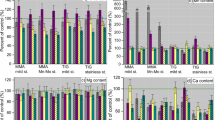
Histological and morphometric studies of brain autopsy material showed that the development of hypoxic changes in miners starts at the early stages of working in the dusty atmosphere. Edema of the pericellular and perivascular zones and the pia mater, degenerative changes in some nerve cells and even their loss and formation of gliosis foci were identified. The revealed changes in neurons progressed with increasing the duration of working under hazardous conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Velitchkovsky BT. Pathogenesis and classification of dust diseases. Med. Truda Prom. Ekol. 2003;(7):8-13. Russian.
Vetrovoy OV, Rybnikova EA, Samoilov MO. Cerebral mechanisms of hypoxic/ischemic postconditioning. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2017;82(3):392-400.
Droblenkov AV, Naumov NV, Monid MV, Valkovich EI, Shabanov PD. Reactive changes of the rat brain cellular elements under different conditions of circulatory hypoxia. Morfologiya. 2013;143(3):14-21. Russian.
Zhukova AG, Sazontova TG, Arkhipenko YuV, Volkov AV. Gender differences in the pro- and antioxidant systems of the brain in the late postresuscitative period (an experimental study). Obshch. Reanimatol. 2010;6(4):54-57. Russian.
Zhukova AG, Ulanova EV, Fomenko DV, Kazitskaya AS, Yadykina TK. Specificity of cellular response to various occupational toxicants. Med. Truda Prom. Ekol. 2011;(7):23-26. Russian.
Chebotarev AG. Current working environment at mines and ways of its improvement. Gornaya Prom. 2012;(2):84-88. Russian.
Chebotarev AG. Working environment and occupational morbidity of mine personnel. Gornaya Prom. 2018;(1):92-95. doi: 10.30686/1609-9192-2018-1-137-92-95. Russian.
Chertok VM, Nevzorova VA, Zakharchuk NV, Chertok AG. The comparative characteristic of the neurons containing the hypoxia-inducible factor lalpha and 2alpha in the brain of rats at hypertension. Tsitologiya. 2018;60(11):883-888. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0041377118110032. Russian.
Armutcu F, Gun BD, Altin R, Gurel A. Examination of lung toxicity, oxidant/antioxidant status and effect of erdosteine in rats kept in coal mine ambience. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007;24(2):106-113. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2007.03.002
Batool AI, Naveed NH, Aslam M, da Silva J, Rehman MFU. Coal dust-induced systematic hypoxia and redox imbalance among coal mine workers. ACS Omega. 2020;5(43):28204-28211. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03977
Cui X, Xing J, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Luo X, Zhang Z, Han W, Wu T, Chen W. COPD and levels of Hsp70 (HSPA1A) and Hsp27 (HSPB1) in plasma and lymphocytes among coal workers: a case-control study. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015;20(3):473- 481. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0572-5
Wang H, Xing J, Wang F, Han W, Ren H, Wu T, Chen W. Expression of Hsp27 and Hsp70 in lymphocytes and plasma in healthy workers and coal miners with lung cancer. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2010;30(4):415-420. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0441-5
Zakharenkov VV, Mikhailova NN, Zhdanova NN, Gorokhova LG, Zhukova AG. Experimental study of the mechanisms of intracellular defense in cardiomyocytes associated with stages of anthracosilicosis development. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015;159(4):431-434. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-2983-9
Zhukova AG, Mikhailova NN, Sazontova TG, Zhdanova NN, Kazitskaya AS, Bugaeva MS, Gorokhova LG, Arkhipenko YV. Participation of free-radical processes in structural and metabolic disturbances in the lung tissues caused by exposure to coal-rock dust and their adaptogenic correction. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020;168(4):439-443. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04727-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 171, No. 2, pp. 228-231, February, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bugaeva, M.S., Bondarev, O.I., Mikhailova, N.N. et al. Pathomorphological Changes in the Brain in Dynamics of Long-Term Dust Exposure. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 258–261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05207-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05207-2