Abstract
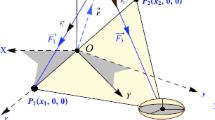
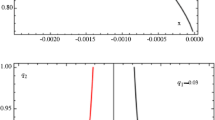
The present paper deals with the photogravitational restricted four-body problem, when the third primary placed at the triangular libration point of the restricted three-body problem is an oblate/prolate body. The third primary \(m_{3}\) is not influencing the motion of the dominating primaries \(m_{1}\) and \(m_{2}\). We have studied the motion of \(m_{4}\), moving under the influence of the three primaries \(m_{i}, i=1,2,3\), but the motion of the primaries is not being influenced by infinitesimal mass \(m_{4}\). The aim of this study is to find the locations of the libration points and their stability. We obtain three collinear and five non-collinear libration points when the third body is an oblate spheroid and source of radiation. The collinear libration points are unstable for all the mass parameter. The non-collinear libration points are stable for different mass parameters and oblateness factors. Further there exist 12 libration points, depending on the mass ratio of dominating primaries, the prolateness, and the radiation pressure of the third primary. We have drawn the zero velocity surface to determine the possible allowed boundary region. We observed that for increasing values of the oblateness coefficient \(A\), the corresponding possible boundary region increases where the particle can freely move from one side to another side. Further, for different values of the Jacobi constant \(C\), we can find the boundary region where the particle can move in the possible allowed partitions. The stability region of the libration points expanded due to the presence of the oblateness coefficient and various values of \(C\). We further apply these findings to the Sun–Jupiter–asteroid–spacecraft system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Ramírez, M., Barrabés, E.: Transport orbits in an equilateral restricted four-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 121, 191–210 (2015)
Bhatnagar, K.B., Chawla, J.M.: A study of Lagrangian points in the photogravitational restricted three body problem. Indian J. Pure Appl. Math. 10(11), 1443–1451 (1979)
Baltagiannis, A.N., Papadakis, K.E.: Families of periodic orbits in the restricted four-body problem. Astrophys. Space Sci. 336, 357–367 (2011)
Ceccaroni, M., Biggs, J.: Extension of low-thrust propulsion to the autonomous coplanar circular restricted four body problem with application to future Trojan asteroid missions. In: 61st International Astronautical Congress, IAC-10-1.1.3, Prague (2010)
Ceccaroni, M., Biggs, J.: Low-thrust propulsion in a coplanar circular restricted four body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 112, 191–219 (2012)
Chand, M.A., Umakant, P., Hassan, M.R., Suraj, M.S.: On the R4BP when third primary is an oblate spheroid. Astrophys. Space Sci. 357, 82 (2015)
Croustalloudi, M.N., Kalvouridis, T.J.: The restricted \(2+2\) body problem: parametric variation of the equilibrium states of the minor bodies and their attracting regions. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 281–849 (2013)
Douskos, C., Kalantonis, V., Markellos, P., Perdios, E.: On Sitnikov-like motions generating new kinds of 3D periodic orbits in the R3BP with prolate primaries. Astrophys. Space Sci. 337, 99–106 (2012)
Moulton, F.R.: On a class of particular solutions of the problem of four bodies. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1, 17–29 (1900)
Papadouris, J.P., Papadakis, K.E.: Equilibrium points in the photogravitational restricted four-body problem. Astrophys. Space Sci. (2014)
Radzievskii, V.V.: Astron. Ž. 27, 250–256 (1950) (in Russian)
Radzievskii, V.V.: Astron. Ž. 28, 363–372 (1951) (in Russian)
Ragos, O., Zafiropoulos, F.A., Vrahatis, M.N.: A numerical study of the influence of the Poynting-Robertson effect on the equilibrium points of the photo-gravitational restricted three-body problem. II. Out of plane case. Astron. Astrophys. 300, 579–590 (1995)
Schuerman, D.: The restricted three-body problem including radiation pressure. Astrophys. J. 238, 337–342 (1980)
Simmons, J.F.L., McDonald, A.J.C., Brown, J.C.: The restricted 3-body problem with radiation pressure. Celest. Mech. 35, 145–187 (1985)
Suraj, M.S., Hassan, M.R.: Sitnikov restricted four-body problem with radiation pressure. Astrophys. Space Sci. 349(2), 705–716 (2014)
Suraj, M.S., Hassan, M.R., Chand, M.A.: The photo-gravitational R3BP when the primaries are heterogeneous spheroid with three layers. J. Astronaut. Sci. : online (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asique, M.C., Prasad, U., Hassan, M.R. et al. On the photogravitational R4BP when the third primary is an oblate/prolate spheroid. Astrophys Space Sci 360, 13 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-015-2522-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-015-2522-1