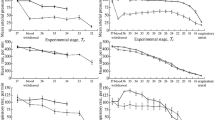
Intravital microscopy was employed to examine cerebral circulation in rats assessed by blood flow in the venules with diameter of 10-30 μ during immersion hypothermia continued to the moment of respiratory arrest and for 10 min thereafter. Circulation in the cerebral microvessels continued during severe hypothermia, and it went on even after hypothermic respiratory arrest while the heart was beating. In pial venules, the blood continued to fl ow for 8-10 min after respiratory arrest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. P. Ivanov, Principles of Organismal Energetics: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Vol. 4, Energy Resources and Physiology of Survival [in Russian], St. Petersburg (2004).
K. P. Ivanov and N. N. Mel’nikova, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 141, No. 6, 666-668 (2006).
S. V. Moskovskaya, K. P. Ivanov, Yu. I. Levkovich, and N. A. Mal’tsev, Ross. Fiziol. Zh., 81, No. 6, 95-98 (1995).
Е. М. Elmistekawy and F. D. Rubens, Perfusion, 26, Suppl. 1, 27-34 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 160, No. 11, pp. 533-535, November, 2015
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mel’nikova, N.N., Petrova, L.A. Effect of Hypothermia-Induced Respiratory Arrest on Cerebral Circulation in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 160, 593–595 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3225-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3225-5