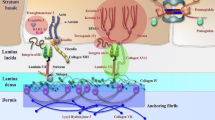
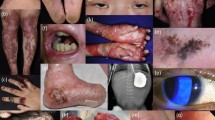
Epidermolysis bullosa is a severe hereditary disease caused by mutations in genes encoding cutaneous basement membrane proteins. These mutations lead to dermal-epidermal junction failure and, as a result, to disturbances in the morphological integrity of the skin. Clinically, it manifests in the formation of blisters on the skin or mucosa that in some cases can turn into non-healing chronic wounds, which not only impairs patient’s quality of life, but also is a live-threatening condition. Now, the main approaches in the treatment of epidermolysis bullosa are symptomatic therapy and palliative care, though they are little effective and are aimed at reducing the pain, but not to complete recovery. In light of this, the development of new treatment approaches aimed at correction of genetic defects is in progress. Various methods based on genetic engineering technologies, transplantation of autologous skin cells, progenitor skin cells, as well as hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells are studied. This review analyzes the pathogenetic methods developed for epidermolysis bullosa treatment based on the latest achievements of molecular genetics and cellular technologies, and discusses the prospects for the use of these technologies for the therapy of epidermolysis bullosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson SD, McGilligan VE, Liao H, Szeverenyi I, Smith FJ, Moore CB, McLean WH. Development of allele-specific therapeutic siRNA for keratin 5 mutations in epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2011;131(10):2079-2086. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.169
Bauer JW, Koller J, Murauer EM, De Rosa L, Enzo E, Carulli S, Bondanza S, Recchia A, Muss W, Diem A, Mayr E, Schlager P, Gratz IK, Pellegrini G, De Luca M. Closure of a large chronic wound through transplantation of gene-corrected epidermal stem cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2017;137(3):778-781. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2016.10.038
Bauer JW, Lanschuetzer C. Type XVII collagen gene mutations in junctional epidermolysis bullosa and prospects for gene therapy. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2003;28(1):53-60. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2230.2003.01192.x
Blanpain C, Horsley V, Fuchs E. Epithelial stem cells: turning over new leaves. Cell. 2007;128(3):445-458. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.014
Burke JF, Mogg AE. Suppression of a nonsense mutation in mammalian cells in vivo by the aminoglycoside antibiotics G-418 and paromomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13(17):6265-6272. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/13.17.6265
Chamorro C, Mencía A, Almarza D, Duarte B, Büning H, Sallach J, Hausser I, Del Río M, Larcher F, Murillas R. Gene editing for the efficient correction of a recurrent COL7A1 mutation in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2016;5(4):e307. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2016.19
Chen ZY, He CY, Ehrhardt A, Kay MA. Minicircle DNA vectors devoid of bacterial DNA result in persistent and high-level transgene expression in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2003;8(3):495-500. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1525-0016(03)00168-0
Chiavérini C, Charlesworth A, Meneguzzi G, Lacour J.P, Ortonne J.P. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy. Dermatol. Clin. 2010;28(2):245-255, viii. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2010.01.001
Conget P, Rodriguez F, Kramer S, Allers C, Simon V, Palisson F, Gonzalez S, Yubero MJ. Replenishment of type VII collagen and re-epithelialization of chronically ulcerated skin after intradermal administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells in two patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(3):429-431. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/14653241003587637
Coulombe PA, Kerns ML, Fuchs E. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: a paradigm for disorders of tissue fragility. J. Clin. Invest. 2009;119(7):1784-1793. doi: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI38177
Coulombe PA, Lee CH. Defining keratin protein function in skin epithelia: epidermolysis bullosa simplex and its aftermath. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012;132(3, Pt 2):763-775. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.450
Cuadrado-Corrales N, Sánchez-Jimeno C, García M, Escámez MJ, Illera N, Hernández-Martín A, Trujillo-Tiebas MJ, Ayuso C, Del Rio M. A prevalent mutation with founder effect in Spanish recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa families. BMC Med. Genet. 2010;11:139. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-11-139
Dang N, Klingberg S, Rubin AI, Edwards M, Borelli S, Relic J, Marr P, Tran K, Turner A, Smith N, Murrell DF. Differential expression of pyloric atresia in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with ITGB4 mutations suggests that pyloric atresia is due to factors other than the mutations and not predictive of a poor outcome: three novel mutations and a review of the literature. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2008;88(5):438-448. doi: https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-0484
Davies J, Gilbert W, Gorini L. Streptomycin, suppression, and the code. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1964;51(5):883-890. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.51.5.883
De Luca M, Pellegrini G, Green H. Regeneration of squamous epithelia from stem cells of cultured grafts. Regen. Med. 2006;1(1):45-57. doi: https://doi.org/10.2217/17460751.1.1.45
De Luca M, Pellegrini G, Mavilio F. Gene therapy of inherited skin adhesion disorders: a critical overview. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009;161(1):19-24. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09243.x
De Ravin SS, Su L, Theobald N, Choi U, Macpherson JL, Poidinger M, Symonds G, Pond SM, Ferris AL, Hughes SH, Malech HL, Wu X. Enhancers are major targets for murine leukemia virus vector integration. J. Virol. 2014;88(8):4504-4513. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00011-14
De Rosa L, Carulli S, Cocchiarella F, Quaglino D, Enzo E, Franchini E, Giannetti A, De Santis G, Recchia A, Pellegrini G, De Luca M. Long-term stability and safety of transgenic cultured epidermal stem cells in gene therapy of junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Stem Cell Reports. 2013;2(1):1-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2013.11.001
Di Nunzio F, Maruggi G, Ferrari S, Di Iorio E, Poletti V, Garcia M, Del Rio M, De Luca M, Larcher F, Pellegrini G, Mavilio F. Correction of laminin-5 deficiency in human epidermal stem cells by transcriptionally targeted lentiviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 2008;16(12):1977-1985. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2008.204
Dul M, Stefanidou M, Porta P, Serve J, O’Mahony C, Malissen B, Henri S, Levin Y, Kochba E, Wong FS, Dayan C, Coulman SA, Birchall JC. Hydrodynamic gene delivery in human skin using a hollow microneedle device. J. Control. Release. 2017;265:120-131. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.02.028
El-Darouti M, Fawzy M, Amin I, Abdel Hay R, Hegazy R, Gabr H, El Maadawi Z. Treatment of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa with bone marrow non-hematopoeitic stem cells: a randomized controlled trial. Dermatol. Ther. 2016;29(2):96-100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.12305
Fine JD. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010;5:12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-5-12
Fine JD, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Eady RA, Bauer EA, Bauer JW, Has C, Heagerty A, Hintner H, Hovnanian A, Jonkman MF, Leigh I, Marinkovich MP, Martinez AE, McGrath JA, Mellerio JE, Moss C, Murrell DF, Shimizu H, Uitto J, Woodley D, Zambruno G. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014;70(6):1103-1126. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2014.01.903
Fine JD, Eady RA, Bauer EA, Briggaman RA, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Christiano A, Heagerty A, Hintner H, Jonkman MF, McGrath J, McGuire J, Moshell A, Shimizu H, Tadini G, Uitto J. Revised classification system for inherited epidermolysis bullosa: Report of the second international consensus meeting on diagnosis and classification of epidermolysis bullosa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000;42(6):1051-1066.
Finkel RS, Flanigan KM, Wong B, Bönnemann C, Sampson J, Sweeney HL, Reha A, Northcutt VJ, Elfring G, Barth J, Peltz SW. Phase 2a study of ataluren-mediated dystrophin production in patients with nonsense mutation Duchenne muscular dystrophy. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e81302. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081302
Gambardella L, Barrandon Y. The multifaceted adult epidermal stem cell. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003;15(6):771-777. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2003.10.011
Georgiadis C, Syed F, Petrova A, Abdul-Wahab A, Lwin SM, Farzaneh F, Chan L, Ghani S, Fleck RA, Glover L, McMillan JR, Chen M, Thrasher AJ, McGrath JA, Di WL, Qasim W. Lentiviral engineered fibroblasts expressing codon-optimized COL7A1 restore anchoring fibrils in RDEB. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2016;136(1):284-292. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/JID.2015.364
Gorell E, Nguyen N, Lane A, Siprashvili Z. Gene therapy for skin diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014;4(4):a015149. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a015149
Gostyńska KB, Yenamandra VK, Lindemans C, Duipmans J, Gostyński A, Jonkman MF, Boelens JJ. Allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation for epidermolysis bullosa: the Dutch experience. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019;99(3):347-348. doi: https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-3097
Gostynski A, Deviaene F.C, Pasmooij AM, Pas HH, Jonkman MF. Adhesive stripping to remove epidermis in junctional epidermolysis bullosa for revertant cell therapy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009;161(2):444-447. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09118.x
Gostyński A, Pasmooij AM, Jonkman MF. Successful therapeutic transplantation of revertant skin in epidermolysis bullosa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014;70(1):98-101. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2013.08.052
Guerra L, Odorisio T, Zambruno G, Castiglia D. Stromal microenvironment in type VII collagen-deficient skin: The ground for squamous cell carcinoma development. Matrix Biol. 2017;63:1-10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2017.01.002
Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Von Kalle C, Schmidt M, McCormack MP, Wulffraat N, Leboulch P, Lim A, Osborne CS, Pawliuk R, Morillon E, Sorensen R, Forster A, Fraser P, Cohen JI, de Saint Basile G, Alexander I, Wintergerst U, Frebourg T, Aurias A, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Romana S, Radford-Weiss I, Gross F, Valensi F, Delabesse E, Macintyre E, Sigaux F, Soulier J, Leiva LE, Wissler M, Prinz C, Rabbitts TH, Le Deist F, Fischer A, Cavazzana-Calvo M. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCIDX1. Science. 2003;302:415-419. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1088547
Hammersen J, Has C, Naumann-Bartsch N, Stachel D, Kiritsi D, Söder S, Tardieu M, Metzler M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Schneider H. Genotype, clinical course, and therapeutic decision making in 76 infants with severe generalized junctional epidermolysis bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2016;136(11):2150-2157. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.609
Haneke E, Anton-Lamprecht I. Ultrastructure of Blister Formation in Epidermolysis Bullosa Hereditaria: V. Ultrastructure of blister formation in epidermolysis bullosa hereditaria: V. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex localisata type Weber-Cockayne. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1982;78(3):219-223. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506502
Has C, Bruckner-Tuderman L. The genetics of skin fragility. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2014;15:245-268. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-090413-025540
Has C, Herz C, Zimina E, Qu HY, He Y, Zhang ZG, Wen TT, Gache Y, Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L. Kindlin-1 is required for RhoGTPase-mediated lamellipodia formation in keratinocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2009;175(4):1442-1452. doi: https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2009.090203
Hovnanian A. Systemic protein therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: how far are we from clinical translation? J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013;133(7):1719-1721. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.137
Kaviarasan PK, Prasad PV, Shradda, Viswanathan P. Kindler syndrome. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2005; 71(5):348-350. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.16788
Kiritsi D, Huilaja L, Franzke CW, Kokkonen N, Pazzagli C, Schwieger-Briel A, Larmas M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Has C, Tasanen K. Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with LAMB3 splice-site mutations. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015;95(7):849-851. doi: https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-2073
Kocher T, Peking P, Klausegger A, Murauer EM, Hofbauer JP, Wally V, Lettner T, Hainzl S, Ablinger M, Bauer JW, Reichelt J, Koller U. Cut and paste: efficient homology-directed repair of a dominant negative KRT14 mutation via CRISPR/Cas9 nickases. Mol. Ther. 2017;25(11):2585-2598. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.08.015
Koga H, Prost-Squarcioni C, Iwata H, Jonkman MF, Ludwig RJ, Bieber K. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: the 2019 update. Front. Med (Lausanne). 2019;5:362. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00362
LaFave MC, Varshney GK, Gildea DE, Wolfsberg TG, Baxevanis AD, Burgess SM. MLV integration site selection is driven by strong enhancers and active promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(7):4257-4269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1399
Lai-Cheong JE, McGrath JA, Uitto J. Revertant mosaicism in skin: natural gene therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2011;17(3):140-148. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2010.11.003
Leachman SA, Hickerson RP, Schwartz ME, Bullough EE, Hutcherson SL, Boucher KM, Hansen CD, Eliason MJ, Srivatsa GS, Kornbrust DJ, Smith FJ, McLean WI, Milstone LM, Kaspar RL. First-in-human Mutation-targeted siRNA Phase Ib Trial of an Inherited Skin Disorder. Mol. Ther. 2010;18(2):442-446. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2009.273
Lee HL, Dougherty JP. Pharmaceutical therapies to recode nonsense mutations in inherited diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012;136(2):227-266. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.07.007
Longo V, Rebulla P, Pupella S, Zolla L, Rinalducci S. Proteomic characterization of platelet gel releasate from adult peripheral and cord blood. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2016;10(8):870-882. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201500126
Mabuchi E, Umegaki N, Murota H, Nakamura T, Tamai K, Katayama I. Oral steroid improves bullous pemphigoid-like clinical manifestations in non-Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa with COL17A1 mutation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007;157(3):596-598. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08046.x
March OP, Reichelt J, Koller U. Gene editing for skin diseases: designer nucleases as tools for gene therapy of skin fragility disorders. Exp. Physiol. 2018;103(4):449-455. doi: https://doi.org/10.1113/EP086044
Mauritz P, Jonkman MF, Visser SS, Finkenauer C, Duipmans JC, Hagedoorn M. Impact of painful wound care in epidermolysis bullosa during childhood: an interview study with adult patients and parents. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019;99(9):783-788. doi: https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-3179
Mavilio F, Pellegrini G, Ferrari S, Di Nunzio F, Di Iorio E, Recchia A, Maruggi G, Ferrari G, Provasi E, Bonini C, Capurro S, Conti A, Magnoni C, Giannetti A, De Luca M. Correction of junctional epidermolysis bullosa by transplantation of genetically modified epidermal stem cells. Nat. Med. 2006;12(12):1397-1402. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1504
McBride JD, Rodriguez-Menocal L, Candanedo A, Guzman W, Garcia-Contreras M, Badiavas EV. Dual mechanism of type VII collagen transfer by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles to recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa fibroblasts. Biochimie. 2018;155:50-58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2018.04.007
McGrath JA. Recently identified forms of epidermolysis bullosa. Ann. Dermatol. 2015;27(6):658-666. doi: https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.658
Morgan CP, Allen DSI, Millington-Ward S, O’Dwyer GE, Palfi A, Jane Farrar G. A mutation-independent therapeutic strategy for dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013;133(12):2793-2796. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.241
Murauer EM, Gache Y, Gratz IK, Klausegger A, Muss W, Gruber C, Meneguzzi G, Hintner H, Bauer JW. Functional correction of type VII collagen expression in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2011;131(1):74-83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2010.249
Murauer EM, Koller U, Pellegrini G, De Luca M, Bauer JW. Advances in gene/cell therapy in epidermolysis bullosa. Keio J. Med. 2015;64(2):21-25. doi: https://doi.org/10.2302/kjm.2014-0013-RE
Naldini L, Blömer U, Gallay P, Ory D, Mulligan R, Gage FH, Verma IM, Trono D. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science. 1996;272:263-267. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5259.263
Nanba D. Human keratinocyte stem cells: from cell biology to cell therapy. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019;96(2):66-72. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2019.10.002
Nayerossadat N, Maedeh T, Ali PA. Viral and nonviral delivery systems for gene delivery. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2012;1:27. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.98152
Nyström A, Bruckner-Tuderman L. Gene therapy for epidermolysis bullosa: sticky business. Mol. Ther. 2016;24(12):2035-2036. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2016.199
O’Connor N, Mulliken JB, Banks-Schlegel S, Kehinde O, Green H. Grafting of burns with cultured epithelium prepared from autologous epidermal cells. Lancet. 1981;1:75-78.
Peking P, Koller U, Hainzl S, Kitzmueller S, Kocher T, Mayr E, Nyström A, Lener T, Reichelt J, Bauer JW, Murauer EM. A gene gun-mediated nonviral RNA trans-splicing strategy for Col7a1 repair. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2016;5:e287. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2016.3
Peking P, Koller U, Murauer EM. Functional therapies for cutaneous wound repair in epidermolysis bullosa. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018;129:330-343. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.12.003
Pendaries V, Gasc G, Titeux M, Tonasso L, Mejía JE, Hovnanian A. siRNA-mediated allele-specific inhibition of mutant type VII collagen in dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012;132(6):1741-1743. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.11
Perdoni C, Osborn MJ, Tolar J. Gene editing toward the use of autologous therapies in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Transl. Res. 2016;168:50-58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2015.05.008
Petrof G, Lwin SM, Martinez-Queipo M, Abdul-Wahab A, Tso S, Mellerio JE, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Boelens JJ, Tolar J, Veys P, Ofuya M, Peacock JL, Martinez AE, McGrath JA. Potential of systemic allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for children with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015;135(9):2319-2321. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2015.158
Petrof G, Martinez-Queipo M, Mellerio JE, Kemp P, Mc-Grath JA. Fibroblast cell therapy enhances initial healing in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa wounds: results of a randomized, vehicle-controlled trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013;169(5):1025-1033. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.12599
Prow TW, Grice JE, Lin LL, Faye R, Butler M, Becker W, Wurm EM, Yoong C, Robertson TA, Soyer HP, Roberts MS. Nanoparticles and microparticles for skin drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011;63(6):470-491. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.01.012
Sallach J, Di Pasquale G, Larcher F, Niehoff N, Rübsam M, Huber A, Chiorini J, Almarza D, Eming SA, Ulus H, Nishimura S, Hacker UT, Hallek M, Niessen CM, Büning H. Tropismmodified AAV vectors overcome barriers to successful cutaneous therapy. Mol. Ther. 2014;22(5):929-939. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2014.14
Schepeler T, Page ME, Jensen KB. Heterogeneity and plasticity of epidermal stem cells. Development. 2014;141(13):2559-2567. doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.104588
Schröder AR, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry C, Ecker JR, Bushman F. HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell. 2002;110(4):521-529. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00864-4
Shinkuma S. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a review. Clin. Cosmet. Invest. Dermatol. 2015;8:275-284. doi https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S54681
Shinkuma S, Guo Z, Christiano AM. Site-specific genome editing for correction of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113(20):5676-5681. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512028113
Siprashvili Z, Nguyen NT, Bezchinsky MY, Marinkovich MP, Lane AT, Khavari PA. Long-term type VII collagen restoration to human epidermolysis bullosa skin tissue. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010;21(10):1299-1310. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2010.023
Siprashvili Z, Nguyen NT, Gorell ES, Loutit K, Khuu P, Furukawa LK, Lorenz HP, Leung TH, Keene DR, Rieger KE, Khavari P, Lane AT, Tang JY, Marinkovich MP. Safety and wound outcomes following genetically corrected autologous epidermal grafts in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. JAMA. 2016;316(17):1808-1817. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.15588
Soro L, Bartus C, Purcell S. Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a review of disease pathogenesis and update on future therapies. J. Clin. Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8(5):41-46.
Tockner B, Kocher T, Hainzl S, Reichelt J, Bauer JW, Koller U, Murauer EM. Construction and validation of an RNA transsplicing molecule suitable to repair a large number of COL7A1 mutations. Gene Ther. 2016;23(11):775-784. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2016.57
Tolar J, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Riddle M, McElmurry RT, Osborn M, Xia L, Lund T, Slattery C, Uitto J, Christiano AM, Wagner JE, Blazar BR. Amelioration of epidermolysis bullosa by transfer of wild-type bone marrow cells. Blood. 2009;113(5):1167-1174. doi: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-06-161299
Turczynski S, Titeux M, Pironon N, Hovnanian A. Antisensemediated exon skipping to reframe transcripts. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012;867:221-238. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-767-5_15
Uitto J, Bruckner-Tuderman L, McGrath JA, Riedl R, Robinson C. EB2017 — Progress in epidermolysis bullosa research toward treatment and cure. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2018;138(5):1010-1016. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.12.016
Umegaki-Arao N, Pasmooij AM, Itoh M, Cerise JE, Guo Z, Levy B, Gostyński A, Rothman LR, Jonkman MF, Christiano AM. Induced pluripotent stem cells from human revertant keratinocytes for the treatment of epidermolysis bullosa. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014;6(264):264ra164. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009342
Ussar S, Moser M, Widmaier M, Rognoni E, Harrer C, Genzel-Boroviczeny O, Fässler R. Loss of Kindlin-1 causes skin atrophy and lethal neonatal intestinal epithelial dysfunction. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(12):e1000289. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000289
van den Akker PC, Jonkman MF, Rengaw T, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Has C, Bauer JW, Klausegger A, Zambruno G, Castiglia D, Mellerio JE, McGrath JA, van Essen AJ, Hofstra RM, Swertz MA. The international dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patient registry: An online database of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients and their COL7A1 mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2011;32(10):1100-1107. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.21551
Vanden Oever M, Twaroski K, Osborn MJ, Wagner JE, Tolar J. Inside out: regenerative medicine for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatr. Res. 2018;83(1-2):318-324. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2017.244.
Wagner JE, Ishida-Yamamoto A, McGrath JA, Hordinsky M, Keene DR, Woodley DT, Chen M, Riddle MJ, Osborn MJ, Lund T, Dolan M, Blazar BR, Tolar J. Bone marrow transplantation for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;363(7):629-639. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0910501
Wally V, Brunner M, Lettner T, Wagner M, Koller U, Trost A, Murauer EM, Hainzl S, Hintner H, Bauer JW. K14 mRNA reprogramming for dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010;19(23):4715-4725. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq405
Wally V, Klausegger A, Koller U, Lochmüller H, Krause S, Wiche G, Mitchell LG, Hintner H, Bauer JW. 5’ trans-splicing repair of the PLEC1 gene. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2008;128(3): 568-574. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701152
Weber F, Bauer JW, Sepp N, Högler W, Salmhofer W, Hintner H, Fritsch P. Squamous cell carcinoma in lunctional and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2001;81:189-192. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/000155501750376285
Wong T, Gammon L, Liu L, Mellerio JE, Dopping-Hepenstal PJ, Pacy J, Elia G, Jeffery R, Leigh IM, Navsaria H, McGrath JA. Potential of fibroblast cell therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2008;128(9):2179-2189. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.78
Woodley DT, Cogan J, Hou Y, Lyu C, Marinkovich MP, Keene D, Chen M. Gentamicin induces functional type VII collagen in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients. J. Clin. Invest. 2017;127(8):3028-3038. doi: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI92707
Wu W, Lu Z, Li F, Wang W, Qian N, Duan J, Zhang Y, Wang F, Chen T. Efficient in vivo gene editing using ribonucleoproteins in skin stem cells of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa mouse model. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114(7):1660-1665. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1614775114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 1, pp. 3-17, March, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryumina, I.I., Goryunov, K.V., Silachev, D.N. et al. Pathogenetic Therapy of Epidermolysis Bullosa: Current State and Prospects. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 109–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05182-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05182-8