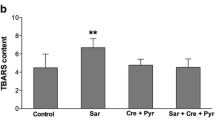
We studied LPO intensity and respiration of mitochondria in brain and heart cells of rats receiving 5% ethanol for 20 weeks and treated with derivatives of neuroactive amino acids. Chronic semicompulsory alcohol intoxication increased the concentration of LPO products in cardiac and cerebral mitochondria by 46 and 45% (diene conjugates), by 97 and 8% (diketones), and by 28 and 81% (malondialdehyde), respectively, reduced activity of antioxidant enzymes in cardiac and cerebral mitochondria by 24 and 45% (glutathione peroxidase) and by 22 and 26% (superoxide dismutase), respectively, and uncoupled the process of respiration and ATP synthesis, which manifested in a decrease in respiratory control (V3/V4 ratio according to Chance). Glutamic acid derivative Neuroglutam (26 mg/kg) and GABA derivative succicard (44 mg/kg) administered intraperitoneally daily for 28 days after termination of alcoholization decreased the levels of primary and secondary LPO products, up-regulated activity of antioxidant enzymes in mitochondria of the heart and brain, and moderated the mitochondrial dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boitsov SA, Samorodskaya IV, Semyonov VYu. Role of medical and non-medical factors in mortality rate: alcohol. Sots. Klin. Psikhiatriya. 2016;26(2):97-105. Russian.
Petrov VI, Tjurenkov IN, Bagmetova VV, Samotrueva MA, Berestovitskaja VM, Vasil’eva OS, Ostrogljadov ES. Patent RU No. 2429834. Antidepressant, anxiolytic, neuroprotective and immunostimulating agent. Bull. No. 27. Published September 27, 2011.
Perfilova VN, Tyurenkov IN. Possible mechanisms of the antianginal action of GABA derivatives. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2005;68(5):68-71. Russian.
Perfilova VN, Tyurenkov IN, Berestovitskaya VM, Vasil’eva OS. Cardioprotective effect of GABA derivatives under acute alcohol intoxication conditions. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2006;69(4):23-27. Russian.
Perfilova VN, Tyurenkov IN, Popova TA, Mokrousov IS, Prokof’ev II, Mikhailova LI, Zhakupova GA, Miroshnikova AS. Effect of New GABA Derivative on the Development of Oxidative Stress in Rats under Conditions of Acute Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2015;78(9):8-12. Russian.
Brand MD, Nicholls DG. Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells. Biochem. J. 2011;435(2):297-312.
Lanza IR, Nair KS. Functional assessment of isolated mitochondria in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 2009;475:349-372.
Obad A, Peeran A, Little JI, Haddad GE, Tarzami ST. Alcohol-mediated organ damages: heart and brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:81. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00081
Piano MR. Alcohol’s effects on the cardiovascular system. Alcohol Res. 2017;38(2):219-241.
Piano MR, Phillips SA. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy: pathophysiologic insights. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2014;14(4):291-308.
Song BJ, Akbar M, Abdelmegeed MA, Byun K, Lee B, Yoon SK, Hardwick JP. Mitochondrial dysfunction and tissue injury by alcohol, high fat, nonalcoholic substances and pathological conditions through post-translational protein modifications. Redox Biol. 2014;3:109-123.
Tapia-Rojas C, Mira RG, Torres AK, Jara C, Pérez MJ, Vergara EH, Cerpa W, Quintanilla RA. Alcohol consumption during adolescence: A link between mitochondrial damage and ethanol brain intoxication. Birth Defects Res. 2017;109(20):1623-1639.
Yang F, Luo J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and ethanol neurotoxicity. Biomolecules. 2015;5(4):2538-2553.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 2, pp. 176-181, February, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popova, T.A., Khusainova, G.K., Prokofiev, I.I. et al. Correction of Alcohol-Induced Damage to Mitochondria in Cardiac and Cerebral Cells by Derivatives of Neuroactive Amino Acids. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 218–223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04854-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04854-1