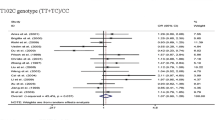
Associations between 5-HTR2A -1438A/G and 5-HTR2C Cys23Ser polymorphisms and depression and its severity were studied in CHD patients with consideration for the trigger factors, pathogenetic characteristics of CHD, and personal anxiety. The study was carried out in 169 men aged 31-84 (59.0±8.8) years with verifi ed CHD. Depression was more severe (Hamilton score) if it was caused by manifestation or exacerbation of CHD (nosogenic factor) and in the presence of the painful syndrome caused by the cardiac disease, high personal anxiety, and presence of allele G polymorphism -1438A/G in the genotype. The risk of medium-severe and severe depression in allele G carriers was 2.4-fold higher than in AA genotype carriers. The nosogenic factor modulated the association between allele G and severity of depression symptoms. The risk of medium-severe and severe depression was almost 4-fold higher in carriers of this allele in the presence of this factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. I. Barskii, M. G. Aksenova, O. B. Kozlova, et al., Gig. San., No. 6, 47-50 (2010).
T. G. Noskova, A. V. Kazantseva, A. E. Gareeva, et al., Genetika, 45, No. 6, 842-848 (2009).
M. J. Choi, H. J. Lee, H. J. Lee, et al., Neuropsychobiology, 49, No. 1, 38-41 (2004).
B. Lerer, F. Macciardi, R. H. Segman, et al., Mol. Psychiatry, 6. No. 5, 579-585 (2001).
M. Masellis, V. Basile, H. Y. Meltzer, et al., Neuropsychopharmacology, 19, No. 2, 123-132 (1998).
D. Nakatani, H. Sato, Y. Sakata, et al., Am. Heart J., 150, No. 4, 652-658 (2005).
C. Otte, J. McCaffery, S. Ali, and M. A. Whooley, Am. J. Psychiatry, 164, No. 9, 1379-1384 (2007).
C. Otte, S. Wüst, S. Zhao, et al., Psychoneuroendocrinology, 34, No. 10, 1574-1581 (2009).
B. Phillips-Bute, J. P. Mathew, J. A. Blumenthal, et al., Psychosom. Med., 70, No. 9, 953-959 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 156, No. 11, pp. 626-629, November, 2013
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golimbet, V.E., Volel’, B.A., Dolzhikov, A.V. et al. Association of 5-HTR2A and 5-HTR2C Serotonin Receptor Gene Polymorphisms with Depression Risk in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 156, 680–683 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2424-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2424-1