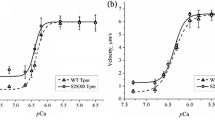
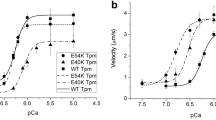
Tropomyosin plays an important role in the regulation of actin—myosin interaction in striated muscles. Mutations in the tropomyosin gene disrupt actin—myosin interaction and lead to myopathies and cardiomyopathies. Tropomyosin with mutations in the α-chain is expressed in both the myocardium and skeletal muscles. We studied the effect of mutations in the α-chain of tropomyosin related to hypertrophic (D175N and E180G) and dilated cardiomyopathies (E40K and E54K) on calcium regulation of the actin–myosin interaction in skeletal muscles. We analyzed the calcium-dependent sliding velocity of reconstructed thin filaments containing F-actin, troponin, and tropomyosin over myosin surface in an in vitro motility assay. Mutations D175N and E180G in tropomyosin increased the sliding velocity and its calcium sensitivity, while mutation E40K reduced both these parameters. E54K mutation increased the sliding velocity of thin filaments, but did not affect its calcium sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai F, Groth HL, Kawai M. DCM-related tropomyosin mutants E40K/E54K over-inhibit the actomyosin interaction and lead to a decrease in the number of cycling cross-bridges. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47471.
Bai F, Weis A, Takeda AK, Chase PB, Kawai M. Enhanced active cross-bridges during diastole: molecular pathogenesis of tropomyosin’s HCM mutations. Biophys. J. 2011;100(4):1014-1023.
Bing W, Knott A, Redwood C, Esposito G, Purcell I, Watkins H, Marston S. Effect of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations in human cardiac muscle alpha-tropomyosin (Asp175Asn and Glu180Gly) on the regulatory properties of human cardiac troponin determined by in vitro motility assay. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2000;32(8):1489-1498.
Bottinelli R, Coviello DA, Redwood CS, Pellegrino MA, Maron BJ, Spirito P, Watkins H, Reggiani C. A mutant tropomyosin that causes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is expressed in vivo and associated with an increased calcium sensitivity. Circ. Res. 1998;82(1):106-115.
Boussouf SE, Maytum R, Jaquet K, Geeves MA. Role of tropomyosin isoforms in the calcium sensitivity of striated muscle thin filaments. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2007;28(1):49-58.
Gupte TM, Haque F, Gangadharan B, Sunitha MS, Mukherjee S, Anandhan S, Rani D.S, Mukundan N, Jambekar A, Thangaraj K, Sowdhamini R, Sommese RF, Nag S, Spudich JA, Mercer JA. Mechanistic heterogeneity in contractile properties of a-tropomyosin (TPM1) mutants associated with inherited cardiomyopathies. J. Biol. Chem. 2015;290(11):7003-7015.
Janco M, Kalyva A, Scellini B, Piroddi N, Tesi C, Poggesi C, Geeves MA. a-Tropomyosin with a D175N or E180G mutation in only one chain differs from tropomyosin with mutations in both chains. Biochemistry. 2012;51(49):9880-9890.
Matyushenko AM, Artemova NV, Shchepkin DV, Kopylova GV, Bershitsky SY, Tsaturyan AK, Sluchanko NN, Levitsky DI. Structural and functional effects of two stabilizing substitutions, D137L and G126R, in the middle part of a-tropomyosin molecule. FEBS J. 2014;281(8):2004-2016.
Mirza M, Robinson P, Kremneva E, Copeland O, Nikolaeva O, Watkins H, Levitsky D, Redwood C, El-Mezgueldi M, Marston S. The effect of mutations in alpha-tropomyosin (E40K and E54K) that cause familial dilated cardiomyopathy on the regulatory mechanism of cardiac muscle thin filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282(18):13487-13497.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 7, pp. 50-53, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopylova, G.V., Shchepkin, D.V., Borovkov, D.I. et al. Effect of Cardiomyopathic Mutations in Tropomyosin on Calcium Regulation of the Actin—Myosin Interaction in Skeletal Muscle. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 42–44 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3540-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3540-x