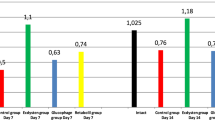
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, serum activities of MMP-2 and MMP-7 were substantially decreased in comparison with apparently healthy individuals. At the decompensation stage, along with the increased content of glucose and glycated hemoglobin, a pronounced (3-fold) increase in proinsulin concentration was observed. On the contrary, MMP activity and C-peptide concentration decreased at this stage. The ratio of proinsulin concentration to MMP activity at the stages of diabetes mellitus compensation and subcompensation was approximately 1:50, while at the stage of decompensation it was 1:12. Thus, the ratio of these blood serum parameters can be used as an additional diagnostic marker of diabetes decompensation and severity of its complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bondar’ IA, Klimontov VV. The role of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the development of renal fibrosis in the patients with diabetes mellitus. Probl. Endokrinol. 2012;58(1):39-44. Russian.
Poteryaeva ON, Russkich GS, Panin LE. Analysis of serum activities of matrix metalloproteinases and α1-proteinase inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012;152(5):578-579.
Poteryaeva ON, Russkikh GS, Chernysheva AS, Mokrushnikov PV. Method for martix proteinas action determination in blood serum. J. Sib. Med. Sci. 2010;(6). [URL: http://ngmu.ru/cozo/mos/article/text_full.php? id=461].
EASD/ESC recommendations for diabetes, pre-diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Ross. Kardiol. Zh. 2014;(3):7-61. Russian.
Khasigov PZ, Ktsoeva SA, Gatagonova TM, Grachev SV, Tareeva IE, Grachev SV, Berezov TT. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in the development of diabetic nephropathy. Biokhimiya. 2000;65(5):613-619. Russian.
Anderson SS, Wu K, Nagase H, Stettler-Stevenson WG, Kim Y, Tsilibary EC. Effect of matrix glycation on expression of type IV collagen, MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 by human mesangial cells. Cell. Adhes. Commun. 1996;4(2):89-101.
Ban CR, Twigg SM, Franjic B, Brooks BA, Celermajer D, Yue DK, McLennan SV. Serum MMP-7 is increased in diabetic renal disease and diabetic diastolic dysfunction. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010;87(3):335-341.
Ebihara I, Nakamura T, Shimada N, Koide H. Increased plasma metalloproteinase-9 concentrations precede development of microalbuminuria in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998;32(4):544-550.
Lan CC, Liu IH, Fang AH, Wen CH, Wu CS. Hyperglycaemic conditions decrease cultured keratinocyte mobility: implications for impaired wound healing in patients with diabetes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008;159(5):1103-1115.
McLennan SV, Kelly DJ, Schache M, Waltham M, Dy V, Langham RG, Yue DK, Gilbert RE. Advanced glycation end products decrease mesangial cell MMP-7: a role in matrix accumulation in diabetic nephropathy? Kidney Int. 2007;72(4):481-488.
Perez SE, Cano DA, Dao-Pick T, Rougier JP, Werb Z, Hebrok M. Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 are dispensable for pancreatic islet formation and function in vivo. Diabetes. 2005;54(3):694-701.
Rysz J, Banach M, Stolarek RA, Pasnik J, Cialkowska-Rysz A, Koktysz R, Piechota M, Baj Z. Serum matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 and metalloproteinase tissue inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in diabetic nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2007;20(4):444-452.
Thrailkill KM, Clay Bunn R, Fowlkes JL. Matrix metalloproteinases: their potential role in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Endocrine. 2009;35(1):1-10.
Wang J, Li Y, Xu M, Li D, Wang Y, Qi J, He K. C-peptide exhibits a late induction effect on matrix metallopeptidase-9 in high glucose-stimulated rat mesangial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016;12(6):4142-4146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 164, No. 12, pp. 697-700, December, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poteryaeva, O.N., Russkikh, G.S., Zubova, A.V. et al. Changes in Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Serum Concentrations of Proinsulin and C-Peptide Depending on the Compensation Stage of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Bull Exp Biol Med 164, 730–733 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4068-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4068-z