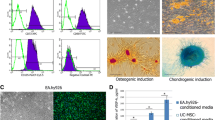
Short-term cell culturing on basement membrane matrix is a common and very convenient in vitro model of angiogenesis. We studied the possibility of interaction of multipotent stromal cells from the umbilical cord and Ea.hy926 endothelial cells on this model at the early and late periods of the experiment. Multipotent stromal cells alone and in combination with endothelial cells formed an unstable tubular network. Clusters formed after its disassembling later became the sprouting centers in co-culture of the two cell types, but not in pure culture of multipotent stromal cells. Multipotent stromal cells with CD31+ phenotype constitute the structural basis of newly formed stable 3D capillary-like network. Prolongation of the time of culturing and combination of the two in vitro models of angiogenesis (tubulogenesis and sprouting) allowed more complete assessment of the angiogenic potential of multipotent stromal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Albini, C. Marchisone, F. Del Grosso, et al., Am. J. Pathol., 156, No. 4, 1381-1393 (2000).
B. Annabi, Y. T. Lee, S. Turcotte, et al., Stem Cells, 21, No. 3, 337-347 (2003).
I. Arnaoutova, J. George, H. K. Kleinman, and H. K. Kleinman, Angiogenesis, 12, No. 3, 267-274 (2009).
A. Blocki, Y. Wang, M. Koch, et al., Stem Cells Dev., 22, No. 17, 2347-2355 (2013).
D. Bouïs, G. A. Hospers, C. Meijer, et al., Angiogenesis, 4, No. 2, 91-102 (2001).
A. Burlacu, G. Grigorescu, A. M. Rosca, et al., Stem Cells Dev., 22, No. 4, 643-53 (2013).
M. Y. Chen, P. C. Li, Z. L. Li, and X. Wei, Exp. Hematol., 37, No. 5, 629-640 (2009).
M. Choi, H. S. Lee, P. Naidansaren, et al., Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 45, No. 3, 560-570 (2013).
M. Dominici, K. Le Blanc, I. Mueller, et al., Cytotherapy, 8, No. 4, 315-317 (2006).
R. Estrada, N. Li, H. Sarojini, et al., J. Cell. Physiol., 219, No. 3, 563-571 (2009).
S.A. Gomes, E. B. Rangel, C. Premer, et al., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 110, No. 8, 2834-2839 (2013).
D. Guidolin, G. Albertin, and D. Ribatti, Microscopy: Science, Technology, Applications and Education, Eds. A. Mendez-Vilas, J. Diaz, Badajos (2010), pp. 876-884.
C. S. Hughes, L. M. Postovit, and G. A. Lajoie, Proteomics, 10, No. 9, 1886-1890 (2010).
K. Janeczek Portalska, A. Leferink, N. Groen, et al., PLoS One, 7, No. 10, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046842 (2012).
G. Jin, D. Bausch, T. Knightly, et al., Surgery, 150, No. 3, 429-435 (2011).
H. K. Kleinman, M. L. McGarvey, J. R. Hassell, et al., Biochemistry, 25, No. 2, 312-318 (1986).
Y. Kubota, H. K. Kleinman, G. R. Martin, T. J. Lawley, J. Cell Biochem., 107, No. 4, 1589-1598 (1988).
T. P. Lozito, C. K. Kuo, J. M. Taboas, and R. S. Tuan, J. Cell. Biochem., 107, No. 4, 714-722 (2009).
J. Oswald, S. Boxberger, B. Jorgensen, et al., Stem Cells, 22, No. 3, 377-384 (2004).
S. Pacini and I. Petrini, Front. Cell Dev. Biol., Vol. 2, N 20, doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00020 (2014).
J. Rouwkema, P. E. Westerweel, J. de Boer, et al., Tissue Eng. Part A, 15, No. 8, 2001-2027 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 4, pp. 270-278, October, 2015
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arutyunyan, I.V., Fatkhudinov, T.H., El’chaninov, A.V. et al. Effect of Endothelial Cells on Angiogenic Properties of Multipotent Stromal Cells from the Umbilical Cord during Angiogenesis Modeling in the Basement Membrane Matrix. Bull Exp Biol Med 160, 575–582 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3221-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3221-9