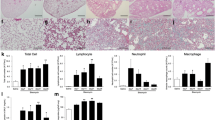
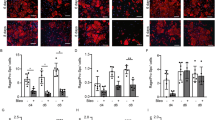
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis can be caused by different factors, including accumulation of pathological extracellular matrix (ECM) with abnormal composition, stiffness, and architecture in the lung tissue. We studied the effect of ECM produced by lung fibroblasts of healthy mice or mice with bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis on the process of endothelialto- mesenchymal transition, one of the main sources of effector myofibroblasts in fibrosis progression. Despite stimulation of spontaneous and TGFβ-1-induced differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts by fibrotic ECM, the appearance of α-SMA, the main marker of myofibroblasts, and its integration in stress fibrils in endotheliocytes were not observed under similar conditions. However, the expression of transcription factors SNAI1 and SNAI2/Slug and the production of components of fibrotic ECM (specific EDA-fibronectin splice form and collagen type I) were increased in endotheliocytes cultured on fibrotic ECM. Endothelium also demonstrated increased cell velocity in the models of directed cell migration. These data indicate activation of the intermediate state of the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in endotheliocytes upon contact with fibrotic, but not normal stromal matrix. In combination with the complex microenvironment that develops during fibrosis progression, it can lead to the replenishment of myofibroblasts pool from the resident endothelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basalova N, Sagaradze G, Arbatskiy M, Evtushenko E, Kulebyakin K, Grigorieva O, Akopyan Z, Kalinina N, Efimenko A. Secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells prevents myofibroblasts differentiation by transferring fibrosis-associated micrornas within extracellular vesicles. Cells. 2020;9(5):1272. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051272
Hashimoto N, Phan S. H, Imaizumi K, Matsuo M, Nakashima H, Kawabe T, Shimokata K, Hasegawa Y. Endothelialmesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010;43(2):161-172. doi: https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2009-0031OC
Herrera J, Henke CA, Bitterman PB. Extracellular matrix as a driver of progressive fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2018;128(1):45-53. doi: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI93557
Hinz B. Formation and function of the myofibroblast during tissue repair. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2007;127(3):526-537. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700613
Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009;326:1216-1219. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176009
Murphy PA, Hynes RO. Alternative splicing of endothelial fibronectin is induced by disturbed hemodynamics and protects against hemorrhage of the vessel wall. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014;34(9):2042-2050. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303879
Novoseletskaya E, Grigorieva O, Nimiritsky P, Basalova N, Eremichev R, Milovskaya I, Kulebyakin K, Kulebyakina M, Rodionov S, Omelyanenko N, Efimenko A. Mesenchymal stromal cell-produced components of extracellular matrix potentiate multipotent stem cell responce to differentiation stimuli. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020;8:555378. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.555378
Robertson IB, Horiguchi M, Zilberberg L, Dabovic B, Hadjiolova K, Rifkin DB. Latent TGF-β-binding proteins. Matrix Biol. 2015;47:44-53. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2015.05.005
Shinde AV, Kelsh R, Peters JH, Sekiguchi K, Van De Water L, McKeown-Longo PJ. The α4β1 integrin and the EDA domain of fibronectin regulate a profibrotic phenotype in dermal fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2015;41:26-35. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2014.11.004
Wang H, Luo X, Leighton J. Extracellular matrix and integrins in embryonic stem cell differentiation. Biochem. Insights. 2015;8(Suppl. 2):15-21. doi: https://doi.org/10.4137/BCI.S30377
Weiss A, Attisano L. The TGFbeta superfamily signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2013;2(1):47-63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/wdev.86
Xiao L, Dudley AC. Fine-tuning vascular fate during endothelial– mesenchymal transition. J. Pathol. 2017;241(1):25-35. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4814
Yoshimatsu Y, Watabe T. Roles of TGFβ-1 signals in endothelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac fibrosis. Int. J. Inflam. 2011;2011:724080. doi: https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/724080
Zeisberg EM, Potenta S, Xie L, Zeisberg M, Kalluri R. Discovery of endothelial to mesenchymal transition as a source for carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 2007;67(21):10123-10128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 2, pp. 97-106, June, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grigorieva, O.A., Vigovskiy, M.A., Dyachkova, U.D. et al. Mechanisms of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Induction by Extracellular Matrix Components in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 523–531 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05264-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05264-7