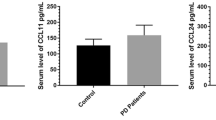
Plasma cytokine concentration in patients with Parkinson’s disease and mutation in GBA gene, in patients with sporadic Parkinson’s disease, and in healthy volunteers were measured by ELISA and multiplex analysis. In patients with Parkinson’s disease and mutation in GBA gene, elevated plasma concentrations of IL-1β and TNFα were revealed by ELISA in comparison with both controls and patients with sporadic form of Parkinson’s disease. Multiplex analysis revealed enhanced secretion of IL-1β, IL-2, IFNγ and reduced plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in patients with Parkinson’s disease and mutation in GBA gene (in comparison with other groups) and increased plasma levels of IL-13 (only in comparison with the healthy volunteers). Our results support the hypothesis that the concentrations of inflammatory mediators are increased in patients with Parkinson’s disease and mutation in GBA gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milyukhina IV, Karpenko MN, Klimenko VM. Clinical parameters and the level of certain cytokines in blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Klin. Med. 2015;93(1):51-55. Russian.
Senkevich KA, Miliukhina IV, Beletskaia MV, Gracheva EV, Kudrevatykh AV, Nikolaev MA, Emelyanov AK, Kopytova AE, Timofeeva AA, Yakimovskii AF, Pchelina SN. The clinical features of Parkinson’s disease in patients with mutations and polymorphic variants of GBA gene. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. 2017;117(10):81-86. Russian.
Chahine LM, Qiang J, Ashbridge E, Minger J, Yearout D, Horn S, Colcher A, Hurtig HI, Lee VM, Van Deerlin VM, Leverenz JB, Siderowf AD, Trojanowski JQ, Zabetian CP, Chen-Plotkin A. Clinical and biochemical differences in patients having Parkinson disease with vs without GBA mutations. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70(7):852-858.
Emelyanov AK, Usenko TS, Tesson C, Senkevich KA, Nikolaev MA, Miliukhina IV, Kopytova AE, Timofeeva AA, Yakimovsky AF, Lesage S, Brice A, Pchelina SN. Mutation analysis of Parkinson’s disease genes in a Russian data set. Neurobiol. Aging. 2018;71:267.e7-267.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging. 2018.06.027
Gardai SJ, Mao W, Schüle B, Babcock M, Schoebel S, Lorenzana C, Alexander J, Kim S, Glick H, Hilton K, Fitzgerald JK, Buttini M, Chiou SS, McConlogue L, Anderson JP, Schenk DB, Bard F, Langston JW, Yednock T, Johnston JA. Elevated alpha-synuclein impairs innate immune cell function and provides a potential peripheral biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One. 2013;8(8). e71634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071634
Ilyechova EY, Miliukhina IV, Orlov IA, Muruzheva ZM, Puchkova LV, Karpenko MN. A low blood copper concentration is a co-morbidity burden factor in Parkinson’s disease development. Neurosci. Res. 2018;135:54-62. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2017.11.011
Karpenko MN, Vasilishina AA, Gromova EA, Muruzheva ZM, Miliukhina IV, Bernadotte A. Interleukin-1β, interleukin- 1 receptor antagonist, interleukin-6, interleukin-10, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in CSF and serum in relation to the clinical diversity of Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Immunol. 2018;327:77-82. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.02.011
Koziorowski D, Tomasiuk R, Szlufik S, Friedman A. Inflammatory cytokines and NT-proCNP in Parkinson’s disease patients. Cytokine. 2012;60(3):762-766. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2012.07.030
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015;30(12):1591-1601. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26424
Sacino AN, Brooks M, McKinney AB, Thomas MA, Shaw G, Golde TE, Giasson BI. Brain injection of α-synuclein induces multiple proteinopathies, gliosis, and a neuronal injury marker. J. Neurosci. 2014;34(37):12,368-12,378. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2102-14.2014
Sidransky E, Lopez G. The link between the GBA gene and parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(11):986-998. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70190-4
Wang XM, Zhang YG, Li AL, Long ZH, Wang D, Li XX, Xia JH, Luo SY, Shan YH. Relationship between levels of inflammatory cytokines in the peripheral blood and the severity of depression and anxiety in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016;20(18):3853-3856.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 168, No. 10, pp. 404-407, October, 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miliukhina, I.V., Usenko, T.S., Senkevich, K.A. et al. Plasma Cytokines Profile in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease Associated with Mutations in GBA Gene. Bull Exp Biol Med 168, 423–426 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04723-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04723-x