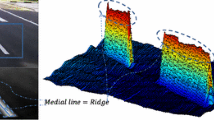
Abstract
Lane estimation for autonomous driving can be formulated as a curve estimation problem, where local sensor data provides partial and noisy observations of spatial curves forming lane boundaries. The number of lanes to estimate are initially unknown and many observations may be outliers or false detections (due e.g. to shadows or non-boundary road paint). The challenges lie in detecting lanes when and where they exist, and updating lane estimates as new observations are made.
This paper describes an efficient probabilistic lane estimation algorithm based on a novel curve representation. The key advance is a principled mechanism to describe many similar curves as variations of a single basis curve. Locally observed road paint and curb features are then fused to detect and estimate all nearby travel lanes. The system handles roads with complex multi-lane geometries and makes no assumptions about the position and orientation of the vehicle with respect to the roadway.
We evaluate our algorithm using a ground truth dataset containing manually-labeled, fine-grained lane geometries for vehicle travel in two large and diverse datasets that include more than 300,000 images and 44 km of roadway. The results illustrate the capabilities of our algorithm for robust lane estimation in the face of challenging conditions and unknown roadways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostoloff, N., & Zelinsky, A. (2004). Vision in and out of vehicles: Integrated driver and road scene monitoring. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 23(4–5), 513–538.
Bar-Shalom, Y., & Li, X. R. (2001). Estimation with applications to tracking and navigation. New York: Wiley.
Bates, C. (2010) Chile earthquake moved whole city 10 feet to the west. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/-sciencetech/article-1256597/Chile-earthquake-moved-Concepcion-city-10ft-west.html.
Bertozzi, M., & Broggi, A. (1998). GOLD: a parallel real-time stereo vision system for generic obstacle and lane detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 7(1), 62–80.
Bertozzi, M., Broggi, A., & Fascioli, A. (2000). Vision-based intelligent vehicles: state of the art and perspectives. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 1, 1–16.
Blake, A., & Isard, M. (1998). Active contours. Berlin: Springer.
Commonwealth of Massachusetts Office of Geographic and Environmental Information (2008). MassGIS planning roads datalayer description. http://www.mass.gov/mgis/eotroads.htm.
Dickmanns, E., & Mysliwetz, B. (1992). Recursive 3-D road and ego-state recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14(2), 199–213.
Huang, A. S., & Teller, S. (2009). Lane boundary and curb estimation with lateral uncertainties. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. on intelligent robots and systems, St. Louis, Missouri.
Huang, A. S., & Teller, S. (2010). Probabilistic lane estimation using basis curves. In Robotics: science and systems (RSS), Zaragoza, Spain.
Huang, A. S., Moore, D., Antone, M., Olson, E., & Teller, S. (2009). Finding multiple lanes in urban road networks with vision and lidar. Autonomous Robots, 26(2–3), 103–122.
Kim, Z. (2008). Robust lane detection and tracking in challenging scenarios. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 9(1), 16–26.
Matsushita, Y., & Miura, J. (2009). On-line road boundary modeling with multiple sensory features, flexible road model, and particle filter. In Proc. European conference on mobile robots.
McCall, J. C., & Trivedi, M. M. (2006). Video-based lane estimation and tracking for driver assistance: survey, system, and evaluation. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 7(1), 20–37.
Neira, J., & Tardos, J. D. (2001). Data association in stochastic mapping using the joint compatibility test. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(6), 890–897. doi:10.1109/70.976019.
Pomerleau, D., & Jochem, T. (1996). Rapidly adapting machine vision for automated vehicle steering. IEEE Expert: Special Issue on Intelligent Systems and their Applications, 11(2), 19–27, see also IEEE Intelligent Systems.
Rasmussen, C. E., & Williams, C. K. I. (2006). Gaussian processes for machine learning. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Sehestedt, S., Kodagoda, S., Alempijevic, A., & Dissanayake, G. (2007). Robust lane detection in urban environments. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. on intelligent robots and systems, San Diego, CA, USA.
Southall, B., & Taylor, C. J. (2001). Stochastic road shape estimation. In Proc. int. conference on computer vision (pp. 205–212). doi:10.1109/ICCV.2001.937519.
Thorpe, C., Hebert, M., Kanade, T., & Shafer, S. (1988). Vision and navigation for the Carnegie-Mellon Navlab. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 10(3), 362–373.
Thrun, S., Burgard, W., & Fox, D. (2005). Probabilistic robotics. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Urmson, C., Anhalt, J., Bagnell, D., Baker, C., Bittner, R., Clark, M., Dolan, J., Duggins, D., Galatali, T., Geyer, C., Gittleman, M., Harbaugh, S., Hebert, M., Howard, T., Kolski, S., Kelly, A., Likhachev, M., McNaughton, M., Miller, N., Peterson, K., Pilnick, B., Rajkumar, R., Rybski, P., Salesky, B., Seo, Y. W., Singh, S., Snider, J., Stentz, A., Whittaker, W., Wolkowicki, Z., Ziglar, J., Bae, H., Brown, T., Demitrish, D., Litkouhi, B., Nickolaou, J., Sadekar, Zhang W. V, Struble, J., Taylor, M., Darms, M., & Ferguson, D. (2009). Autonomous driving in urban environments: Boss and the urban challenge. In M. Buehler, K. Iagnemma, & S. Singh (Eds.), Springer tracts in advanced robotics: Vol. 56. The DARPA urban challenge (pp. 1–59). Berlin: Springer.
Voigt, K. (2011) Quake moved japan coast 8 feet, shifted earth’s axis. http://www.cnn.com/2011/WORLD/-asiapcf/03/12/japan.earthquake.tsunami.earth.
Wang, Y., Teoh, E. K., & Shen, D. (2004). Lane detection and tracking using B-Snake. Image and Vision Computing, 22(4), 269–280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, A.S., Teller, S. Probabilistic lane estimation for autonomous driving using basis curves. Auton Robot 31, 269–283 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-011-9251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-011-9251-2