Abstract
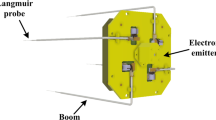
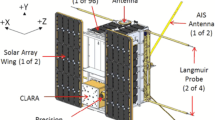
We investigate numerically the impact of magnetic field orientation on needle Langmuir probe (NLP) onboard nano-satellites. For this purpose, we model the interaction between the CubeSat and ionospheric plasma under realistic plasma conditions by using the 3D Particle-In-Cell code PTetra. The magnetic field and plasma parameters are estimated from the International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF) and International Reference Ionosphere (IRI) models, respectively. The study demonstrates the effect of magnetic field connectivity by computing the current-voltage characteristics of the NLP on a 3U CubeSat. Three different orientations of the magnetic field are considered such that the probe-spacecraft system is either magnetically connected or magnetically disconnected. The magnetically connected case corresponds to the orientation of the magnetic field in which the magnetic field lines intersect the NLP and the satellite body. Conversely, in the magnetically disconnected case the magnetic field lines intersect the probe but do not intersect the spacecraft body. The current characteristics of the needle probe computed for the cases considered, illustrate the sensitivity of the collected current to the orientation of the magnetic field. It can be inferred that the effect of the magnetic field connectivity can also be taken in to account for the interpretation of in situ measurements of the needle Langmuir probes on CubeSats. The present study will be helpful to understand the detailed interaction between nano-satellites and the low Earth orbit plasma environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The simulation results presented in this study are obtained from open MPI code, PTetra. These results can be reproduced, and simulation results can be provided upon request.
Code Availability
The simulation results are obtained from the open MPI code PTetra which is developed by the co-author Richard Marchand.
References
Albarran, R.M., Barjatya, A.: J. Spacecr. Rockets 53(3), 393–400 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A33402
Barjatya, A.: PhD thesis, Utah State University (2007). http://digitalcommons.usu.edu/etd/274
Barjatya, A., Merritt, W.: Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89(4), 043507 (2018)
Barjatya, A., Swenson, C.M., Thompson, D.C., Wright, K.H. Jr.: Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80(4), 041301 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3116085. PMID: 19405644
Barjatya, A., St-Maurice, J.P., Swenson, C.M.: J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 7316–7328 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JA018788
Brace, L.H.: Langmuir Probe Measurements in the Ionosphere. Washington DC American Geophysical Union Monograph Series, vol. 23 (2012)
Chen, F.F.: Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 21, 055013 (2012)
Deca, J., Lapenta, G., Marchand, R., Markidis, S.: Phys. Plasmas 20, 102902 (2013)
Diaz-Cabrera, J.M., Lucena-Polonio, M.V., Palop, J.I., Crespo, R.M., Hernandez, M.A., Tejero-del-Caz, A., Ballesteros, J.: J. Appl. Phys. 111(6), 063303 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3698313
Dote, T., Amemiya, H.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 22(1), 270–276 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1143/jpsj.22.270
Edward, S.P., Peter, T.Z.: Memorandum rept., Naval Research Lab Washington DC 3683, ADA077043 (1979)
Eriksson, A.I., Bostrom, R., Gill, R., Ahlen, L., Jansson, S.E., Wahlund, J.E., Andre, M., Malkki, A., Holtet, J.A., Lybekk, B., Pedersen, A., Blomberg, L.G.: Space Sci. Rev. 128, 713–728 (2007)
Geuzaine, C., Remacle, J.F.: Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 79(11), 1309–1331 (2009)
Gubsky, V.F.: Geomagn. Aeron. 49, 1257–1259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793209080441
Gurnett, D.A., Kurth, W.S., Kirchner, D.L., Hospodarsky, G.B., et al.: Space Sci. Rev. 114, 395–463 (2004)
Gustafsson, G., Bostrom, R., Holback, B., et al.: Space Sci. Rev. 79, 137–156 (1997)
Imtiaz, N., Marchand, R.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 360(1) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-015-2526-x
Imtiaz, N., Marchand, R.: Proc. Int. Astron. Union 13, 162–166 (2017)
Imtiaz, N., Marchand, R., Lebreton, J.P.: Phys. Plasmas 20, 052903 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4804336
Jacobsen, K.S., Pedersen, A., Moen, J.I., Bekkeng, T.A.: Meas. Sci. Technol. 21(8), 085902 (2010)
Laframboise, G., Rubinstein, J.: Phys. Fluids 19, 1900 (1976). No. 061060-12-T, Space Physics Research Laboratory, Dept. of Atmospheric and Oceanic Science, University of Michigan
Lebreton, J.P., Stverak, S., Travnicek, P., Maksimovic, M., Klinge, D., Merikallio, S., Lagoutte, D., Poirier, B., Blelly, P.L., Kozacek, Z., Salaquarda, M.: Planet. Space Sci. 54, 472–486 (2006)
Lopez-Arreguin, A.J.R., Stoll, E.: Results Phys. 14(102442), 2211–3797 (2019)
Marchand, R.: IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40(2), 217–229 (2012)
Marchand, R.: IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 45(8), 1923–1926 (2016)
Marchand, R., Lira, P.A.R.: IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 45(4), 535–554 (2017)
Marholm, S., Marchand, R.: Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 023016 (2020)
Marholm, S., Marchand, R., Darian, D., Miloch, W.J., Mortensen, M.: IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47, 3658–3666 (2019)
Merlino, R.: Am. J. Phys. 75, 1078 (2007)
Miller, N.J.: J. Geophys. Res. 77, 2851–2861 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1029/ja077i016p02851
Moen, J., Oksavik, K., Abe, T., Lester, M., Saito, Y., Bekkeng, T.A., Jacobsen, K.S.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 39(7), L07104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL051407
Mott-Smith, H.M., Langmuir, I.: Phys. Rev. 28, 727 (1926)
Oksavik, K., Moen, J., Lester, M., Bekkeng, T.A., Bekkeng, J.K.: J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 117(A11), A11301 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JA017835
Rehman, S., Marchand, R., Berthelier, J.J., Oshini, T., Burchill, J.K.: IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 41(12), 3402–3409 (2013)
Waets, A., Cipriani, F., Ranvier, S.: IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 47(8), 3689–3698 (2019)
Zhang, J.M., Hong, L., Zhi-Peng, C., Chen, L., Jin-Lin, X., Tao, L., A-Di, L., Wan-Dong, L.: Chin. Phys. Lett. 29(7), 075201 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The simulations presented in this work made use of the Compute Canada computing facilities. R. Marchand acknowledges the support by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imtiaz, N., Marchand, R. & Rizvi, H. Effect of magnetic connectivity on CubeSat needle probe measurement. Astrophys Space Sci 367, 49 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-022-04078-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-022-04078-x