Abstract
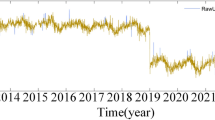
Light curves are usually constructed from discrete observational data by interpolation. In most cases, the observation data is temporally uneven, and therefore the light curve is usually derived by the interpolation of the binned data with the spline function, which is intended for reducing the “high sample noise” (i.e., the variability in the timescales comparable with the bin width). Such a practice of course reduces the time resolution of the light curve. It is known that function approximation is one of the most important applications of the artificial neural networks (ANN). In this work, for the first time we tentatively use the ANN to construct light curves from unevenly sampled variability data. To demonstrate the advantages of ANN for signal reconstruction over commonly used cubic spline function scheme, two sets of simulated periodic functions are used with random noises of varying magnitudes, one single frequency based and one multiple (two) frequency based. These signal reconstruction tests show that the ANN is clearly superior to the cubic spline scheme. As a case study, we use the uneven long-term multi-band monitoring data of BL lacertae to derive the light curves with ANN. It is found that the light curves derived with ANN have higher time resolution than those with the cubic spline function adopted in previous works. We recommend using ANN for the signal reconstruction in astrophysical data analysis as well as that of in other fields.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Błażejowski, M., Blaylock, G., Bond, I.H., et al.: Astrophys. J. 630, 130 (2005)
Bonnett, C.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. (2013, submitted). arXiv:1312.1287
Chatterjee, R., Jorstad, S.G., Marscher, A.P., et al.: Astrophys. J. 689, 79 (2008)
Fan, J.H., Qian, B.C., Tao, J.: Astron. Astrophys. 369, 758 (2001)
Fan, J.H., Peng, Q.S., Tao, J., Qian, B.C., Shen, Z.Q.: Astron. J. 138, 1428 (2009)
Farley, B., Clark, W.A.: IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 4, 76 (1954)
Hartman, R.C., Böttcher, M., Aldering, G., et al.: Astrophys. J. 553, 683 (2001)
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation. Prentice Hall, New York (1999)
Jacek, M.Z.: Introduction to Artificial Neural System. West Pub. Company, New York (1992)
Krawczynski, H., Hughes, S.B., Horan, D., et al.: Astrophys. J. 601, 151 (2004)
McCulloch, W., Pitts, W.: Bull. Math. Biophys. 5, 115 (1943)
Ulrich, M.-H., Maraschi, L., Urry, C.M.: Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 35, 445 (1997)
Villata, M., Raiteri, C.M., Aller, H.D., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 424, 497 (2004)
Villata, M., Raiteri, C.M., Larionov, V.M., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 501, 455 (2009)
Wang, Q.-J., Liao, D.-C., Zhou, Y.-H., Liao, X.-H.: Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 32, 342 (2008)
Wehrle, A.E., Pian, E., Urry, C.M., et al.: Astrophys. J. 497, 178 (1998)
Zhang, X.-H., Wang, Q.-J., Zhu, J.-J., Zhang, H.: Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 36, 86 (2012)
Acknowledgements
We thank Claudia M. Raiteri for providing us the optical and radio data of BL Lacertae. This work is supported by the NSFC (grants U1231105, 11173043, and 11233006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, QJ., Cao, X. Reconstruct light curves from unevenly sampled variability data with artificial neural networks. Astrophys Space Sci 352, 51–55 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-1891-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-1891-1