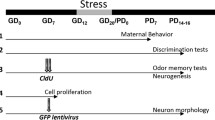
Early experience, mediated by mother’s care, exerts long-term effects on the formation of behavioral phenotype. However, there are no published data on the effects of such experience on the results of early learning. We investigated the effects of maternal deprivation associated with handling in 129Sv mice during postnatal days 3-6 on the results of olfactory learning with mother’s grooming imitation used as the reinforcement on postnatal day 8. Mother deprivation and handling procedure are shown to impair early olfactory learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. M. Cameron, F. A. Champagne, C. Parent, et al., Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 29, Nos. 4-5, 843–865 (2005).
S. E. Claessens, N. P. Daskalakis, R. van der Veen, et al., Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 214, No. 1, 141–154 (2011).
C. Contet, J. N. Rawlins, and R. M. Deacon, Behav. Brain Res., 124, No. 1, 33–46 (2001).
J. N. Crawley, J. K. Belknap, A. Collins, et al., Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 132, No. 2, 107–124 (1997).
A. S. Fleming, D. H. O’Day, and G. W. Kraemer, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 23, No. 5, 673–685 (1999).
D. W. Hedges and F. L. Woon, Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 214, No. 1, 121–130 (2011).
C. Heim, C. B. Nemeroff, Biol. Psychiatry, 49, No. 12, 1023–1039 (2001).
T. A. Kosten, H. J. Lee, and J. J. Kim, Brain Res., 1154, 144–153 (2007).
S. Levine, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 30, No. 10, 939–946 (2005).
D. Liu, J. Diorio, B. Tannenbaum, et al., Science, 277, 1659–1662 (1997).
P. Meerlo, K. M. Horvath, G. M. Nagy, et al., J. Neuroendocrinol., 11, No. 12, 925–933 (1999).
R. M. Sullivan, J. L. McGaugh, and M. Leon, Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res., 60, No. 2, 219–228 (1991).
B. Zimmerberg, A. J. Rosenthal, and A. C. Stark, Dev. PsychobiolN, 42, No. 1, 52–63 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 153, No. 5, pp. 724-726, May, 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burenkova, O.V., Aleksandrova, E.A. & Zarayskaya, I.Y. Maternal Deprivation in Early Ontogeny Impairs Olfactory Learning with Mother’s Grooming Imitation in 129Sv Mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 153, 761–763 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1820-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1820-7