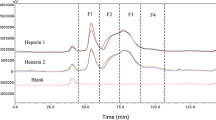
The study demonstrates the formation of heparin complexes with prolyl-glycine peptide and proline and glycine amino acids. The method was developed for in vitro production of these complexes at 1:1 dipeptide to heparin molar ratio and 2:1 amino acid to heparin molar ratio. These complexes, unlike the constituents, proline and glycine, exhibited significant anticoagulant, antiplatelet, and fibrin-depolymerization activities of varying degree in vitro and in vivo. The heparin–dipeptide complex produced maximum effect. The dipeptide by itself also showed anticoagulant properties, but less pronounced than in the complex with heparin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. P. Ashmarin, Pathological Physiology and Biochemistry [in Russian], Moscow (2005).
A. L. Berkovskii, A. Vasil’ev, and L. V. Zherdeva, Manual on Evaluation of Adhesion and Aggregation Activity of Platelets [in Russian], Moscow (2003).
L. A. Lyapina, M. E. Grigor’eva, T. Yu, Obergan, T. A. Shubina, Theoretical and Practical Problems in Studies of the Functional Status of the Anticoagulant System of the Blood [in Russian], Moscow (2012).
L. A. Lyapina, T. Y. Obergan, and V. E. Pastorova, Regulatory role of heparin compounds with low molecular ligands of blood in plasma and thromocyte hemostasis. Biol. Bull., 38, No. 2, 165-175 (2011).
T. Yu. Obergan, E. S. Maystrenko, and L. A. Lyapina, Leucine-heparin complex and its effect on hemostatic parameters. Tromboz, gemostaz, reologiya, No. 4. 73-78 (2012).
J. Fareed, W. Jeske, V. Eschenfelder, O. Iqbal, D. Hoppensteadt, and A. Ahsan, Preclinical studies on a low molecular weight heparin. Thromb. Res., 81, No. 2, Suppl., S1-S27 (1996).
S. K. Cooper, J. Pandhare, and J. M. Phang, A hypothesized regulatory function for hydroxyproline metabolism in apoptosis. Pro Amer. Asso Cancer Res., 46, 1260 (2005).
D. L. Rabenstein, Heparin and heparan sulfate: structure and function. Nat. Prod. Rep., 19, No. 3, 312-331 (2002).
T. W. Stief, Inhibition of thrombin in plasma by heparin or arginine. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost., 13, No. 2, 146-153 (2007).
J. Wang and D. L. Rabenstein, Interaction of heparin with two synthetic peptides that neutralize the anticoagulant activity of heparin. Biochemistry, 45, No. 51, 15,740-15,747 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 1, pp. 64-67, January, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grigorieva, M.E., Obergan, T.Y., Maystrenko, E.S. et al. Anticoagulant Effects of Heparin Complexes with Prolyl-Glycine Peptide and Glycine and Proline Amino Acids. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 54–57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3343-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3343-0