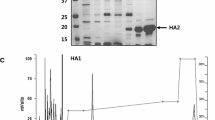
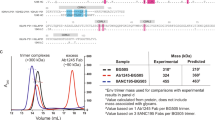
Major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) plays an important role not only in the adaptive immune responses to foreign pathogens, but also in the development of some autoimmune diseases. Non-classical MHC, HLA-DM is directly involved in MHC II loading with the peptide. To study this process, we synthesized recombinant proteins HLA-DR1 and HLA-DM. α/β-Chains of DR1 heterodimer contained C-terminal leucine domains of the fos and jun factors, respectively. Each DM chain contained constant fragment of human antibody heavy chain fused via a long linker domain. In addition, DM α-chain carried N165D substitution suppressing potential glycosylation at this site. We observed significant acceleration of DR1 peptide loading with influenza HA306–318 hemagglutinin in the presence of DM, which indicates functionality of recombinant DR1–DM protein couple. Our results can be used to study the presentation of other viral and self-antigens and can become the basis for the development of new drug modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. K. Anders, M. J. Call, M. S. Schulze, K. D. Fowler, D. A. Schubert, N. P. Seth, E. J. Sundberg, and K. W. Wucherpfennig, HLA-DM captures partially empty HLA-DR molecules for catalyzed removal of peptide. Nat Immunol., 12, No. 1, 54–61 (2011).
C. Cresswell, Assembly, transport, and function of MHC class II molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 12, 259–293 (1994).
L. K. Denzin and C. Cresswell, HLA-DM induces CLIP dissociation from MHC class II alpha beta dimers and facilitates peptide loading. Cell, 82, No. 1, 155–165 (1995).
R. N. Germain and A. G. Rinker Jr, Peptide binding inhibits protein aggregation of invariant-chain free class II dimers and promotes surface expression of occupied molecules. Nature, 363, 725–728 (1993).
P. Ghosh, M. Amaya, E. Mellins, and D. Wiley,The structure of an intermediate in class II MHC maturation: CLIP bound to HLA-DR3. Nature, 378, 457–462 (1995).
C. S. Hsieh, P. deRoos, K. Honey, C. Beers, A. Y. Rudensky, A role for cathepsin L and cathepsin S in peptide generation for MHC class II presentation. J. Immunol., 168, No. 6, 2618–2625 (2002).
A. Jasanoff, S. J. Park, and D. Wiley, Direct observation of disordered regions in the major histocompatibility complex class II-associated invariant chain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 92, No. 21, 9900–9904 (1995).
P. A. Roche, C. Cresswell, Invariant chain association with HLA- DR molecules inhibits immunogenic peptide binding. Nature, 345, 615–618 (1990).
E. F. Rosloniec, K. B. Whittington, D. M. Zaller, and A. H. Kang, HLA-DR1 (DRB1*0101) and DR4 (DRB1*0401) use the same anchor residues forbinding an immunodominant peptide derived from human type II collagen. J. Immunol., 168, No. 1, 253–259 (2002).
L. Santambrogio, I. Potolicchio, S. P. Fessler, S. H. Wong, G. Raposo, and J. L. Strominger, Involvement of caspasecleaved and intact adaptor protein 1 complex in endosomal remodeling in maturing dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol., 6, No. 10, 1020–1028 (2005).
M. A. Sherman, D. A. Weber, and P. E. Jensen, DM enhances peptide binding to class II MHC by release of invariant chainderivedpeptide. Immunity, 3, No. 2, 197–205 (1995).
V. S. Sloan, P. Cameron, G. Porter, M. Gammon, M. Amaya, E. Mellins, and D. M. Zaller, Mediation by HLA-DM of dissociation of peptides from HLA-DR. Nature, 375, 802–806 (1995).
A. B. Vogt, H. Kropshofer, G. Moldenhauer, and G. J. Hammerling, Kinetic analysis of peptide loading onto HLA-DR molecules mediated by HLA-DM. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 93, No. 18, 9724–9729 (1996).
D. A. Weber, B. D. Evavold, and P. E. Jensen, Enhanced dissociation of HLA-DR-bound peptides in the presence of HLADM. Science, 274, 618–620 (1996).
K. W. Wucherpfennig, A. Sette, S. Southwood, C. Oseroff, M. Matsui, J. L. Strominger, and D. A. Hafler, Structural requirements for binding of an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide to DR2 isotypes and for its recognition by human T cell clones. J. Exp. Med., 179, No. 1, 279–290 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 1, pp. 101–105, January, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamedov, A.E., Ponomarenko, N.A., Belogurov, A.A. et al. Heterodimer HLA-DM Fused with Constant Fragment of the Heavy Chain of the Human Immunoglobulin Accelerates Influenza Hemagglutinin HA306–318 Loading to HLA-DR1. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 92–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3353-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3353-y