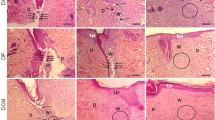
We studied the effect of mesenchymal stromal cells and conditioned media on healing of full-thickness skin wound in rats. Cell transplantation to the wound bed did not accelerate wound closing and had no effect on the severity of inflammation, but increased vasculariza - tion of the granulation tissue in 14 days after injury. After injection of conditioned medium to the wound, less pronounced inflammation or enhanced epithelialization was observed. The angiogenic effect was observed only after repeated administration of conditioned medium and was associated with slower regeneration, probably due to skin traumatization by repeated injections. At the same time, fetal skin fibroblasts stimulated angiogenesis only after transplantation in high doses and the medium conditioned by these fibroblasts had no effect on wound healing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Domaratskaya EI, Payushina OV. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as a Resource for Regeneration of Damaged Skin. Uspekhi Sovremen. Biol. 2017;137(1):56-69. Russian.
Payushina OV, Butorina NN, Sheveleva ON, Kozhevnikova MN, Bukhinnik SS, Starostin VI. Mesenchymal stromal cells of rat spleen during pre-and postnatal ontogeny: Comparative analysis of clonal growth, phenotype and differentiation potencies. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014;156(4):571-577.
Chen L, Tredget EE, Wu PY, Wu Y. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One. 2008;3(4):e1886. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001886.
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop Dj, Horwitz E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
Falanga V, Iwamoto S, Chartier M, Yufit T, Butmarc J, Kouttab N, Shrayer D, Carson P. Autologous bone marrow-derived cultured mesenchymal stem cells delivered in a fibrin spray accelerate healing in murine and human cutaneous wounds. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(6):1299-1312.
Kim JW, Lee JH, Lyoo YS, Jung DI, Park HM. The effects of topical mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in canine experimental cutaneous wounds. Vet. Dermatol. 2013;24(2):242-e53.
Tamari M, Nishino Y, Yamamoto N, Ueda M. Acceleration of wound healing with stem cell-derived growth factors. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2013;28(6):e369-e375.
Ueno T, Nakashima A, Doi S, Kawamoto T, Honda K, Yokoyama Y, Doi T, Higashi Y, Yorioka N, Kato Y, Kohno N, Masaki T. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental peritoneal fibrosis by suppressing inflammation and inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling. Kidney Int. 2013;84(2):297-307.
Uysal CA, Tobita M, Hyakusoku H, Mizuno H. The effect of bone-marrow-derived stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells on wound contraction and epithelization. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014;3(6):405-413.
Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG, Tredget EE. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.
Yoon YS, Wecker A, Heyd L, Park JS, Tkebuchava T, Kusano K, Hanley A, Scadova H, Qin G, Cha DH, Johnson KL, Aikawa R, Asahara T, Losordo DW. Clonally expanded novel multipotent stem cells from human bone marrow regenerate myocardium after myocardial infarction. J. Clin. Invest. 2005;115(2):326-338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 2, pp. 117-120, June, 2018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Payushina, O.V., Butorina, N.N., Sheveleva, O.N. et al. Effect of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Conditioned Media on Healing of Skin Wound. Bull Exp Biol Med 165, 572–575 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4215-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4215-6