Abstract
Code completion is a widely used productivity tool. It takes away the burden of remembering and typing the exact names of methods or classes: As a developer starts typing a name, it provides a progressively refined list of candidates matching the name. However, the candidate list usually comes in alphabetic order, i.e., the environment is only second-guessing the name based on pattern matching, relying on human intervention to pick the correct one. Finding the correct candidate can thus be cumbersome or slower than typing the full name.
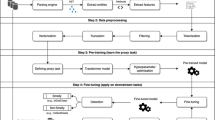
We present an approach to improve code completion based on recorded program histories. We define a benchmarking procedure measuring the accuracy of a code completion engine and apply it to several completion algorithms on a dataset consisting of the history of several systems. Further, we use the change history data to improve the results offered by code completion tools. Finally, we propose an alternative interface for completion tools that we released to developers and evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arisholm, E., Gallis, H., Dybå, T., Sjøberg, D.I.K.: Evaluating pair programming with respect to system complexity and programmer expertise. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 33(2), 65–86 (2007)
Bajracharya, S., Ngo, T., Linstead, E., Dou, Y., Rigor, P., Baldi, P., Lopes, C.: Sourcerer: a search engine for open source code supporting structure-based search. In: OOPSLA ’06: Companion to the 21st ACM SIGPLAN Symposium on Object-Oriented Programming Systems, Languages, and Applications, pp. 681–682. ACM, New York (2006). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1176617.1176671
Bruch, M., Monperrus, M., Mezini, M.: Learning from examples to improve code completion systems. In: ESEC/FSE’09: Proceedings of the 7th Joint Meeting of the European Software Engineering Conference and the ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 213–222 (2009)
Conradi, R., Westfechtel, B.: Version models for software configuration management. ACM Comput. Surv. 30(2), 232–282 (1998)
Dehnadi, S., Bornat, R.: The camel has two humps (working title) (2006). http://www.cs.mdx.ac.uk/research/PhDArea/saeed/paper1.pdf
Fazly, A.: The use of syntax in word completion utilities. Master’s thesis, University of Toronto (2002)
Murphy, G., Kersten, M., Findlater, L.: How are java software developers using the eclipse ide? IEEE Softw. (2006)
Kersten, M., Murphy, G.C.: Using task context to improve programmer productivity. In: FSE ’06: Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 1–11 (2006)
Little, G., Miller, R.C.: Keyword programming in Java. In: ASE ’07: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 84–93 (2007)
Lung, J., Aranda, J., Easterbrook, S.M., Wilson, G.V.: On the difficulty of replicating human subjects studies in software engineering. In: ICSE ’08: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 191–200 (2008)
Miller, G.A.: The magical number seven. plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychol. Rev. 63, 81–97 (1956). http://users.ecs.soton.ac.uk/~harnad/Papers/Py104/Miller/miller.html
Reiss, S.P.: Semantics-based code search. In: ICSE ’09: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 243–253 (2009)
Robbes, R.: Mining a change-based software repository. In: MSR ’07: Proceedings of Fourth International Workshop on Mining Software Repositories, p. 15. ACM Press, New York (2007)
Robbes, R., Lanza, M.: An approach to software evolution based on semantic change. In: FASE ’07: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Fundamental Approaches to Software Engineering, pp. 27–41 (2007a)
Robbes, R., Lanza, M.: Characterizing and understanding development sessions. In: ICPC ’07: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Program Comprehension, pp. 155–164 (2007b)
Robbes, R., Lanza, M.: Spyware: a change-aware development toolset. In: ICSE ’08: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 847–850 (2008)
Sharon, Y.: Eclipseye—spying on eclipse. Bachelor’s thesis, University of Lugano (2007)
Sim, S.E., Easterbrook, S.M., Holt, R.C.: Using benchmarking to advance research: A challenge to software engineering. In: ICSE ’03: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 74–83 (2003)
Sim, S.E., Holt, R.C., Easterbrook, S.: On using a benchmark to evaluate C++ extractors. In: IWPC ’02: Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Program Comprehension, p. 114. IEEE Computer Society, Washington (2002)
Wuyts, R.: Roeltyper: a fast type reconstructor for smalltalk. http://decomp.ulb.ac.be/roelwuyts/smalltalk/roeltyper/ (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robbes, R., Lanza, M. Improving code completion with program history. Autom Softw Eng 17, 181–212 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10515-010-0064-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10515-010-0064-x