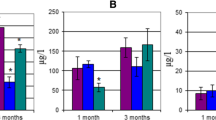
This article describes models for the study of acute desynchronosis: jetlag syndrome and acute desynchronosis under physical stress for possible pharmacological correction of these disorders. The cosinor analysis allowed assessing significance of changes in biological rhythms in 2 biological models: the jetlag-type diurnal rhythm shift model and the model with changed light mode. The revealed changes in the rhythms of biochemical parameters in the blood serum of animals with acute desynchronosis indicate significant changes in the intensity of carbohydrate-lipid metabolism, which affected the processes of cell bioenergetics. These changes are most pronounced in the group of animals that were kept under conditions of constant darkness, which can serve as a marker of the initial stage of pathological desynchronosis. The jetlag-type model can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the pharmacological correction of physiological desynchronosis. The model with modified light regimen can be used for evaluation of the effectiveness of pharmacological correction of pathological desynchronosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batotsyrenova EG. The influence of disbalance light conditions on the parameters of acid-base balance after intensive physical exercise. Medline.ru. Ross. Biomed. Zh. 2018;19(4):1204- 1216. Russian.
Batotsyrenova EG, Kashuro VA, Ivanov MB. Markers of energy metabolism in destabilization of circadian rhythms. Vopr. Biol., Med. Farm. Khimii. 2017;20(11):39-42. Russian.
Batotsyrenova EG, Kashuro VA, Ivanov MB, Stepanov SV, Skomorokhova EB. Change in the indicators of energy metabolism under condition of desynchronosis. Acta Naturae. 2016;(Suppl. 1):182-186. Russian.
Karp VP, Katinas GS. Mathematical methods of analysis of biological rhythms. Chronobiology and chronomedicine. Moscow, 1989. P. 29-45. Russian.
Chronobiology and chronomedicine. Rapoport SI, Frolov VA, Khetagurova LG, eds. Moscow, 2012. Russian.
Eckel-Mahan K, Sassone-Corsi P. Metabolism control by the circadian clock and vice versa. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009;16(5):462-467. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1595
Gao S, Casals N, Keung W, Moran TH, Lopaschuk GD. Differential effects of central ghrelin on fatty acid metabolism in hypothalamic ventral medial and arcuate nuclei. Physiol. Behav. 2013;118:165-70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.03.030
Green CB, Takahashi JS, Bass J. The meter of metabolism. Cell. 2008;134(5):728-742. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.022
Shearman LP, Sriram S, Weaver DR, Maywood ES, Chaves I, Zheng B, Kume K, Lee CC, van der Horst GT, Hastings MH, Reppert SM. Interacting molecular loops in the mammalian circadian clock. Science. 2000;288:1013-1019.
Taïb B, Bouyakdan K, Hryhorczuk C, Rodaros D, Fulton S, Alquier T. Glucose regulates hypothalamic long-chain fatty acid metabolism via AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) in neurons and astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288(52):37 216-37 229. doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.506238
Tseng HL, Yang SC, Yang SH, Shieh KR. Hepatic circadianclock system altered by insulin resistance, diabetes and insulin sensitizer in mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(3). e0120380. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120380
Zeng L, Ming C, Li Y, Su LY, Su YH, Otecko NO, Liu HQ, Wang MS, Yao YG, Li HP, Wu DD, Zhang YP. Rapid Evolution of Genes Involved in Learning and Energy Metabolism for Domestication of the Laboratory Rat. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017;34(12):3148-3153. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 170, No. 8, pp. 155-159, August, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batotsyrenova, E.G., Bakulev, S.E., Nevzorova, T.G. et al. Changes in the Biorhythms of Biochemical Parameters in Animals with Modeled Acute Desynchronosis. Bull Exp Biol Med 170, 191–195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-05030-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-05030-1