Abstract
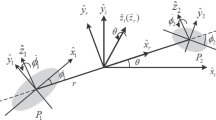
The positions and dynamical characteristics of artificial equilibrium points (AEPs) in the vicinity of a binary asteroid with continuous low-thrust are studied. The restricted ellipsoid–ellipsoid model of binary system is employed for the binary asteroid system. The positions of AEPs are obtained by this model. It is found that the set of the point \(L_{1}\) or \(L_{2}\) forms a shape of an ellipsoid while the set of the point \(L_{3}\) forms a shape like a “banana”. The effect of the continuous low-thrust on the feasible region of motion is analyzed by zero velocity curves. Because of using the low-thrust, the unreachable region can become reachable. The linearized equations of motion are derived for stability’s analysis. Based on the characteristic equation of the linearized equations, the stability conditions are derived. The stable regions of AEPs are investigated by a parametric analysis. The effect of the mass ratio and ellipsoid parameters on stable region is also discussed. The results show that the influence of the mass ratio on the stable regions is more significant than the parameters of ellipsoid.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliasi, G., Mengali, G., Quarta, A.A.: Artificial equilibrium points for a generalized sail in the circular restricted three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 110(4), 343–368 (2011)
Aliasi, G., Mengali, G., Quarta, A.A.: Artificial equilibrium points for electric sail with constant attitude. J. Spacecr. Rockets 50(6), 1295–1298 (2013)
Aliasi, G., Mengali, G., Quarta, A.A.: Artificial periodic orbits around L1-type equilibrium points for a generalized sail. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 38(9), 1847–1852 (2015)
Baig, S.M., McInnes, C.R.: Artificial three-body equilibria for hybrid low-thrust propulsion. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 31(6), 1644–1655 (2008)
Baig, S.M., Mcinnes, C.R.: Artificial halo orbits for low-thrust propulsion spacecraft. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 104(4), 321–335 (2009)
Bellerose, J., Scheeres, D.J.: Restricted full three-body problem: application to binary system 1999 KW4. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 31(1), 162–171 (2008)
Bombardelli, C., Peláez, J.: On the stability of artificial equilibrium points in the circular restricted three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 109(1), 13–26 (2011)
Bookless, J., McInnes, C.R.: Control of Lagrange point orbits using solar sail propulsion. Acta Astronaut. 62(62), 159–176 (2008)
Broschart, S.B., Scheeres, D.J.: Control of hovering spacecraft near small bodies: application to Asteroid 25143 Itokawa. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 28(2), 343–354 (2005)
Dusek, H.M.: Motion in the vicinity of libration points of a generalized restricted three-body model. Prog. Astronaut. Rocket. 17, 37–54 (1966)
Fan, S.: A new extracting formula and a new distinguishing means on the one variable cubic equation. Nat. Sci. J. Hainan Teach. Coll. 2(2), 91–98 (1989)
Heiligers, J., Macdonald, M., Parker, J.S.: Extension of Earth–Moon libration point orbits with solar sail propulsion. Astrophys. Space Sci. 361(7), 241 (2016)
Hou, X.Y., Liu, L.: Collinear libration points with continuous low thrust. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 45(2), 265–273 (2013)
Kunitsyn, A.L., Perezhogin, A.A.: On the stability of triangular libration points of the photogravitational restricted circular three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 18(4), 395–408 (1978)
McInnes, C.R.: Artificial Lagrange points for a partially reflecting flat solar sail. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 22(1), 185–187 (1999)
McInnes, C.R., McDonald, A.J.C., Simmons, J.F.L.: Solar sail parking in restricted three-body systems. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 17(2), 399–406 (1994)
Morimoto, M.Y., Yamakawa, H., Uesugi, K.: Artificial equilibrium points in the low-thrust restricted three-body problem. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 30(5), 1563–1568 (2007)
Ostro, S.J., Margot, J.L., Benner, L.A.: Radar imaging of binary near-Earth asteroid (66391) 1999 KW4. Science 314(5803), 1276–1280 (2006)
Perezhogin, A.A.: Stability of the sixth and seventh libration points in the photogravitational restricted circular three-body problem. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2(4), 481–484 (1976)
Perezhogin, A.A., Tureshbaev, A.T.: Stability of coplanar libration points in the photo gravitational restricted three-body problem. Sov. Astron. Lett. 33(4), 445–448 (1989)
Ranjana, K., Kumar, V.: On the artificial equilibrium points in a generalized restricted problem of three bodies. Int. J. Astron. Astrophys. 3(4), 508–516 (2013)
Schuerman, D.W.: The restricted three-body problem including radiation pressure. Astrophys. J. 238 337–342 (1980)
Simmons, J.F., McDonald, A.J.C., Brown, J.C.: The restricted 3-body problem with radiation pressure. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 35(2), 145–187 (1984)
Wang, Y.K.: Research on orbit design and optimization of asteroid exploration mission (2016)
Waters, T.J., McInnes, C.R.: Solar sail dynamics in the three-body problem: homoclinic paths of points and orbits. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 43(6), 490–496 (2008)
Williams, T., Abate, M.: Capabilities of furlable solar sails for asteroid proximity operations. J. Spacecr. Rockets 46(5), 967–975 (2009)
Yang, H.W., Zeng, X.Y., Baoyin, H.X.: Feasible region and stability analysis for hovering around elongated asteroids with low thrust. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 15(9), 1571–1586 (2015)
Zeng, X.Y., Jiang, F.H., Li, J.F.: Asteroid body-fixed hovering using non-ideal solar sails. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 15(4), 597–607 (2015)
Zeng, X.Y., Gong, S.P., Li, J.F., Alfriend, K.T.: Solar sail body-fixed hovering over elongated asteroids. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 39, 1223–1231 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The work described in this paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11672126), Innovation Funded Project of Shanghai Aerospace Science and Technology (Grant No. SAST2015036), the Opening Grant from the Key Laboratory of Space Utilization, Chinese Academy of Sciences (LSU-2016-07-01). The authors fully appreciate their financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, S., Li, S. & Yang, H. Artificial equilibrium points in binary asteroid systems with continuous low-thrust. Astrophys Space Sci 362, 137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-017-3119-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-017-3119-7