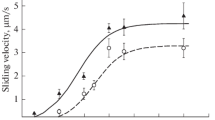
We studied the modulating role of cardiac myosin-binding protein C (cMyBP-C) in tropomyosin regulation of the actin—myosin interaction. The effect of cMyBP-C on the velocity of actin-tropomyosin filament sliding over cardiac and slow skeletal myosins was evaluated using in vitro motility assay. The effect of cMyBP-C on the actin-tropomyosin filaments sliding depended on the type of myosin. The regulatory effect of cMyBP-C differs for cardiac and slow skeletal myosin because of the presence of specific essential light chain (LC1sa) in slow skeletal myosin isoform.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gordon AM, LaMadrid MA, Chen Y, Luo Z, Chase PB. Calcium regulation of skeletal muscle thin filament motility in vitro. Biophys. J. 1997;72(3):1295-1307.
Harris SP, Belknap B, Van Sciver RE, White HD, Galkin VE. C0 and C1 N-terminal Ig domains of myosin binding protein C exert different effects on thin filament activation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113(6):1558-1563
Hartzell HC, Glass DB. Phosphorylation of purified cardiac muscle C-protein by purified cAMP-dependent and endogenous Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259(24):15 587-15 596.
Margossian SS, Lowey S. Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):55-71.
Mun JY, Previs MJ, Yu HY, Gulick J, Tobacman LS, Beck Previs S, Robbins J, Warshaw DM, Craig R. Myosin-binding protein C displaces tropomyosin to activate cardiac thin filaments and governs their speed by an independent mechanism. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111(6):2170-2175.
Nikitina LV, Kopylova GV, Shchepkin DV, Nabiev SR, Bershitsky SY. Investigations of molecular mechanisms of actinmyosin interactions in cardiac muscle. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2015;80(13):1748-1763.
Pardee JD, Spudich JA. Purification of muscle actin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):164-181.
Reiser PJ, Bicer S. Multiple isoforms of myosin light chain 1 in pig diaphragm slow fibers: correlation with maximal shortening velocity and force generation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006;456(2):112-118.
Richard P, Charron P, Carrier L, Ledeuil C, Cheav T, Pichereau C, Benaiche A, Isnard R, Dubourg O, Burban M, Gueffet JP, Millaire A, Desnos M, Schwartz K, Hainque B, Komajda M; EUROGENE Heart Failure Project. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: distribution of disease genes, spectrum of mutations, and implications for a molecular diagnosis strategy. Circulation. 2003;107(17):2227-2232.
Saber W, Begin KJ, Warshaw DM, Van Buren P. Cardiac myosin binding protein-C modulates actomyosin binding and kinetics in the in vitro motility assay. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008;44(6):1053-1061.
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol. Rev. 2011;91(4):1447-1531.
Shchepkin DV, Kopylova GV, Nikitina LV, Katsnelson LB, Bershitsky SY. Effects of cardiac myosin binding protein-C on the regulation of interaction of cardiac myosin with thin filament in an in vitro motility assay. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;401(1):159-163.
Smillie LB. Preparation and identification of alpha- and betatropomyosins. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):234-241.
Tonge DP, Jones SW, Bardsley RG, Parr T. Characterisation of the sarcomeric myosin heavy chain multigene family in the laboratory guinea pig. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010;11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-52.
Whitten AE, Jeffries CM, Harris SP, Trewhella J. Cardiac myosin-binding protein C decorates F-actin: implications for cardiac function. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105(47):18,360-18,365.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 7, pp. 54-57, July, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shchepkin, D.V., Kopylova, G.V. & Nikitina, L.V. Effect of Cardiac Myosin-Binding Protein C on Tropomyosin Regulation of Actin—Myosin Interaction Using In Vitro Motility Assay. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 45–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3541-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3541-9