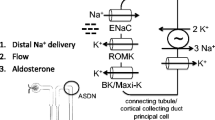
Experiments on Wistar rats showed that exenatide (0.015–0.5 nmol per 100 g body weight) somewhat increased renal excretion of potassium from 7 ± 1 to 16 ± 1 μmol/h/100 g body weight (p < 0.05) in animals with normal serum concentration of glucose (4.6 ± 0.4 mM) and potassium (4.3 ± 0.1 mM). Exenatide dramatically enhanced excretion of potassium under conditions of hyperkalemia (11.4 ± 0.4 mM) produced by intraperitoneal injection of 1.25% KCl solution (5 ml per 100 g body weight). During the fi rst postinjection hour, potassium excretion increased 2-fold and attained 97 ± 11 μmol/h/100 g body weight in comparison with potassium load alone (47 ± 9 μmol/h/100 g body weight, p < 0.05). The data attest to a possible role of peptide regulators in normalization of potassium balance via renal mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu. V. Natochin, Kidney Ion-Controlling Function [in Russian], Leningrad (1976).
Yu. V. Natochin and N. A. Mukhin, Introduction to Nephrology [in Russian], Moscow (2007).
D. A. Sheiman, Renal Pathophysiology [in Russian], St. Petersburg (2010).
M. Allon, A. Takeshian, and N. Shanklin, Kidney Int., 43, No. 1, 212–217 (1993).
D. A. D’Alessio, S. E. Kahn, C. R. Leusner, and J. W. Ensinck, J. Clin. Invest., 93, No. 5, 2263–2266 (1994).
K. B. Degn, B. Brock, C. B. Juhl, et al., Diabetes, 53, No. 9, 2397–2403 (2004).
K. J. Evans and A. Greenberg, J. Intensive Care Med., 20, No. 5, 272–290 (2005).
A. Lehnhardt and M. J. Kemper, Pediatr. Nephrol., 26, No. 3, 377–384 (2011).
S. Lim, Acta Med. Indones., 39, No. 1, 56–64 (2007).
M. Su, C. Stork, S. Ravuri, et al., J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol., 39, No. 6, 641–648 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 152, No. 8, pp. 137–139, August 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marina, A.S., Kutina, A.V. & Natochin, Y.V. Exenatide enhances kaliuresis under conditions of hyperkalemia. Bull Exp Biol Med 152, 177–179 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-011-1481-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-011-1481-y