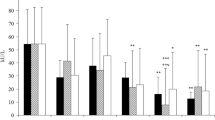
The effects of TLR4 blocker on blood cell morphology, concentrations proinflammatory cytokines, and functional state of the liver and kidneys were studied in outbred male rats (n=60) after intravenous injection of 20 mg/kg LPS isolated from opportunistic Proteus mirabilis strain ATCC 51393. TLR4 blocker TLR4-IN-C34 was injected intravenously in a dose of 1 mg/kg/day over 3 days. Systemic inflammatory reaction induced by LPS was characterized by elevation of serum TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocytosis, and thrombocytosis. Increased activity of hepatocyte enzymes (ALT, alkaline phosphatase, and lactate dehydrogenase), retention of nitrogen metabolites (urea and creatinine), elevated content of protein oxidation products, and enhanced protein catabolism were also observed. Administration of TLR4 blocker reduced parameters of inflammatory reaction and prevented the development of hypercatabolic syndrome; endotoxicosis and kidney function indicators approached the normal levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiselev OI, Vasin AV, Deeva EG, Sivak KV, Egorov VV, Tsvetkov VB, Egorov AY, Romanovskaya-Romanko EA, Stepanova LA, Komissarov AB, Tsybalova LM, Ignatjev GM, Shevyryova M.P. Ebola hemorrhagic fever: properties of the pathogen and development of vaccines and chemotherapeutic agents. Mol. Biol. 2015;49(4):480-493.
Korovkina ES, Kazharova SV. The Toll-like receptors role in inflammatory diseases of the bronchopulmonary system pathogenesis. Infektsiya Immunitet. 2016;6(2):109-116. Russian.
Kosinets VA. Changes in the immune system in common purulent peritonitis and the possibility of their correction. Novosti Khirurgii. 2012;20(3):36-42. Russian.
Simbirtsev AS. Cytokines in Pathogenesis and Treatment of Human Diseases. St. Petersburg, 2018. Russian.
Tyukavkina SU, Labushkina AV, Oksenyuk OS. The role of Toll-like receptors in the immunopathogenesis of the nephropathies with fibrosis. Zh. Fundament. Med. Biol. 2017;(1):17-26. Russian.
Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN, Peri F. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. Vaccines (Basel). 2017;5(4). pii: E34. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines5040034
Liew FY, Xu D, Brint EK, O’Neill LA. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005;5(6):446-458.
Zhang D, Zhang G, Hayden MS, Greenblatt MB, Bussey C, Flavell RA, Ghosh S. A toll-like receptor that prevents infection by uropathogenic bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1522-1526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 6, pp. 741-743, June, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivak, K.V., Stosman, K.I., Rassokha, T.A. et al. The Effect of TLR4 Blockade on Some Indicators of Systemic Inflammatory Response to Proteus mirabilis LPS in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 795–797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04981-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04981-9