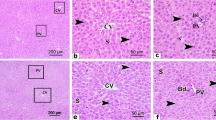
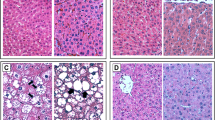
We studied the effects of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor linagliptin on the expression of apoptosis regulator proteins Bcl-2 and Bad in the liver of db/db mice with genetically determined obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The mice received daily linagliptin or saline (placebo) by gavage from week 10 to week 18 of life. In the liver of non-treated mice, the area positively stained for Bad was greater than the area of Bcl-2 expression, which created the conditions for apoptosis activation in liver at this age. Administration of linagliptin decreased Bad stained area and increased Bcl-2 stained area in the liver cells. At the same time, Bad stained area remained larger in treated mice than the area of Bcl-2 expression area, which attested to partial normalization of pro- and antiapoptotic protein balance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michurina SV, Arkhipov SA, Kolesnikov SI. Hepatocyte apoptosis in rats exposed to benzo(a)pyrene. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014;158(1):150-152.
Michurina SV, Ischenko IY, Arkhipov SA, Klimontov VV, Cherepanova MA, Korolev MA, Rachkovskaya LN, Zav’yalov EL, Konenkov VI. Melatonin-Aluminum Oxide-Polymethylsiloxane Complex on Apoptosis of Liver Cells in a Model of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017;164(2):165-169.
Cherepanova MA. Peculiarities of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression in liver in a model of obesity and type 2 diabetes and with linaglyptin correction. Acta Biomedica Scientifica. 2018;3(1):116-119.
Aroor AR, Sowers JR, Jia G, DeMarco VG. Pleiotropic effects of the dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors on the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014;307(4):H477-H492.
Bechmann LP, Gieseler RK, Sowa JP, Kahraman A, Erhard J, Wedemeyer I, Emons B, Jochum C, Feldkamp T, Gerken G, Canbay A. Apoptosis is associated with CD36/fatty acid translocase upregulation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2010;30(6):850-859.
Dey A, Kumar SM. Cytochrome P450 2E1 and hyperglycemiainduced liver injury. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2011;27(4):285-310.
Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Sata M. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4: a key player in chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013;19(15):2298-2306.
Kern M, Klöting N, Niessen HG, Thomas L, Stiller D, Mark M, Klein T, Blüher M. Linagliptin improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38744. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038744.
Knockaert L, Fromenty B, Robin MA. Mechanisms of mitochondrial targeting of cytochrome P450 2E1: physiopathological role in liver injury and obesity. FEBS J. 2011;278(22):4252-4260.
Lockman KA, Baren JP, Pemberton CJ, Baghdadi H, Burgess KE, Plevris-Papaioannou N, Lee P, Howie F, Beckett G, Pryde A, Jaap AJ, Hayes PC, Filippi C, Plevris JN. Oxidative stress rather than triglyceride accumulation is a determinant of mitochondrial dysfunction in in vitro models of hepatic cellular steatosis. Liver Int. 2012;32(7):1079-1092.
Manrique C, Habibi J, Aroor AR, Sowers JR, Jia G, Hayden MR, Garro M, Martinez-Lemus LA, Ramirez-Perez FI, Klein T, Meininger GA, DeMarco VG. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition with linagliptin prevents western diet-induced vascular abnormalities in female mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016;15:94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-016-0414-5.
Michurina SV, Ishenko IJ, Klimontov VV, Archipov SA, Myakina NE, Cherepanova MA, Zavjalov EL, Koncevaya GV, Konenkov VI. Linagliptin alleviates fatty liver disease in diabetic db/db mice. World J. Diabetes. 2016;7(19):534-546.
Renault TT, Floros KV, Elkholi R, Corrigan KA, Kushnareva Y, Wieder SY, Lindtner C, Serasinghe MN, Asciolla JJ, Buettner C, Newmeyer DD, Chipuk JE. Mitochondrial shape governs BAX-induced membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Mol. Cell. 2015;57(1):69-82.
Skrha J Jr, Gáll J, Buchal R, Sedláčková E, Pláteník J. Glucose and its metabolites have distinct effects on the calcium-induced mitochondrial permeability transition. Folia Biol. (Praha). 2011;57(3):96-103.
Wang X, Hausding M, Weng SY, Kim YO, Steven S, Klein T, Daiber A, Schuppan D. Gliptins suppress inflammatory macrophage activation to mitigate inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018;28(2):87-109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 167, No. 2, pp. 157-162, February, 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michurina, S.V., Cherepanova, M.A., Ishchenko, I.Y. et al. Effect of Linagliptin on the Ratio of Apoptosis Regulators in the Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in db/db Mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 167, 210–214 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04493-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04493-1