Abstract
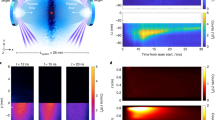
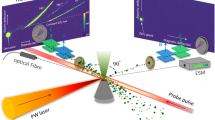
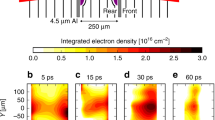
Results from a scaled, collision-free, laser-plasma experiment designed to address aspects of collisionless plasma interaction in a high-plasma β supernova remnant (SNR) are discussed. Ideal magneto-hydrodynamic scaling indicates that the experimental plasma matches the SNR plasma at 500 ps. Experimental data show that the magnetic field can alter the plasma density profile when two similar plasmas interact in a colliding geometry. These results are not explained by magnetic-field pressure; they do, however, suggest magnetic field penetration that localizes the plasma particles to the Larmor radius, which appears smaller than the size of the experiment and the particle mean-free paths and may thus increase the effective collisionality of the interacting plasma system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Courtois, C., et al.: 2004, Phys. Plasmas 11, 3386.
Djaoui, A. and Rose, S.J.: 1992, J. Phys. B 25, 2745.
Decourchelle, A., Ellison, D.C. and Ballet, J.: 2000, ApJ 543, L57.
Drake, R.P.: 2002, Phys. Plasmas 9, 727.
Enomoto, R., et al: 2002, Nature 416, 823.
Gregory, C.D., et al.: 2005, Ap&SS 298, 389.
Remington, B.A., et al.: 2000, Phys. Plasma 7, 1641.
Ryutov, D., et al.: 1999, ApJ 518, 821.
Ryutov, D.D., Remington, B.A., Robey, H.F. and Drake, R.P.: 2001, Phys. Plasmas 8, 1804.
Woolsey, N.C., et al.: 2001, Phys. Plasmas 8, 2439.
Woolsey, N.C., et al.: 2002, Phys. Plasmas 9, 729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Courtois, C., Grundy, R.A.D., Ash, A.D. et al. Experiment on Collisionless Plasma Interaction with Applications to Supernova Remnant Physics. Astrophys Space Sci 298, 93–98 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-005-3917-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-005-3917-1