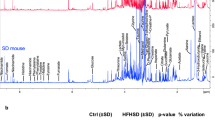
We found no deviations from normalcy in the content of chemical elements (K, Ca, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, Se, Br, Rb, and Sr) in the lungs of rats with mild alimentary obesity, but revealed redistribution of correlations between the elements indicating impaired metabolism in this organ. Zinc supplementation had no effect on the body weight and content of chemical elements (including zinc) in the lung tissue in rats fed high fat diet, but led to significant changes in the correlations between the elements. Bromine, rubidium, and strontium are actively involved in interelement interactions in the lung tissue. These elements should be given more attention in considering biological processes including alimentary obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. K. Barashkov, Medical Bioenergy. Basics, Analysis, Clinic [in Russian], Moscow (2011).
M. A. Grippi, Lung Pathophysiology [in Russian], Moscow; St-Petersburg (1999).
A. P. Zilber, Essays on Respiratory Medicine [in Russian], Moscow (2007).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii, Fundamentals of General Pathophysiology [in Russian], Moscow (2011).
B. V. Churin, V. V. Astashov, E. V. Starkova, and A. S. Chukanov, Eksper. Klin. Gastroenterol., No. 4, 70-72 (2010).
T. Agusa, K. Nomura, T. Kunito, et al., Mar. Pollut. Bull., 57, Nos. 6-12, 807-815 (2008).
E. Barany, I. A. Bergdahl, L. E. Bratteby, et al., Environ. Res., 98, No. 2, 215-223 (2005).
M. D. Chen, P. Y. Lin, V. Cheng, and W. H. Lin, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 52, No. 2, 125-132 (1996).
M. D. Chen, Y. M. Song, P. Y. Lin, Life Sci., 66, No. 22, 2143-2149 (2000).
N. A. Clark, K. Teschke, K. Rideout, and R. Copes, Chemosphere, 70, No. 1, 155-164 (2007).
L. Costarelli, E. Muti, M. Malavolta, et al., J. Nutr. Biochem., 21, No. 5, 432-437 (2010).
G. N. Marreiro, M. Fisberg, and S. M. Cozzolino, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 86, No. 2, 107-122 (2002).
C. L. Ogden, M. D. Carroll, L. Curtin, et al., JAMA, 295, No. 13, 1549-1555 (2006).
Y. Yu, Z. Cai, J. Zheng, et al., Nutr. Res., 32, No. 2, 71-77 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 158, No. 10, pp. 421-426, October, 2014
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Churin, B.V., Trunova, V.A., Sidorina, A.V. et al. Effect of Zinc on the Content of Chemical Elements in the Lung Tissue during Obesity in the Experiment. Bull Exp Biol Med 158, 425–430 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-2777-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-2777-0