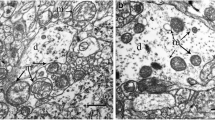
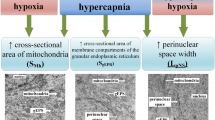
We performed ultrastructural study of cerebral cortex mitochondria in rats with different tolerance to oxygen deficiency (low resistant and highly resistant specimens). Low resistant rats were characterized by the prevalence of mitochondria with lightened matrix due to the nondense packing of cristae. By contrast, mitochondria of highly resistant animals had the dense packing of cristae. The structure of mitochondria underwent adaptive changes at 14-10% O2 in the inspired air. Under these conditions, structural characteristics of the cerebral cortex in hypoxia-sensitive rats resembled those in resistant animals. The decrease in O2 concentration to 8% was accompanied by ultrastructural signs of mitochondrial damage, which correlated with de-energization of the cell and dysfunction of adaptive signaling systems. Ultrastructural features of cerebral cortex mitochondria in animals with low and high tolerance to acute oxygen deficiency confirm the hypothesis that they are associated with two different “functionaland-metabolic portraits”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dudchenko AM, Luk’yanova LD. Effects of adaptation to periodic hypoxia on kinetic parameters of respiratory chain enzymes in rat brain. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1996;121(3):232-235.
Zabolotskii NN, Onishchenko LS, Gakeev ISh. Mitochondrial megacone and pleiocone in the brain of rats as a possible adaptive response to lethal radiation and radiomodifying damage. Morfologiya. 1999;115(3):27-31. Russian.
Ivanchenko MV, Tverdokhleb IV. The impact of intrauterine hypoxia on mitochondrial heterogeneity which is controlled through alterations in rat ventricular myocardium. Vestn. Bolgograd. Gos. Med. Univer. 2014(4):101-106. Russian.
Luk’yanova LD. Bioenergetic hypoxia: Definition, mechanisms, and methods of correction. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1997;124(3):835-843.
Moshkov DA, Romanchenko SP, Parnyshkova EY, Bezgina EN, Zaichkina SI, Pavlik LL. Effect of dopamine on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013;154(5):686-691.
Rozova EV, Mankovskaya IN, Mironova GD. Structural and dynamic changes in mitochondria of rat myocardium under acute hypoxic hypoxia: Role of mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channel. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2015;80(8):994-1000.
Luk’yanova LD, Romanova VE, Chernobaeva GN. Oxidative phosphorylation in brain mitochondria of rats differing in their sensitivity to hypoxia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1991;112(1):962-965.
Sukhorukov VS. Essay on mitochondrial pathology. Moscow, 2011. Russian.
Chan DC. Mitochondrial fusion and fission in mammals. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006;22:79-99.
Chen H, Chomyn A, Chan DC. Disruption of fusion results in mitochondrial heterogeneity and dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280(28):26 185-26 192.
Gomes LC, Scorrano L. Mitochondrial morphology in mitophagy and macroautophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013; 1833(1):205-212.
Liesa M, Palacín M, Zorzano A. Mitochondrial dynamics in mammalian health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2009;89(3):799-845.
Lukyanova LD, Kirova YI. Mitochondria-controlled signaling mechanisms of brain protection in hypoxia. Front. Neurosci. 2015;9:320. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00320.
Skulachev VP. Mitochondrial filaments and clusters as intracellular power-transmitting cables. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001;26(1):23-29.
Wiesner RJ, Hornung TV, Garman JD, Clayton DA, O’Gorman E, Wallimann T. Stimulation of mitochondrial gene expression and proliferation of mitochondria following impairment of cellular energy transfer by inhibition of the phosphocreatine circuit in rat hearts. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1999;31(6):559-567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 164, No. 9, pp. 361-366, September, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlik, L.L., Mikheeva, I.B., Al’-Mugkhrabi, Y.M. et al. Specific Features of Immediate Ultrastructural Changes in Brain Cortex Mitochondria of Rats with Different Tolerance to Hypoxia under Various Modes of Hypoxic Exposures. Bull Exp Biol Med 164, 376–381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-3993-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-3993-1