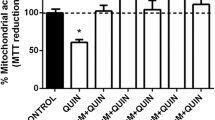
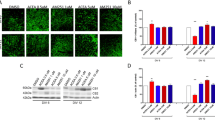
We studied the prolonged action of kainic acid on glutamatergic neurons in the dorsal hippocampus and the endocannabinoid-dependent protection against neurodegeneration. The pyramidal neurons of the CA3 field of the hippocampus, as well as granular and mossy cells of the dentate gyrus were examined. Light and electron microscopy revealed substantial damage to the components of the protein-synthesizing (rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and polyribosomes) and catabolic (lysosomes, autophagosomes, multivesicular structures, and lipofuscin formations) systems in all cells. Pyramidal and mossy neurons die mainly by the necrotic pathway. The death of granular cells occurred through both apoptosis and necrosis. The most vulnerable cells are mossy neurons located in the hilus. Activation of the endocannabinoid system induced by intracerebral injection of URB597, an inhibitor of degradation of endocannabinoid anandamide, protected the normal structure of the hippocampus and prevented neuronal damage and death induced by KA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell VA, Downer EJ. Cannabinoids and neuroprotection. Cannabinoids and the Brain. Köfalvi A, ed. Boston, 2008. P. 317-329.
Chen C, Qin H, Tan J, Hu Z, Zeng L. The role of ubiquitinproteasome pathway and autophagy lysosome pathway in cere bral ischemia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020;2020:5457049. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5457049
Karanian DA, Karim SL, Wood JT, Williams JS, Lin S, Makriyannis A, Bahr BA. Endocannabinoid enhancement protects against kainic acid-induced seizures and associated brain damage. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007;322(3):1059-1066. doi: https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.120147
Kron MM, Zhang H, Parent JM. The developmental stage of dentate granule cells dictates their contribution to seizureinduced plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2010;30(6):2051-2059. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5655-09.2010
Lupica CR, Hu Y, Devinsky O, Hoffman AF. Cannabinoids as hippocampal network administrators. Neuropharmacol. 2017;124:25-37. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.04.003
Méndez-Armenta M, Nava-Ruíz C, Juárez-Rebollar D, Rodríguez-Martínez E, Gómez PY. Oxidative stress asso ciated with neuronal apoptosis in experimental models of epilepsy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014;2014:293689. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/293689
Monory K, Massa F, Egertová M, Eder M, Blaudzun H, Westenbroek R, Kelsch W, Jacob W, Marsch R, Ekker M, Long J, Rubenstein JL, Goebbels S, Nave KA, During M, Klugmann M, Wölfel B, Dodt HU, Zieglgänsberger W, Wotjak CT, Mackie K, Elphick MR, Marsicano G, Lutz B. The endocannabinoid system controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus. Neuron. 2006;51(4):455-466. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.07.006
Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Sydney, 1998.
Scharfman HE. Advances in understanding hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;373(3):643-652. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2750-5
Sulzer D, Mosharov E, Talloczy Z, Zucca FA, Simon JD, Zecca L. Neuronal pigmented autophagic vacuoles: lipofuscin, neuromelanin, and ceroid as macroautophagic responses during aging and disease. J. Neurochem. 2008;106(1):24-36. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05385.x
Thodeson DM, Brulet R, Hsieh J. Neural stem cells and epilepsy: functional roles and disease-in-a-dish models. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;371(1):47-54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2675-z
Vincent P, Mulle C. Kainate receptors in epilepsy and excitotoxicity. Neuroscience. 2009;158(1):309-323. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.066
Yuan Y, Wang H, Wei Z, Li W. Impaired autophagy in hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus and its implication in schizophrenia. J. Genet. Genomics. 2015;42(1):1-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2014.12.001
Zheng XY, Zhang HL, Luo Q, Zhu J. Kainic acid-induced neurodegenerative model: potentials and limitations. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011;2011:457079. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/457079
Zhou H, Chen L, Gao X, Luo B, Chen J. Moderate traumatic brain injury triggers rapid necrotic death of immature neurons in the hippocampus. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012;71(4):348-359. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e31824ea078
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 171, No. 3, pp. 307-312, March, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordon, R.Y., Mikheeva, I.B., Shubina, L.V. et al. Kainate-Induced Degeneration of Hippocampal Neurons. Protective Effect of Activation of the Endocannabinoid System. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 327–332 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05221-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05221-4