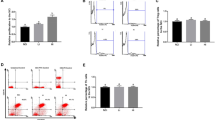
Adjuvant activity of fucoidans in experimental vaccine compositions with ovalbumin was studied on a mouse model. Compositions with sulfated polysaccharides from brown alga Fucus evanescens (native fucoidan in combination with polyphenols, and a product of fucoidan enzymatic hydrolysis) induced multiple productions of antigen-specific antibodies — total IgG, its isotypes IgG1 and, especially, IgG2a, in comparison with an individual ovalbumin. The adjuvant effect of native and structurally modified fucoidans is slightly inferior to that of the traditional licensed aluminum hydroxide adjuvant. The results indicate the prospects of using sulfated polysaccharides from F. evanescens as adjuvants in vaccines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuznetsova TA, Ivanushko LA, Persiyanova EV, Shutikova AL, Ermakova SP, Khotimchenko MYu, Besednova NN. Evaluation of adjuvant effects of fucoidane from brown seaweed Fucus evanescens and its structural analogues for the strengthening vaccines effectiveness. Biomed. Khimiya. 2017;63(6):553-558. Russian.
Makarenkova ID, Akhmatova NK, Ermakova SP, Besednova NN. Morphofunctional changes of dendritic cells induced by sulfated polysaccharides of brown algae. Biomed. Khimiya. 2017;63(1):39-46. Russian.
Anastyuk SD, Shevchenko NM, Dmitrenok PS, Zvyagintseva TN. Structural similarities of fucoidans from brown algae Silvetia babingtonii and Fucus evanescens, determined by tandem MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Carbohydr. Res. 2012;358:78-81.
Hsu HY, Hwang PA. Clinical applications of fucoidan in translational medicine for adjuvant cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019;8(1):15. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-019-0234-9
Hwang PA, Lin HV, Lin HY, Lo SK. Dietary supplementation with low-molecular-weight fucoidan enhances innate and adaptive immune responses and protects against Mycoplasma pneumoniae antigen stimulation. Mar. Drugs. 2019;17(3). pii: E175. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030175
Menshova RV, Shevchenko NM, Imbs TI, Zvyagintseva TN, Malyarenko OS, Ermakova SP, Zaporoshets TS, Besednova NN. Fucoidans from brown alga Fucus evanescens: structure and biological activity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016;3(39):129. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2016.00129
Peng Y, WangY, Wang Q, LuoX, Hu Y, Song Y. Hypolipidemic effects of sulfated fucoidan from Kjellmaniella crassifolia through modulating the cholesterol and aliphatic metabolic pathways. J. Funct. Foods. 2018;51:8-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.10.013
Romagnani S. Th1/Th2 cells. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 1999;5(4): 285-294.
Silchenko AS, Rasin AB, Kusaykin MI, Malyarenko OS, Shevchenko NM, Zueva AO, Kalinovsky AI, Zvyagintseva TN, Ermakova SP. Modification of native fucoidan from Fucus evanescens by recombinant fucoidanase from marine bacteria Formosa algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018;193:189-195.
Song L, Chen X, Liu X, Zhang F, Hu L, Yue Y, Li K, Li P. Characterization and comparison of the structural features, immune-modulatory and anti-avian influenza virus activities conferred by three algal sulfated polysaccharides. Mar. Drugs. 2016;14(1):4. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010004
Sun B, Yu S, Zhao D, Guo S, Wang X, Zhao K. Polysaccharides as vaccine adjuvants. Vaccine. 2018;36(35):5226-5234.
Wang Y, Xing M, Cao Q, Ji A, Liang H, Song S. Biological activities of fucoidan and the factors mediating its therapeutic effects: a review of recent studies. Mar. Drugs. 2019;17(3). pii: E183. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030183
Willhite CC, Karyakina NA, Yokel RA, Yenugadhati N, Wisniewski TM, Arnold IM, Momoli F, Krewski D. Systematic review of potential health risks posed by pharmaceutical, occupational and consumer exposures to metallic and nanoscale aluminum, aluminum oxides, aluminum hydroxide and its soluble salts. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014;44(Suppl. 4):1-80.
Zhang W, Oda T, Yu Q, Jin JO. Fucoidan from Macrocystis pyrifera has powerful immune-modulatory effects compared to three other fucoidans. Mar. Drugs. 2015;13(3):1084-1104.
Zhu L, Ge F, Yang L, Li W, Wei S, Tao Y, Du G. Alginate particles with ovalbumin (OVA) peptide can serve as a carrier and adjuvant for immune therapy in B16-OVA cancer model. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2017;23:166-172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 2, pp. 207-210, February, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Persiyanova, E.V., Kuznetsova, T.A. & Silchenko, A.S. Effect of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Hydrobionts on Humoral Immune Response to Ovalbumin in Mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 246–248 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04860-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04860-3