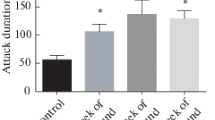
We studied the effect of ultrasonic waves with a frequency of 20-45 kHz on behavioral reactions of rats after 7, 14 and 21 days of continuous exposure. A decrease in the number of social contacts in the social interest test was recorded in all groups, while lengthening of immobility time in Porsolt test was found only in the groups exposed to ultrasound for 2 and 3 weeks. Memory impairment in the new object recognition test was recorded only after 21 days of stressing. Chronic exposure to ultrasound of variable frequencies leads to the development of a depressive-like state in rats and the duration of exposure affects the specificity of the observed disorders. Different protocols of using of this model help to determine the stages of depressive-like condition in rats that can serve as a basis for the development of new methods of depressive disorders treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krupina NA, Kushnareva EY, Khlebnikova NN, Zolotov NN, Kryzhanovskii GN. Behavioral changes in rats induced by a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor methionyl-2(S)-cyanopyrrolidine: experimental model of anxiety-depression disorder. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009;147(3):285-290.
Morozova AY, Zubkov EA, Storozheva ZI, Kekelidze ZI, Chekhonin VP. Effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the development of symptoms of depression and anxiety in rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013;154(6):740-743.
Antikainen R, Hänninen T, Honkalampi K, Hintikka J, Koivumaa-Honkanen H, Tanskanen A, Viinamäki H. Mood improvement reduces memory complaints in depressed patients. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2001;251(1):6-11.
Antunes M, Biala G. The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modification. Cogn. Process. 2012;13(2):93-110.
Brudzynski SM. Principles of rat communication: quantitative parameters of ultrasonic calls in rats. Behav. Genet. 2005;35(1):85-92.
Buwalda B, Geerdink M, Vidal J, Koolhaas JM. Social behavior and social stress in adolescence: a focus on animal models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011;35(8):1713-1721.
Costantini F, D’Amato FR. Ultrasonic vocalizations in mice and rats: social contexts and functions. Dong Wu Xue Bao. 2006;52(4):619-633.
Galecki P, Talarowska M, Moczulski D, Bobinska K, Opuchlik K, Galecka E, Florkowski A, Lewinski A. Working memory impairment as a common component in recurrent depressive disorder and certain somatic diseases. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2013;34(5):436-445.
Hédou G, Pryce C, Di Iorio L, Heidbreder CA, Feldon J. An automated analysis of rat behavior in the forced swim test. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001;70(1):65-76.
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ. Animal models of depression: molecular perspectives. Curr. Top Behav. Neurosci. 2011;7:121-147.
Ottenbreit ND, Dobson KS, Quigley L. An examination of avoidance in major depression in comparison to social anxiety disorder. Behav. Res. Ther. 2014;56:82-90.
Rytsälä HJ, Melartin TK, Leskelä US, Lestelä-Mielonen PS, Sokero TP, Isometsä ET. Determinants of functional disability and social adjustment in major depressive disorder: a prospective study. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2006;194(8):570-576.
Schiller GD, Pucilowski O, Wienicke C, Overstreet DH. Immobility-reducing effects of antidepressants in a genetic animal model of depression. Brain Res. Bull. 1992;28(5):821-823.
Verduijn J, Milaneschi Y, van Hemert A.M, Schoevers RA, Hickie IB, Penninx BW, Beekman AT. Clinical staging of major depressive disorder: an empirical exploration. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2015;76(9):1200-1208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 163, No. 3, pp. 271-274, March, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorlova, A.V., Pavlov, D.A., Ushakova, V.M. et al. Dynamics of the Development of Depressive-Like State in Rats Stressed by Chronic Exposure of Ultrasound of Variable Frequency. Bull Exp Biol Med 163, 296–298 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3788-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3788-9