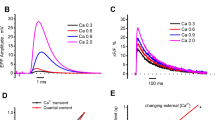
Measurements with extracellular microelectrode technique showed that depolarization of motor nerve terminals in frog cutaneous pectoris muscle with high-potassium solution (40 mM K+) increased frequency of miniature end-plate currents. Both fast intracellular calcium chelator BAPTA-AM and slow chelator EGTA-AM equally moderated the increase in the frequency of miniature end-plate currents. Intravital fluorescent microscopy with FM 1-43 dye showed that under conditions of stimulation of neurotransmitter exocytosis and secretion with high-potassium solution, internalization of the dye into newly-formed endocytotic synaptic vesicles proceeded both in the control and in the presence of EGTA-AM. In contrast, internalization of the dye was not observed in the presence of BAPTA-AM. It was concluded that asynchronous exocytosis of synaptic vesicles goes on in the active zones enriched with Ca-channels due to activation of highaffinity Ca-site in Ca-macrodomain. Endocytosis of vesicles is probably initiated by Camicrodomain during activation of low-affinity Ca-site in the immediate proximity to the Ca channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. L. Zefirov, Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 93, No. 5, 544–557 (2007).
A. L. Zefirov, M. M. Abdrakhmanov, and P. N. Grigor’ev, Ibid., 91, No. 6, 973–984 (2005).
A. L. Zefirov, M. M. Abdrakhmanov, P. N. Grigor’ev, et al., Ibid., 48, No. 1, 34–41 (2006).
J. K. Angleson and W. J. Betz, J. Neurophysiol., 1, 287–294 (2001).
E. M. Adler, G. J. Augustine, S. N. Durry, et al., J. Neurosci., 11, 1496–1507 (1991).
P. De Camilii, V. I. Slepnev, O. Shupiakov, et al., in: Synapses, Baltimore (2001), pp. 217–274.
M. Naraghi, Cell Calcium, 22, 255–268 (1997).
E. Neher, Neuron, 20, 389–399 (1998).
E. F. Stanley, Ibid., 11, 1007–1011 (1993).
E. F. Stanley, Trends Neurosci, 20, 404–409 (1997).
T. C. Sudhof, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 27, 509–547 (2004).
W. Van der Kloot and J. Molgo, Physiol. Rev., 74, 899–991 (1994).
A. L. Zefirov, T. Benish, N. Fatkullin, et al., Nature, 376, 393–394 (1995).
A. L. Zefirov, M. M. Abdrakhmanov, M. A. Mukhamedyarov, et al., Neuroscience, 143, No. 4, 905–910 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 146, No. 12, pp. 608–612, December 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zefirov, A.L., Grigor’ev, P.N. Topography and Affinity of Calcium Sensors of Exo- and Endocytosis in Motor Nerve Terminals. Bull Exp Biol Med 146, 667–670 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-009-0369-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-009-0369-6