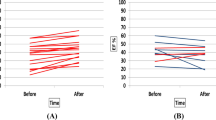
Echocardiographic parameters were assessed in patients with non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome, who underwent emergency percutaneous coronary intervention followed by various outpatient physical cardiac rehabilitation programs. The patients underwent physical rehabilitation for 3 months under conditions of diagnostic centre in the rehabilitation unit according to the standard program including in treadmill or bicycle exercise in the exercise therapy room or with Nordic walking in the main training block. After rehabilitation course, the left ventricular mass index significantly decreased and systolic volume and left ventricular ejection fraction significantly increased in both groups. Nordic walking training for 3 months non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome induced similar positive shifts in the parameters of intracardiac hemodynamics, as standard treadmill or bicycle training program, which allows considering it as an alternative cardiac rehabilitation method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronov DM, Krasnitskij VB, Bubnova MG. Efficacy of physical training and analysis of lipid-lowering therapy in patients with ischemic heart disease after acute coronary incidents. Rats. Farmakoter. Kardiol. 2010;6(1):9-19. Russian.
Basov GV. Sanatorium rehabilitation of patients after myocardial revascularisation using individual physical exercises. Kreml’. Med. Klin. Vestn. 2013;(4):33-36. Russian.
Ivanova O, Ivanova M. Acute ischemic heart disease in children involved in sports. Sport. Med.: Nauka Praktika. 2015;(4):10-20. Russian.
Rehabilitation and Prevention of Complications after Acute Myocardial Infarction with ST Segment Elevation. Russian Clinical Guidelines. Moscow, 2014. Russian.
Rehabilitation in Cardiovascular Diseases. Makarova IN, ed. Moscow, 2010. Russian.
Cherkasova VG, Solomatina NV, Syromyatnikova LI, Svetlakova LV, Andreeva TV. The possibility of using of nordic walking in rehabilitation of patients after acute myocardial infarction. Lech. Fizkul’tura Sport. Med. 2016;(2):22-26. Russian.
Erlikh AD, Gratsiansky NA. Acute non-ST-elevation coronary syndrome in real practice of hospitals in Russia. Comparative data from RECORD 1and 2 registries. Kardiologiya. 2012;52(10):9-16. Russian.
Belardinelli R, Georgiou D, Cianci G, Purcaro A. Effects of exercise training on left ventricular filling at rest and during exercise in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Am. Heart J. 1996;132(1, Pt 1):61-70.
Braith RW, Welsch MA, Feigenbaum MS, Kluess HA, Pepine CJ. Neuroendocrine activation in heart failure is modified by endurance exercise training. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999;34(4):1170-1175.
Fox KA, Eagle KA, Gore JM, Steg PG, Anderson FA; GRACE and GRACE2 Investigators. The global registry of acutec events, 1999 to 2009 — Grace. Heart. 2010;96(14):1095-1101.
Hambrecht R, Gielen S, Linke A, Fiehn E, Yu J, Walther C, Schoene N, Schuler G. Effects of exercise training on left ventricular function and peripheral resistance in patients with chronic heart failure: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2000;283(23):3095-3101.
Haykowsky MJ, Liang Y, Pechter D, Jones LW, McAlister FA, Clark AM. A meta-analysis of the effect of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling in heart failure patients: the benefit depends on the type of training performed. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007;49(24):2329-2336.
Kim C, Kim DY, Lee DW. The impact of early regular cardiac rehabilitation program on myocardial function after acute myocardial infarction. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011;35(4):535-540.
Passino C, Severino S, Poletti R, Piepoli MF, Mammini C, Clerico A, Gabutti A, Nassi G, Emdin M. Aerobic training decreases B-type natriuretic peptide expression and adrenergic activation in patients with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006;47(9):1835-1839.
Schwameder H, Roithner R, Müller E, Niessen W, Raschner C. Knee joint forces during downhill walking with hiking poles. J. Sports Sci. 1999;17(12):969-978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 164, No. 10, pp. 412-417, October, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volodina, K.A., Linchak, R.M., Achkasov, E.E. et al. Effect of Physical Rehabilitation on Echocardiographic Parameters in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Bull Exp Biol Med 164, 420–424 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4003-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4003-3