Abstract
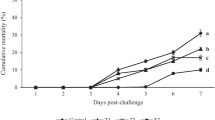
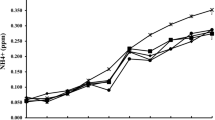
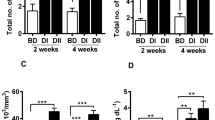
This study was to evaluate the growth, intestinal morphology, intestinal flora, and anti-infection activity against Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp upon adding Bacillus licheniformis to the feed. Four experimental diets supplemented with different concentrations of B. licheniformis were as follows: 0 (CK), 106 colony forming units (CFU)/g (A), 107 CFU/g (B), and 108 CFU/g (C). After 60 days of feeding trial, the fish were intraperitoneally injected with 100 μL of A. hydrophila (LD50=5×106 CFU/mL) every day for a week to measure cytokines. Fish in group C showed the best growth indexes (weight gain rate: 186.88; specific growth rate: 1.76; and feed conversion rate: 1.07). The final body weight, weight gain rate, and specific growth rate in group C were increased by 47.9%, 87.4%, and 53.0%, feed conversion ratio reduced by 42.5%. Fish showed the highest villus height of intestine in group C. The intestinal flora analysis showed that, the richness of phylum, Firmicutes in the treatment groups significantly increased, and that of Bacteroides decreased remarkably. After the infection with A. hydrophila, B. licheniformis at 108 CFU/g significantly upregulated protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β) compared with the control group. These results indicated that dietary supplementation of B. licheniformis not only increased the growth and influenced the intestinal development and disease resistance of common carp, but also altered the intestine microbiota structure. Furthermore, in our study, the optimal concentration of B. licheniformis in diets for common carp was equal to 108 CFU/g.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Abdallah IN, Ragab SH, Abd EBA, Shoeib ARS, Yasser A, Dina F (2011) Frequency of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in gut microbiota in obese and normal weight Egyptian children and adults [J]. Arch Med Sci 7:501–507
Azarin H, Aramli MS, Imanpour MR, Rajabpour M (2015) Effect of a probiotic containing Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis and ferroin solution on growth performance, body composition and haematological parameters in Kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum) fry. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 7(1):31–37
Byndloss MX, Bäumler AJ (2018) The germ-organ theory of non-communicable diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:103–110
Carnevali O, Zamponi MC, Sulpizio R, Rollo A, Cresci A (2004) Administration of probiotic strain to improve sea bream wellness during development [J]. Aquac Int 12(4):377–386
Chandni T, Shekhar N, Rup L, Ram KN (2018) Fish gut microbiome: current approaches and future perspectives. Indian J Microbiol 58(4):397–414
Chang XL, Feng JC, Guo XR, Huang MY, Nie GX, Zhang JX (2018) Dietary supplementation with Rehmannia glutinosa affects the composition of intestinal microorganisms in common carp. J Basic Microbiol 58(12):1023–1032
Chiu KH, Liu WS (2014) Dietary administration of the extract of Rhodobacter sphaeroides WL-APD911 enhances the growth performance and innate immune responses of seawater red tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus×Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 418-419:32–38
De Rodriganez MS, Diaz-Rosales P, Chabrillon M, Smidt H, Arijo S, Leon-Rubio J, Alarcon F, Balebona M, Morinigo M, Cara J, Moyano F (2010) Effect of dietary administration of probiotics on growth and intestine functionality of juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup 1858). Aquac Nutr 15(2):177–185
Delwin AE, Cai J, Lu Y, Yu H, Chen L, Jian J, Tang J, Liang J, Kuebutornye FK (2018) Effects of a commercial probiotic BS containing Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth, immune response and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol 82:229–238
Dimitroglou A, Merrifield DL, Moate R, Davies SJ, Spring P, Sweetman J, Bradley G (2009) Dietary mannan oligosaccharide supplementation modulates intestinal microbial ecology and improves gut morphology of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) [J]. J Anim Sci 87(10):3226–3234
Felix KA, Kuebutornye DAE, Lu YS (2019) A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol 87:820–828
Feng JC, Chang XL, Zhang YR, Yan X, Zhang JX, Nie GX (2019) Effects of Lactococcus lactis from Cyprinus carpio L. as probiotics on growth performance, innate immune response and disease resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 93:73–81
Gao XL, Zhang M, Li X, Han Y, Wu FC, Liu Y (2018) Effects of a probiotic (Bacillus licheniformis) on the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Fish Shellfish Immunol 76:143–152
Gobi N, Vaseeharan B, Chen JC, Rekha R, Vijayakumar S, Anjugam M, Iswarya A (2018) Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis Dahb1 improves growth performance, mucus and serum immune parameters, antioxidant enzyme activity as well as resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 76:501–508
Gomez-Gil B, Roque A, Turnbull JF (2000) The use and selection of probiotic bacteria for use in the culture of larval aquatic organisms. Aquaculture 191(1-3):259–270
Hai NV (2015) Research findings from the use of probiotics in tilapia aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(2):592–597
Han B, Long WQ, He JY, Liu YJ, Si YQ, Tian LX (2015) Effects of dietary Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immunological parameters, intestinal morphology and resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 46(2):225–231
Hong HA, Hong DL, Cutting SM (2010) The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29(4):813–835
Irianto A, Austin B (2002) Use of probiotics to control furunculosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 25(6):333–342
Lazado CC, Caipang Christopher Marlowe A (2014) Mucosal immunity and probiotics in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 39(1):78–89
Lee SY, Lee BH (2010) Esterolytic and lipolytic activities of Lactobacillus Casei-subsp-Casei LLG. J Food Sci 55(1):119–122
Li MO, Flavell RA (2008) Contextual regulation of inflammation: a duet by transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-10. Immunity 28:468–476
Li HD, Tian XL, Dong SL (2018) Growth performance, non-specific immunity, intestinal histology and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei fed on a diet supplemented with live cells of Clostridium butyricum. Aquaculture 498:470–481
Madani NSH, Adorian TJ, Farsani HG, Hoseinifar SH (2018) The effects of dietary probiotic Bacilli (Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis) on growth performance, feed efficiency, body composition and immune parameters of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) postlarvae. Aquac Res 49(5):1926–1933
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Bradley G, Baker RTM, Davies SJ (2010) Soybean meal alters autochthonous microbial populations, microvilli morphology and compromises intestinal enterocyte integrity of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 32(9):755–766
Midhun SJ, Neethu S, Arun D, Vysakh A, Divya L, Radhakrishnan EK, Jyothis M (2019) Dietary supplementation of Bacillus licheniformis HGA8B improves growth parameters, enzymatic profile and gene expression of Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 505(30):289–296
Najeeb A, Wu B, Mahmood MA, Muhammad M (2015) Probiotics and prebiotics associated with aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(2):733–741
Panigrahi A, Kiron V, Satoh S, Hirono I, Kobayashi T, Sugita H, Puangkaew J, Aoki T (2007) Immune modulation and expression of cytokine genes in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss upon probiotic feeding. Dev Comp Immunol 31:372–382
Peddie S, Zou J, Secombes CJ (2002) Immunostimulation in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following intraperitoneal administration of Ergosan. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 86(1-2):101–113
Pérez-Sánchez T, Balcázar JL, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Gioacchini G, Blas ID, Ruiz-Zarzuela I (2011) Expression of immune-related genes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) induced by probiotic bacteria during Lactococcus garvieae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31(2):196–201
Qin L, Xiang JH, Xiong F, Wang GT, Zou H, Li WX, Li M, Wu SG (2020) Effects of Bacillus licheniformis on the growth, antioxidant capacity, intestinal barrier and disease resistance of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:344–350
Salze G, Mclean E, Schwarz MH, Craig SR (2008) Dietary mannan oligosaccharide enhances salinity tolerance and gut development of larval cobia. Aquaculture 274(1):148–152
Sha YJ, Wang L, Liu M, Jiang KY, Xin F, Wang BJ (2016) Effects of lactic acid bacteria and the corresponding supernatant on the survival, growth performance, immune response and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 452:28–36
Sugita H, Tanaka K, Yoshinami M, Deguchi Y (1995) Distribution of Aeromonas species in the intestinal tracts of river fish. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(11):4128–4130
Tarnecki AM, Burgos FA, Ray CL, Arias CR (2017) Fish intestinal microbiome: diversity and symbiosis unravelled by metagenomics. J Appl Microbiol 123(1):1–17
Thacker PA, Aumaitre A, Lee BD, Ha JK (2000) Recent advances in the use of enzymes with special reference to β-glucanases and pentosanases in swine rations. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 13:376–385
Tsuchiya C, Sakata T, Sugita H (2010) Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett Appl Microbiol 46(1):43–48
Udayangani RMC, Dananjaya SHS, Nikapitiya C, Heo GJ, Lee J, Zoysa MD (2017) Metagenomics analysis of gut microbiota and immune modulation in zebrafish (Danio rerio) fed chitosan silver nanocomposites. Fish Shellfish Immunol 66:173–184
Vine NG, Leukes WD, Kaiser H (2006) Probiotics in marine larviculture. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30(3):404–427
Wang JL, Meng X, Lu RH, Wu C, Luo YT, Yan X (2015) Effects of Rehmannia glutinosa on growth performance, immunological parameters and disease resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquaculture 435:293–300
Wang XT, Sun YX, Wang LL, Li XY, Qu KL, Xu YP (2017) Synbiotic dietary supplement affects growth, immune responses and intestinal microbiota of Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 68:232–242
Xia JH, Lin G, Fu GH, Wan ZY, Lee M, Wang L, Liu XJ, Yue GH (2014) The intestinal microbiome of fish under starvation. BMC Genomics 15(1):266
Zhang CN, Li XF, Xu WN, Zhang DD, Lu KL, Wang LN, Tian HY, Liu WB (2014) Combined effects of dietary fructooligosaccharide and Bacillus licheniformison growth performance, body composition, intestinal enzymes activities and gut histology of triangular bream (Megalobrama terminalis). Aquac Nutr 21:755–766
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31902361), the Key Technology Research Project of Henan Province (202102110106), and the Key Research Projects of Henan Higher Education Institutions (19B240001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianxin Zhang is responsible for the design of the research and the writing of the paper. Mengyuan Huang is responsible for the completion of the entire process of the experiment, data analyzing, and paper writing. Junchang Feng and Xulu Chang are responsible for the guidance of the experimental process and revision of the paper. Yongyan Chen and Meng Li are helpful to assist the experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We strictly comply with and reference the Henan Normal University Research Council’s “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” and “Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.”
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Gavin Burnell
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Huang, M., Feng, J. et al. Effects of dietary Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, intestinal morphology, intestinal microbiome, and disease resistance in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquacult Int 29, 1343–1358 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00701-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00701-w