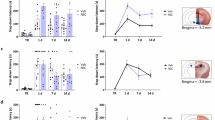
Activity of NMDA receptors is a prerequisite for numerous but not all forms of neuronal plasticity and learning. The present study examined the role of NMDA receptors in standard, weak, and repeated passive avoidance training in young chicks. Injection of MK-801, an antagonist of NMDA receptor, prior to strong training episode impaired subsequent memory recall. Moreover, repeated training did not restore the lost memory. In the double weak training protocol, the impairing effect of MK-801 was observed only when it was injected prior to the second but not to the first training episode. These results suggest that activation of NMDA receptors is not a necessary stage for memory acquisition in the weak training task. In contrast, the mechanisms of strong training depending on activation of NMDA receptors can be probably involved into the second training episode performed against the background of existing NMDA receptor-independent memory about the first training episode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nikitin VP, Solntseva SV. Mechanisms of amnesia induced by impairment of long-term memory reconsolidation in edible snail. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012;153(5):609-613.
Solnceva SV, Nikitin VP. Neurochemical mechanisms of food aversion conditioning consolidation in snail Helix lucorum. Ross. Fiziol. Zh. 2008;94(8):860-870. Russian.
Solntseva V, Nikitin VP. Protein synthesis is necessary for induction of amnesia, elicited by disruption of long-term memory reconsolidation. Ross. Fiziol. Zh. 2010;96(3):247-258. Russian.
Bannerman DM, Good MA, Butcher SP, Ramsay M, Morris RG. Distinct components of spatial learning revealed by prior training and NMDA receptor blockade. Nature. 1995;378:182-186.
Burchuladze R, Rose SP. Memory formation in day-old chicks requires NMDA but not Non-NMDA glutamate receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1992;4(6):533-538.
Butcher SP, Davis S, Morris RG. A dose-related impairment of spatial learning by the NMDA receptor antagonist, 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (AP5). Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1990;1(1):15-20.
Cercato MC, Colettis N, Snitcofsky M, Aguirre AI, Kornisiuk EE, Baez MV, Jerusalinsky DA. Hippocampal NMDA receptors and the previous experience effect on memory. J. Physiol. Paris. 2014;108(4-6):263-269.
McCabe BJ, Davey JE, Horn G. Impairment of learning by localized injection of an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist into the hyperstriatum ventrale of the domestic chick. Behav. Neurosci. 1992;106(6):947-953.
Morris RG. NMDA receptors and memory encoding. Neuropharmacology. 2013;74:32-40.
Paoletti P, Bellone C, Zhou Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013;14:383-400.
Shiflett MW, Tomaszycki ML, Rankin AZ, DeVoogd TJ. Long-term memory for spatial locations in a food-storing bird (Poecile atricapilla) requires activation of NMDA receptors in the hippocampal formation during learning. Behav. Neurosci. 2004;118(1):121-130.
Tiunova A, Anokhin K, Rose SP, Mileusnic R. Involvement of glutamate receptors, protein kinases, and protein synthesis in memory for visual discrimination in the young chick. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 1996;65(3):233-234.
Wang SH, Redondo RL, Morris RG. Relevance of synaptic tagging and capture to the persistence of long-term potentiation and everyday spatial memory. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107(45):19,537-19,542.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 7, pp. 4-6, July, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiunova, A.A., Komissarova, N.V., Bezryadnov, D.V. et al. Paradoxical Effect of NMDA Receptor Blockade in Chicks on Learning and Memory in Passive Avoidance Model. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 1–3 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3529-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3529-5