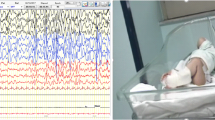
The effects of general anesthetics ketamine and midazolam, the drugs that cause neuroapoptosis at the early stages of CNS development, on electrical activity of the somatosensory cortex in newborn rats were studied using extracellular recording of local field potentials and action potentials of cortical neurons. Combined administration of ketamine (40 mg/kg) and midazolam (9 mg/kg) induced surgical coma and almost completely suppressed early oscillatory patterns and neuronal firing. These effects persisted over 3 h after injection of the anesthetics. We concluded that general anesthesia induced by combined administration of ketamine and midazolam profoundly suppressed cortical activity in newborn rats, which can trigger neuroapoptosis in the developing brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. M. Brambrink, A. S. Evers, M. S. Avidan, N. B. Farber, D. J. Smith, L. D. Martin, G. A. Dissen, C. E. Creeley, and J. W. Olney, Ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the fetal and neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology, 116, No. 2, 372-384 (2012).
C. Ikonomidou, F. Bosch, M. Miksa, P. Bittigau, J. Vöckler, K. Dikranian, T. I. Tenkova, V. Stefovska, L. Turski, and J. W. Olney, Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science, 283, 70-74 (1999).
V. Jevtovic-Todorovic, R. E. Hartman, Y. Izumi, N. D. Benshoff, K. Dikranian, C. F. Zorumski, J. W. Olney, and D. F. Wozniak, Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J. Neurosci., 23, No. 3, 876-882 (2003).
I. Khalilov, V. Dzhala, Y. Ben-Ari, and R. Khazipov, Dual role of GABA in the neonatal rat hippocampus. Dev. Neurosci., 21, Nos. 3-5, 310-319 (1999).
R. Khazipov and H. J. Luhmann, Early patterns of electrical activity in the developing cerebral cortex of humans and rodents. Trends Neurosci., 29, No. 7, 414-418 (2006).
R. Khazipov, M. Minlebaev, and G. Valeeva, Early gamma oscillations. Neuroscience, 250, 240-252 (2013).
R. Khazipov, A. Sirota, X. Leinekugel, G. L. Holmes, Y. Ben-Ari, and G. Buzsáki, Early motor activity drives spindle bursts in the developing somatosensory cortex. Nature, 432, 758-761 (2004).
K. Kirmse, M. Kummer, Y. Kovalchuk, O. W. Witte, O. Garaschuk, and K. Holthoff, GABA depolarizes immature neurons and inhibits network activity in the neonatal neocortex in vivo. Nat. Commun., 6, doi: 10.1038/ncomms8750 (2015).
S. Mennerick and C. F. Zorumski, Neural activity and survival in the developing nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol., 22, Nos. 1-3, 41-54 (2000).
M. Minlebaev, Y. Ben Ari, and R. Khazipov, NMDA receptors pattern early activity in the developing barrel cortex in vivo. Cereb. Cortex, 19, No. 3, 688-696 (2009).
M. Minlebaev, Y. Ben-Ari, and R. Khazipov, Network mechanisms of spindle-burst oscillations in the neonatal rat barrel cortex in vivo. J. Neurophysiol., 97, No. 1, 692-700 (2007).
J. W. Olney, Focus on apoptosis to decipher how alcohol and many other drugs disrupt brain development. Front. Pediatr., 2, 81, doi: 10.3389/fped.2014.00081 (2014).
P. L. Purdon, A. Sampson, K. J. Pavone, and E. N. Brown, Clinical electroencephalography for anesthesiologists: part I: background and basic signatures. Anesthesiology, 123, No. 4, 937-960 (2015).
G. Sitdikova, A. Zakharov, S. Janackova, E. Gerasimova, J. Lebedeva, A. R. Inacio, D. Zaynutdinova, M. Minlebaev, G. L. Holmes, and R. Khazipov, Isoflurane suppresses early cortical activity. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol., 1, No. 1, 15-26 (2014).
C. Young, V. Jevtovic-Todorovic, Y. Q. Qin, T. Tenkova, H. Wang, J. Labruyere, and J. W. Olney, Potential of ketamine and midazolam, individually or in combination, to induce apoptotic neurodegeneration in the infant mouse brain. Br. J. Pharmacol., 146, No. 2, 189-197 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 1, pp. 23-27, January, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedeva, Y.A., Zakharova, A.V., Sitdikova, G.F. et al. Ketamine-Midazolam Anesthesia Induces Total Inhibition of Cortical Activity in the Brain of Newborn Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 15–19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3334-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3334-1