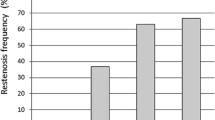
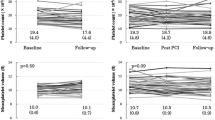
The study was carried out in 126 patients with stable angina pectoris, who underwent elective coronary artery stenting with drug-eluting stents and follow-up angiography within 6-12 months thereafter. Five significant risk factors of restenosis were identified by binary comparisons of different variables. The logistic regression equation that included the level of CD45-positive platelets, diabetes, small vessel stenting, number of simultaneously implanted stents in one patient, and lesion length demonstrates the highest level of prediction of in-stent restenosis (OR=22.8; p<0.001). ROC-analysis demonstrated high prognostic value of the logit model (area under ROC curve 0.87, p<0.001). The data suggest that a close relationship exists between the development of restenosis and the level of circulating CD45+ platelets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burger D, Schock S, Thompson CS, Montezano AC, Hakim AM, Touyz RM. Microparticles: biomarkers and beyond. Clin. Sci. (Lond). 2013;124(7):423-441.
Craft JA, Masci PP, Roberts MS, Brighton TA, Garrahy P, Cox S, Marsh NA. Increased platelet-derived microparticles in the coronary circulation of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty patients. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis. 2004;15(6):475-482.
Gabbasov Z, Ivanova O, Kogan-Yasny V, Ryzhkova E, Saburova O, Vorobyeva I, Vasilieva E. Activated platelet chemiluminescence and presence of CD45+ platelets in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Platelets. 2014;25(6):405-408.
Inoue T, Komoda H, Kotooka N, Morooka T, Fujimatsu D, Hikichi Y, Soma R, Uchida T, Node K. Increased circulating platelet-derived microparticles are associated with stent-induced vascular inflammation. Atherosclerosis. 2008;196(1):469-476.
Mitra AK, Agrawal DK. In stent restenosis: bane of the stent era. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006;59(3):232-239.
Rozmyslowicz T, Majka M, Kijowski J, Murphy SL, Conover DO, Poncz M, Ratajczak J, Gaulton GN, Ratajczak MZ. Platelet- and megakaryocyte-derived microparticles transfer CXCR4 receptor to CXCR4-null cells and make them susceptible to infection by X4-HIV. AIDS. 2003;17(1):33-42.
Sousa JE, Costa MA, Abizaid A, Feres F, Seixas AC, Tanajura LF, Mattos LA, Falotico R, Jaeger J, Popma JJ, Serruys PW, Sousa AG. Four-year angiographic and intravascular ultrasound follow-up of patients treated with sirolimus-eluting stents. Circulation. 2005;111(18):2326-2329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 10, pp. 528-532, October, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabbasov, Z.A., Kozlov, S.G., Byazrova, S.V. et al. Relationship between the Level of Circulating CD45+ Platelets and Development of Restenosis after Implantation of Drug-Eluting Stents to Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 524–527 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3653-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3653-x