9 can be implicated in NAFLD genesis, while Tau can preventively or therapeutically diminish the damage to the liver and ileal mucosa in rats with this disease by down-regulating the expression of TGF-β and IL-9.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd Elwahab AH, Ramadan BK, Schaalan MF, Tolba AM. A Novel Role of SIRT1/FGF-21 in Taurine Protection Against Cafeteria Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis in Rats. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017;43(2):644-659. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480649
Chackelevicius CM, Gambaro SE, Tiribelli C, Rosso N. Th17 involvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016;22(41):9096-9103. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9096
Chakraborty S, Kubatzky KF, Mitra DK. An Update on Interleukin-9: From Its Cellular Source and Signal Transduction to Its Role in Immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20(9):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092113.
Chang YY, Chou CH, Chiu CH, Yang KT, Lin YL, Weng WL, Chen YC. Preventive effects of taurine on development of hepatic steatosis induced by a high-fat/cholesterol dietary habit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011;59(1):450-457. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf103167u
Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Kwon H, Galileos G, Gao W, Sobel RA, Mitsdoerffer M, Strom TB, Elyaman W, Ho IC, Khoury S, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-4 inhibits TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-beta, generates IL-9+ IL-10+ Foxp3(-) effector T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008;9(12):1347-1355. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1677
Demir M, Lang S, Steffen HM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - current status and future directions. J. Dig. Dis. 2015;16(10):541-557. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-2980.12291
Dietrich P, Hellerbrand C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014;28(4):637-653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2014.07.008
Feldman A, Eder SK, Felder TK, Kedenko L, Paulweber B, Stadlmayr A, Huber-Schönauer U, Niederseer D, Stickel F, Auer S, Haschke-Becher E, Patsch W, Datz C, Aigner E. Clinical and Metabolic Characterization of Lean Caucasian Subjects With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017;112(1):102-110. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2016.318
Fukuda N, Yoshitama A, Sugita S, Fujita M, Murakami S. Dietary taurine reduces hepatic secretion of cholesteryl ester and enhances fatty acid oxidation in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo). 2011;57(2):144-149. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.57.144
Liu F, Zhao JM, Rao HY, Yu WM, Zhang W, Theise ND, Wee A, Wei L. Second Harmonic Generation Reveals Subtle Fibrosis Differences in Adult and Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017;148(6):502-512. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/aqx104
Murakami S, Ono A, Kawasaki A, Takenaga T, Ito T. Taurine attenuates the development of hepatic steatosis through the inhibition of oxidative stress in a model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in vivo and in vitro. Amino Acids. 2018;50(9):1279-1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2605-8
Qin SY, Wang JX, Chen M, Yang XW, Jiang HX. Role and recruitment of Th9 cells in liver cirrhosis patients. Asian Pacific J. Trop. Biomed. 2016;6(4):330-334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.11.010
Tan C, Gery I. The unique features of Th9 cells and their products. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012;32(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevimmunol.v32.i1.10
Tan H, Wang S, Zhao L. A tumour-promoting role of Th9 cells in hepatocellular carcinoma through CCL20 and STAT3 pathways. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017;44(2):213-221. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12689
Zhu W, Chen S, Chen R, Peng Z, Wan J, Wu B. Taurine and tea polyphenols combination ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2017;17(1):455. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-1961-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 171, No. 5, pp. 613-619, May, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Z., Liang, G., Lv, Z.L. et al. Taurine Reduces Liver Damage in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model in Rats by Down-Regulating IL-9 and Tumor Growth Factor TGF-β. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 638–643 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05285-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05285-2