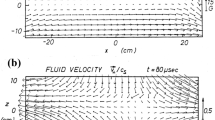
Abstract
We investigate the evolution of reconnection inflow using a fully kinetic approach. Three types of inflow are detailed, namely the collapse inflow, the vortex inflow and the reverse inflow. They are formed dynamically at different stages of reconnection via self-organizing processes, but are closely interrelated with each other. The reconnection starts from a small perturbation, which can trigger off a chain of pressure-induced collapses propagating into the inflow region. The pressure gradient results in the collapse inflow toward the reconnection site. Then due to the continuous injection of hot plasma carried by the reconnection outflows, the expanding exhaust causes its adjacent region to be compressed. The combined effects of the compression and the reflection of conducting walls lead to the formation of the vortex inflow. Subsequently, the reverse inflow develops gradually within the exhaust. Under the modulation of these inflows, the reconnection rate shows a transient oscillation. We also discussed the possible occurrence of the self-organization inflow available in different contexts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelopoulos, V., McFadden, J.P., Larson, D., Carlson, C.W., Mende, S.B., Frey, H., Phan, T., Sibeck, D.G., Glassmeier, K.-H., Auster, U., Donovan, E., Mann, I.R., Rae, I.J., Russell, C.T., Runov, A., Zhou, X.-Z., Kepko, L.: Tail reconnection triggering substorm onset. Science 321, 931 (2008)
Beidler, M.T., Cassak, P.A.: Model for incomplete reconnection in sawtooth crashes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 255002 (2011)
Birn, J., Drake, J.F., Shay, M.A., Rogers, B.N., Denton, R.E., Hesse, M., Kuznetsova, M., Ma, Z.W., Bhattacharjee, A., Otto, A., Pritchett, P.L.: Geospace environmental modeling (GEM) magnetic reconnection challenge. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 3715 (2001)
Cai, H.J., Lee, L.C.: The generalized Ohm’s law in collisionless magnetic reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 4, 509 (1997)
Chandra, M., Verma, M.K.: Flow reversals in turbulent convection via vortex reconnections. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 114503 (2013)
Daughton, W.: Kinetic theory of the drift kink instability in a current sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 29429 (1998)
Daughton, W., Lapenta, G., Ricci, P.: Nonlinear evolution of the lower-hybrid drift instability in a current sheet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 105004 (2004)
Daughton, W., Scudder, J., Karimabadi, H.: Fully kinetic simulations of undriven magnetic reconnection with open boundary conditons. Phys. Plasmas 13, 072101 (2006)
Egedal, J., Fox, W., Katz, N., Porkolab, M., Reim, K., Zhang, E.: Laboratory observations of spontaneous magnetic reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 015003 (2007)
Esirkepov, T.Z.: Exact charge conservation scheme for particle-in-cell simulation with an arbitrary form-factor. Comput. Phys. Commun. 135, 144 (2001)
Fujimoto, K.: Time evolution of the electron diffusion region and the reconnection rate in fully kinetic and large system. Phys. Plasmas 13, 072904 (2006)
Jin, S.P., Yang, H.A., Wang, X.G.: Hall effect and fine structures in magnetic reconnection with high plasma \(\beta \). Phys. Plasmas 12, 042902 (2005)
Harris, E.G.: On a plasma sheath separating regions of oppositely directed magnetic field. Nuovo Cimento 23, 115 (1962)
Hasegawa, H., Wang, J., Dunlop, M.W., Pu, Z.Y., Zhang, Q.-H., Lavraud, B., Taylor, M.G.G.T., Constantinescu, O.D., Berchem, J., Angelopoulos, V., McFadden, J.P., Frey, H.U., Panov, E.V., Volwerk, M., Bogdanova, Y.V.: Evidence for a flux transfer event generated by multiple X-line reconnection at the magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L16101 (2010)
Hoshino, M.: The electrostatic effect for the collisionless tearing mode. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 7368 (1987)
Huang, Y.-M., Bhattacharjee, A., Sullivan, B.P.: Onset of fast reconnection in Hall magnetohydrodynamics mediated by the plasmoid instability. Phys. Plasmas 18, 072109 (2011)
Karimabadi, H., Dorelli, J., Roytershteyn, V., Daughton, W., Chacón, L.: Flux pileup in collisionless magnetic reconnection: bursty interaction of large flux ropes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 025002 (2011)
Lapenta, G.: Self-feeding turbulent magnetic reconnection on macroscopic scales. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 235001 (2008)
Liu, C., Feng, X., Guo, J., Ye, Y.: Study of small-scale plasmoid structures in the magnetotail using Cluster observations and Hall MHD simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 118, 2087 (2013)
Liu, C., Feng, X., Nakamura, R., Guo, J., Wang, R.: Double-peaked core field of flux ropes during magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 6374 (2017a)
Liu, Y.-H., Hesse, M., Guo, F., Daughton, W., Li, H., Cassak, P.A., Shay, M.A.: Why does steady-state magnetic reconnection have a maximum local rate of order 0.1? Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 085101 (2017b)
Lu, Q., Lu, S., Huang, C., Wu, M., Wang, S.: Self-reinforcing process of the reconnection electric field in the electron diffusion region and onset of collisionless magnetic reconnection. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 55, 085019 (2013)
Ma, Z.W., Bhattacharjee, A.: Hall magnetohydrodynamic reconnection: the geospace environment modeling challenge. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 3773 (2001)
Matthaeus, W.H.: Reconnection in two dimensions: localization of vorticity and current near magnetic X-points. Geophys. Res. Lett. 9, 660 (1982)
Mandt, M.E., Denton, R.E., Drake, J.F.: Transition to whistler mediated magentic reconnection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 73 (1994)
Øieroset, M., Phan, T.D., Fujimoto, M., Lin, R.P., Lepping, R.P.: In situ detection of collisionles reconnection in the Earth’s magnetotail. Nature 412, 414 (2001)
Øieroset, M., Phan, T.D., Eastwood, J.P., Fujimoto, M., Daughton, W., Shay, M.A., Angelopoulos, V., Mozer, F.S., McFadden, J.P., Larson, D.E., Glassmeier, K.-H.: Direct evidence for a three-dimensional magnetic flux rope flanked by two active magnetic reconnection X lines at Earth’s magnetopause. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 165007 (2011)
Shay, M.A., Drake, J.F.: The role of electron dissipation on the rate of collisionless magnetic reconnection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 3759 (1998)
Treumann, R.A., Nakamura, R., Baumjohann, W.: Collisionless reconnection: mechanism of self-ignition in thin plane homogeneous current sheets. Ann. Geophys. 28, 1935 (2010)
Ugai, M.: Self-consistent development of fast magnetic reconnection with anomalous plasma resistivity. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 26, 1549 (1984)
Vasyliunas, V.M.: Theoretical models of magnetic field line merging. Rev. Geophys. 13, 303 (1975)
Wan, W., Lapenta, G.: Electron self-reinforcing process of magnetic reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 015001 (2008)
Wang, R., Lu, Q., Nakamura, R., Huang, C., Du, A., Guo, F., Teh, W., Wu, M., Lu, S., Wang, S.: Coalescence of magnetic flux ropes in the ion diffusion region of magnetic reconnection. Nat. Phys. 12, 263 (2016)
Yang, H.A., Jin, S.P., Zhou, G.C.: Density depletion and Hall effect in magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A11223 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 41231068, 41531073, 41204127 and 61872047), and the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories. We acknowledge the use of computer resources at National Space Science Center, CAS. The software used in this work in part developed in pCANS at Chiba University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Feng, X., Wan, M. et al. Dynamic patterns of self-organization inflow in collisionless magnetic reconnection. Astrophys Space Sci 364, 127 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-019-3619-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-019-3619-8