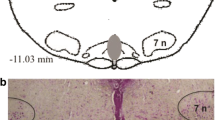
The role of GABAergic inhibition in the regulation of activity of the parafacial respiratory group was studied on narcotized mature rats. Microinjections of GABAA agonist muscimol into the parafacial respiratory group inhibited external respiration and bioelectrical activity of the diaphragmatic muscle resulting in diminished tidal volume and decreased respiration rate accompanied by prolonged inspiration, expiration, and intervals between the inspiratory bursts in the phrenic electromyogram. In contrast, microinjections of GABAA antagonist bicuculline into this group stimulated respiration and markedly increased its volumetric parameters. In addition, blockade of GABAA receptors affected the expiratory phase and interburst intervals in the phrenic electromyogram, but produced no effect on respiration rate. These findings attested to contribution of GABAA-mediated inhibition into the performance of parafacial respiratory group. The study revealed different roles of GABAA receptors in modulation of the mechanisms of respiration rate control in mature rats and formation of inspiratory motor outputs originating from the parafacial respiratory group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarakanov IA, Safonov VA. GABAergic mechanisms of respiratory rhythm disturbances. Patol. Fiziol. Eksp. Ter. 1998: (2):48-54. Russian.
Abbott SB, Stornetta RL, Coates MB, Guyenet PG. Phox2bexpressing neurons of the parafacial region regulate breathing rate, inspiration, and expiration in conscious rats. J. Neurosci. 2011;31(45):16,410-16,422.
Bochorishvili G, Stornetta RL, Coates MB, Guyenet PG. Pre-Bötzinger complex receives glutamatergic innervation from galaninergic and other retrotrapezoid nucleus neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012;520(5):1047-1061.
Feldman JL, Del Negro CA, Gray PA. Understanding the rhythm of breathing: So near, yet so far. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013;75:423-452.
Fortuna MG, West GH, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG. Bötzinger expiratory-augmenting neurons and the parafacial respiratory group. J. Neurosci. 2008;28(10):2506-2515.
Huckstepp RT, Cardoza KP, Henderson LE, Feldman JL. Role of parafacial nuclei in control of breathing in adult rats. J. Neurosci. 2015;35(3):1052-1067.
Janczewski WA, Tashima A, Hsu P, Cui Y, Feldman JL. Role of inhibition in respiratory pattern generation. J. Neurosci. 2013;33(13):5454-5465.
Onimaru H, Homma I. A novel functional neuron group for respiratory rhythm generation in the ventral medulla. J. Neurosci. 2003;23(4):1478-1486.
Onimaru H, Ikeda K, Kawakami K. Phox2b, RTN/pFRG neurons and respiratory rhythmogenesis. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009;168(1-2):13-18.
Pagliardini S, Janczewski WA, Tan W, Dickson CT, Deisseroth K, Feldman JL. Active expiration induced by excitation of ventral medulla of adult anesthetized rats. J. Neurosci. 2011;31(8):2895-2905.
Rosin DL, Chang DA, Guyenet PG. Afferent and efferent connections of the rat retrotrapezoid nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006;499(1):64-89.
Takakura A.C, Colombari E, Menani JV, Moreira TS. Ventrolateral medulla mechanisms involved in cardiorespiratory responses to central chemoreceptor activation in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011;300(2):R501-R510.
Takita K, Morimoto Y. Effects of sevoflurane on respiratory rhythm oscillators in the medulla oblongata. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010;173(1):86-94.
Vedyasova OA, Man’shina NG, Safonov VA, Tarakanov IA. Respiratory reactions to microinjection of GABA and baclofen into the Betzinger and pre-Betzinger complexes in rats. J. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2014;44(2):231-237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 165, No. 6, pp. 664-668, June, 2018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vedyasova, O.A., Kovaleva, T.E. Role of GABAA Receptors of Parafacial Respiratory Group in Control of Respiration in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 165, 711–714 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4248-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4248-x