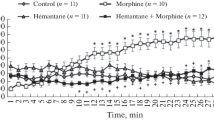
The effect of non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics on the ethanol-induced hyperlocomotion and behavioral sensitization was assessed in male DBA/2 mice. Selank that enhances activity of the endogenous opioid system (0.3 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), similar to the nonselective opiate receptor blocker naloxone (1.0 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), prevented the development of ethanol-induced (2.0 g/kg intraperitoneally) hyperlocomotion, in contrast to σ1-receptors agonist Afobazole (1.0 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) that did not inhibit ethanol-induced behavioral stimulation. Single dose of Selank significantly blocked manifestation of motor sensitization without affecting its formation. These findings suggest that Selank can modulate the motivational effects of ethanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nadorova AV, Kolik LG, Klodt PM, Narkevich VB, Naplyokova PL, Kozlovskaya MM, Kudrin VS. The relationship between the anxiolytic action of selank and the level of serotonin in brain structures during the modeling of alcohol abstinence in rats. Neurochem. J. 2014;8(2):115-120.
Seredenin SB, Antipova TA, Voronin MV, Kurchashova SY, Kuimov AN. Interaction of afobazole with sigma1-receptors. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009;148(1):42-44.
Solov’ev BV, Gengin MT, Latynova IV, Zhigaeva LV, Sollertinskaya TN. Effect of Selank on the main carboxypeptidases in the rat nervous tissue. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2012;48(3):306-309.
Botia B, Legastelois R, Houchi H, Naassila M. Basal anxiety negatively correlates with vulnerability to ethanol-induced behavioral sensitization in DBA/2J mice: modulation by diazepam. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015;39(1):45-54.
Cador M, Bjijou Y, Stinus L. Evidence of a complete independence of the neurobiological substrates for the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine. Neuroscience. 1995;65(2):385-395.
Camarini R, Nogueira Pires ML, Calil HM. Involvement of the opioid system in the development and expression of sensitization to the locomotor-activating effect of ethanol. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000;3(4):303-309.
Kostowski W, Sikora J, Bisaga A, Rosnowska E. Effects of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists on ethanol-induced hyperlocomotion in mice. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1995;47(4):293-297.
Linsenbardt DN, Boehm SL 2nd. Ethanol-induced locomotor sensitization in DBA/2J mice is associated with alterations in GABA(A) subunit gene expression and behavioral sensitivity to GABA(A) acting drugs. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010;95(3):359-366.
Liu Y, Matsumoto RR. Alterations in fos-related antigen 2 and sigma1 receptor gene and protein expression are associated with the development of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization: time course and regional distribution studies. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008;327(1):187-195.
Maurice T, Casalino M, Lacroix M, Romieu P. Involvement of the sigma 1 receptor in the motivational effects of ethanol in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003;74(4):869-76.
Melón LC, Boehm SL 2nd. Role of genotype in the development of locomotor sensitization to alcohol in adult and adolescent mice: comparison of the DBA/2J and C57BL/6J inbred mouse strains. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011;35(7):1351-1360.
Robinson TE, Berridge KC. The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1993;18(3):247-291.
Steketee JD, Kalivas PW. Drug wanting: behavioral sensitization and relapse to drug-seeking behavior. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011;63(2):348-365.
Zolotarev IuA, Sokolov OIu, Kost NV, Vas’kovskiĭ BV, Miasoedov NF, Zozulia AA. Leu-enkephalin homogeneously labeled with tritium in studying the Selank inhibiting effect on the enkephalin-degrading enzymes of human plasma. Bioorg. Khim. 2004;30(3):234-240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 7, pp. 67-71, July, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolik, L.G., Nadorova, A.V. & Seredenin, S.B. Selank Inhibits Ethanol-Induced Hyperlocomotion and Manifestation of Behavioral Sensitization in DBA/2 Mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 56–59 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3544-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3544-6