Abstract
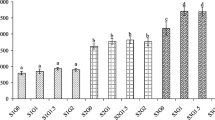
A 28-day indoor trial was conducted to evaluate the water quality, phytoplankton composition and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei in an integrated biofloc system with Gracilaria birdiae and Gracilaria domingensis. The experimental design was completely randomized with three treatments: control (shrimp monoculture); SB (shrimp and G. birdiae) and SD (shrimp and G. domingensis), all with three replicates. Random sampling was done (6 % of total population per experimental unit) to confirm white spot syndrome Virus (WSSV) infection using nested-PCR analysis due to suspicion of presence of the virus in the experiment (treatment and control groups). Shrimp L. vannamei (2.63 ± 0.10 g) were stocked in experimental tanks at a density of 425 shrimp m−3, and the Gracilaria was stocked at a biomass of 2.0 kg m−3. Shrimp mortality began in both the experimental and control groups at 10 days of culture. The integrated biofloc system (shrimp and seaweed) increased settleable solids (by 26–52 %); final weight (by 6–21 %); weekly growth (by 17–43 %); weight gain (by 17–43 %); specific growth rate (by 16–36 %); and yield (by 5–7 %) and decreased feed conversion ratio (by 21–28 %) and Cyanobacteria density about 16 % as compared to the control (shrimp monoculture). The use of red seaweed Gracilaria in an integrated biofloc system can enhance shrimp growth and reduce Cyanobacteria density in the presence of WSSV.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TAN:
-
Total ammonia nitrogen
- NO2-N:
-
Nitrite-nitrogen
- NO3-N:
-
Nitrate-nitrogen
- PO 34 -P:
-
Orthophosphate
- TSS:
-
Total suspended solids
- SS:
-
Settleable solids
- SGR:
-
Specific growth rate
- FCR:
-
Feed conversion ratio
- SB:
-
Shrimp and G. birdiae in an integrated biofloc system
- SD:
-
Shrimp and G. domingensis in an integrated biofloc system
- WSSV:
-
White spot syndrome Virus
References
ABCC (2013) Levantamento da infraestrutura produtiva e dos aspectos tecnológicos, econômicos, sociais e ambientais da carcinicultura marinha no Brasil em 2011. Associação Brasileira de Criadores de Camarão, Natal
Abreu MH, Pereira R, Yarish C, Buschmann AH, Sousa-Pinto I (2011) IMTA with Gracilaria vermiculophylla: productivity and nutrient removal performance of the seaweed in a land-based pilot scale system. Aquaculture 312(1–4):77–87
Al-Hafedh YS, Alam A, Buschmann HA, Fitzsimmons KM (2012) Experiments on an integrated aquaculture system (seaweeds and marine fish) on the Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia: efficiency comparison of two local seaweed species for nutrient biofiltration and production. Rev Aquac 4(1):21–31
Anand PSS, Kumar S, Panigrahi A, Ghoshal TK, Dayal JS, Biswas G, Sundaray JK, De D, Ananda RR, Deo AD, Pillai SM, Ravichandran P (2012) Effects of C:N ratio and substrate integration on periphyton biomass, microbial dynamics and growth of Penaeus monodon juveniles. Aquacult Int 21:511–524
A.P.H.A. (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. A.P.H.A., Washington
Asaduzzaman M, Rahman SMS, Azim ME, Islam MA, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ, Verreth JAJ (2010) Effects of C/N ratio and substrate addition on natural food communities in freshwater prawn monoculture ponds. Aquaculture 306(1–4):127–136
Audelo-Naranjo JM, Voltolina D, Romero-Bltrán E (2012) Cultural of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei Boone, 1931) with zero with exchange and no food addition: an eco-friendly approach. Lat Am J Aquatic Res 40(2):441–447
Avnimelech Y (2009) Biofloc technology—a pratical guide book. The world Aquaculture Society, Baton Rouge
Ballester ELC, Abreu PC, Cavalli RO, Emerenciano M, Abreu L, Wasielesky W Jr (2010) Effect of practical diets with different protein levels on the performance of Farfantepenaeus paulensis juveniles nursed in a zero exchange suspended microbial flocs intensive system. Aquac Nutr 16(2):163–172
Barrington K, Ridler N, Chopin T, Robinson S, Robinson B (2010) Social aspects of the sustainability on integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquacul Int 18(2):201–211
Brito LO, Arantes R, Magnotti C, Derner R, Pchara F, Olivera A, Vinatea L (2014) Water quality and growth of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in co-culture with green seaweed Ulva lactuca (Linaeus) in intensive system. Aquac Int 22(2):497–508
Campos SS, Silva UL, Lúcio MZ, Correia ES (2009) Natural food evaluation and water quality in zero water exchange culture of Litopenaeus vannamei fertilized with wheat bran. Aquac Int 17(2):113–124
Cohen JM, Samocha TM, Fox JM, Gandy RL, Lawrence AL (2005) Characterization of water quality factors during intensive raceway production of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei using limited discharge and biosecure management tools. Aquac Eng 32(3–4):425–442
Crab R, Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Verstraete W (2012) Biofloc technology in aquaculture: beneficial effects and future challenges. Aquaculture 356–357:351–356
Cruz-Suárez LE, León A, Penã-Rodríguez A, Rodríguez-Penã G, Moll B, Ricque-Marie D (2010) Shrimp Ulva co-culture: a sustainable alternative to diminish the need for artificial feed and improve shrimp quality. Aquaculture 301(1–4):64–68
Du R, Liu L, Wang A, Wang Y (2013) Effects of temperature, algae biomass and ambient nutrient on the absorption of dissolved nitrogen and phosphate by Rodophyte Gracilaria asiatica. Chin J Oceanol Limn 31(2):353–365
Ebeling JM, Timmons MB, Bisogni JJ (2006) Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia-nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 257(1–4):346–358
Emerenciano M, Ballester ELC, Cavalli RO, Wasielesky W Jr (2011) Effect of biofloc technology (BFT) on the early postlarval stage of pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis: growth performance, floc composition and salinity stress tolerance. Aquac Int 19(5):891–901
Emerenciano M, Cuzon G, Paredes A, Gaxiola G (2013) Evaluation of biofloc technology in pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus duorarum culture: growth performance, water quality, microorganisms profile and proximate analysis of biofloc. Aquac Int 21(6):1381–1394
Escobedo-Bonilla CM, Alday-Sanz V, Wille M, Sorgeloos P, Pensaert MB, Nauwynck HJ (2008) A review on the morphology, molecular characterization, morphogenesis and pathogenesis of white spot syndrome virus. J Fish Dis 31(1):1–18
Feijó RG, Kamimura MT, Oliveira-Neto JM, Vila-Nova CMVM, Gomes ACS, Coelho MGL, Vasconcelos RF, Gesteira TCV, Marins LF, Maggioni R (2013) Infectious myonecrosis virus and white spot syndrome virus co-infection in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farmed in Brazil. Aquaculture 380–383:1–5
Felföldy L, Szabo E, Tothl L (1987) A biológiai vizminösités. Vizügyi Hodrobiológia Vizdok, Budapest
Gamboa-Delgado J, Peña-Rodríguez A, Ricque-Marie D, Cruz-Suárez LE (2011) Assessment of nutrient allocation and metabolic turnover rate in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei co-fed live macroalgae Ulva clathrata and inert feed: dual stable isotope analysis. J Shellfish Res 30(3):969–978
Gao L, Shan HW, Zhang TW, Bao WY, Ma S (2012) Effects of carbohydrate addition on Litopenaeus vannamei intensive culture in a zero-water exchange systems. Aquaculture 342–343:89–96
Gitterle T, Salte R, Gjerde B, Cock J, Johansen H, Salazar M, Lozano C, Rye M (2005) Genetic (co) variation in resistance to White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) and harvest weight in Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei. Aquaculture 246(1–4):139–149
Golterman HJ, Clymo RS, Ohnstad MA (1978) Methods for physical and chemical analysis of freshwaters. Scientific Publications, London
Guerrelhas ACB, Teixeira AP (2012) Panorama da situação da mancha branca no Nordeste. Panorama Aquicult 22(129):38–41
Hopkins JE, Hamilton R, Sandifer P, Browdy C, Stokes A (1993) Effect of water exchange rate on production, water quality, effluent characteristics and nitrogen budgets of intensive shrimp ponds. J World Aquac Soc 24(3):304–320
Hopkins JE, Sandifer P, Browdy C, Stokes A (1994) Sludge management in intensive pond culture of shrimp: effect of management regime on water quality, sludge characteristics, nitrogen extinction, and shrimp production. Aquac Eng 13(1):11–30
Huo YZ, Xu SN, Wang YY, Zhang JH, Zhang YJ, Wu WN, Chen YQ, He PM (2011) Bioremediation efficiencies of Gracilaria verrucosa cultivated in a enclosed sea area of Hangzhou Bay China. J Appl Phycol 23(2):173–182
Huo Y, Wu H, Chai Z, Xu S, Han F, Dong L, He P (2012) Bioremediation efficiency of Gracilaria verrucosa for an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system with Pseudosciaena crocea in Xiangshan harbor, China. Aquaculture 326–329:99–105
Huynh TG, Yeh ST, Lin YC, Shyn LL, Chen JC (2011) White shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei immersed in seawater containing Sargassum hemiphyllum var. chinense powder and its extract showed increased immunity and resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish Immun 31(2):286–293
Immanuel G, Sivagnamavelmurugan M, Marudhupandi T, Radhakrishnam S, Palavesam A (2012) The effect of fucoidan from brown seaweed Sargassum wightii on WSSV resistance and immune activity in shrimp Penaeus monodon (Fab). Fish Shellfish Immun 32(3):551–564
Izzati M (2011) The role of seaweeds Sargassum polycistum and Gracilaria verrucosa on growth performance and biomass production of tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon Frab). J Coast Dev 14(3):235–241
Ju ZY, Forster L, Conquest L, Dominy W, Kuo WC, Horgen FD (2008) Determination of microbial community structures of shrimp floc cultures by biomarkers and analysis of floc amino acid profiles. Aquac Res 39(1):118–133
Kanjana K, Radtanatip T, Asuvapongratana S, Withyachummarnkul B, Wongprasert K (2011) Solvent extracts of the red seaweed Gracilaria fisheri prevent Vibrio harveyi infection in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish Immun 30(1):389–396
Khoi LV, Fotedar R (2011) Integration of western king prawn (Penaeus latisulcatus Kishinouye, 1986) and green seaweed (Ulva lactuca Linaeus, 1753) in closed recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 322–323:201–209
Koroleff F (1976) Determination of nutrients. In: Grasshoff K (ed) Methods of seawater analysis. Verlag Chemie Weinhein, New York
Lin YC, Yeh ST, Li CC, Chen LL, Cheng AC, Chen JC (2011) An immersion of Gracilaria tenuistipitata extract improves the immunity and survival of white Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish Immun 31(6):1239–1246
Lo CF, Leu JH, Ho CH, Chen CH, Peng SE, Chen YL, Chou CM, Yeh PY, Huang CJ, Chou HY, Wang CH, Kou GH (1996) Detection of baculovirus associated with White spot syndrome (WSBV) in penaeid shrimps using polymerase chain reaction. Dis Aquat Org 25(1–2):133–141
Lobban CS, Harrison PJ, Duncan MJO (1985) The physiological ecology of seaweeds. Cambridge University Press, New York
Lombardi JV, Almeida MHL, Lima PRT, Sale BOJ, Paula EJ (2006) Cage polyculture of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and the Philippines seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii. Aquaculture 258(1–4):412–415
Mackereth FJH, Heron J, Talling JF (1978) Water analysis: some revised methods for limnologists. Scientic Publications, London
Mai H, Fotedar R, Fewtrell J (2010) Evaluation of Sargassum sp. as a nutrient-sink in an integrated seaweed-prawn (ISP) culture system. Aquaculture 310:91–98
Marinho-Soriano E, Nunes SO, Carneiro MAA, Pereira DC (2009a) Nutrient’s removal from aquaculture wastewater using the seaweed Gracilaria birdiae. Biomass Bioenerg 33(2):327–331
Marinho-Soriano E, Panucci RA, Carneiro MAA, Pereira DC (2009b) Evaluation of Gracilaria caudata J. Agardh for bioremediation of nutrients from shrimp farming waste water. Bioresour Technol 100(24):6192–6198
Marinho-Soriano E, Azevedo CAA, Trigueiro TG, Pereira DC, Carneiro MAA (2011) Bioremediation of aquaculture wastewater using macroalgae and Artemia. Int Biodeter Biodegr 65(1):253–257
Márquez JEQ, Andreatta ER, Vinatea L, Olivera A, Brito LO (2012) Efeito da densidade nos índices zootécnicos da criação de camarões Litopenaeus schmitti. Bol Inst Pesca 38(2):145–153
Mayo M (2002) A summary of taxonomic changes recently approved by ICTV. Arch Virol 147(8):1655–1656
Muller IC, Andrade TPD, Tang-Nelson KFJ, Marques MRF, Lightner DV (2010) Genotyping of White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) geographical isolates from Brazil and comparison to other isolates from the Americas. Dis Aquat Org 88(2):91–98
Neal RS, Coyle SD, Tidwel JH, Boudreau BM (2010) Evaluation of stocking density and light level on the growth and survival of the pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, reared in zero-exchange systems. J World Aquac Soc 41(4):533–544
Pantoja C, Lightner DV (2008) Enfermedades virales. In: Morales V, Cuéllar-Anjel J (eds) Guía Técnica—Patología e Inmunología de Camarones Penaeidos, 1st edn. Programa CYTED Red II-D Vannamei, Panamá
Pereira- Neto JB, Dantas DMM, Gálvez AO, Brito LO (2008) Avaliação das comunidades planctônica e bentônica de microalgas em viveiros de camarão (Litopenaeus vannamei). Bol Inst Pesca 34(4):543–551
Pérez F, Volckaert FAM, Calderón J (2005) Pathogenicity of white spot syndrome virus on postlarvae and juveniles of Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei. Aquaculture 250(3–4):586–591
Portillo-Clark G, Casillas-Hernández R, Servín-Villegas R, Magallón-Barajas FJ (2012) Growth and survival of the juvenile yellowleg shrimp Farfantepenaeus californiensis cohabiting with the green feather alga Caulerpa sertularioides at different temperatures. Aquac Res 44(1):22–30
Ray AJ, Lewis BL, Browdy CL, Leffler JW (2010) Suspended solids removal to improve shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) production and an evaluation of a plant-based feed in minimal-exchange, superintensive culture systems. Aquaculture 299(1–4):89–98
Ray AJ, Dellori FS, Lotz JM (2011) Water quality dynamics and shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) production in intensive, mesohaline culture systems with two levels of biofloc management. Aquac Eng 45(3):12–136
Ray AJ, Seaborn G, Vinatea L, Browdy CL, Leffler JW (2012) Effects of biofloc reduction on microbial dynamics in minimal-exchange, superintensive shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, culture systems. J World Aquac Soc 43(6):790–801
Samocha TM, Patnaik S, Speed M, Ali AM, Burger JM, Almeida RV, Ayub Z, Harisanto M, Horowitz A, Brock DL (2007) Use of molasses as carbon source in limited discharge nursery and grow-out systems for Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac Eng 36(2):184–191
Sánchez A, Sánchez-Rodríguez I, Casas-Valdez M (2012) The stable isotope of nitrogen in an experimental culture of Ulva spp. and its assimilation in the nutrition of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, Baja California Sur, Mexico. J Appl Phycol 24(3):507–511
Sánchez-Martínez JG, Aguirre-Guzmán G, Mejía-Ruí H (2007) White spot syndrome virus in cultured shrimp: a review. Aquac Res 38(13):1339–1354
Schveitzer R, Arantes R, Baloi MF, Costódio PFS, Arana LV, Seiffert WQ, Andreatta ER (2013) Use of artificial substrates in the culture of Litopenaeus vannamei (Biofloc System) at different stocking densities: effects on microbial activity, water quality and production rates. Aquac Eng 54:93–103
Selvin J, Manilal A, Sujith S, Kiran GS, Lipton AP (2011) Efficacy of marine green alga Ulva fasciata extract on the management of shrimp bacterial diseases. Lat Am J Aquat Res 39(2):197–204
Silva KR, Wasielesky W Jr, Abreu PC (2013a) Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in the biofloc production of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. J World Aquac Soc 44(1):30–41
Silva GC, Costa RA, Peixoto JRO, Nascimento FEP, Carneiro PBM (2013b) Tropical atlantic marine macroalgae with bioactivity against virulent and antibiotic resistant Vibrio. Lat Am J Aquat Res 41(1):183–188
Sirirustananun N, Chen JC, Lin YC, Yeh ST, Liou CH, Chen LL, Sim SS, Chiew SL (2011) Dietary administration of a Gracilaria tenuistipitata extract enhances the immune response and resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus and White spot syndrome virus in the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immun 31(6):848–855
Skriptsova AV, Miroshnikova NV (2011) Laboratory experiment to determine the potential of two macroalgae from the Russian Far-East as biofilter for integrated multi trophic Aquaculture (IMTA). Bioresour Technol 102(3):3149–3154
Troell M, Joyce A, Chopin T, Neori A, Buschmman A, Fang JG (2009) Ecological engineering in aquaculture—potential for integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) in marine offshore systems. Aquaculture 297(1–4):1–9
Tsutsui I, Kanjanaworakul P, Srisapoome P, Aue-Umneoy D, Hamano K (2010) Growth of giant tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon Fabricus, under co-culture with a discarded filamentous seaweed Chaetomorpha ligustica (Kutzing), at an aquarium-scale. Aquac Int 18(4):545–553
Van Wyk P (1999) Nutrition and feeding of Litopenaeus vannamei in intensive culture systems. In: Van Wyk P, Davis-Hodgkins M, Laramore R, Main KL, Mountain J, Scarpa J (eds) Farming marine shrimp in recirculating freshwater systems, 1st edn. Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services—Harbor Branch Oceanic Institute, Florida
Van Wyk P, Scarpa J (1999) Water quality requirements and management. In: Van Wyk P, Davis-Hodgkins M, Laramore R, Main KL, Mountain J, Scarpa J (eds) Farming marine shrimp in recirculating freshwater systems, 1st edn. Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services—Harbor Branch Oceanic Institute, Florida
Vidal OM, Granja CB, Aranguren F, Brock JA, Salazar M (2001) A profound effect of hyperthermia on survival of Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles infected with white spot syndrome virus. J World Aquac Soc 32(4):364–372
Xu Y, Fang J, Tang Q, Lin J, Le G, Lia LV (2008a) Improvement of water quality by the macroalga, Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta), near aquaculture effluent outlets. J World Aquac Soc 39(4):549–555
Xu Y, Fang J, Wei W (2008b) Application of Gracilaria lichenoides (Rhodophyta) for alleviating excess nutrients in aquaculture. J Appl Phycol 20(2):199–203
Yu WJ, Pan LQ, Sun XH, Huang J (2013) Effects of bioflocos on water quality, and survival, growth and digestive enzyme activities of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in zero-water exchange culture tanks. Aquac Res 44(7):1093–1102
Yusoff FM, Matias-Peralta HB, Shariff M (2010) Phytoplankton population patterns in marine shrimp culture ponds with different sources of water supply. Aquat Ecosyst Health 13(4):458–464
Zhou Q, Li K, Jun X, Bo L (2009) Role and functions of beneficial microorganisms in sustainable Aquaculture. Bioresour Technol 100(16):3780–3786
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP) for research support. The authors also would like to thank Clarissa Vilela and Tereza Santos (DEPAq, UFRPE, Brazil) for their contributions in this study. Thanks are also to anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions. Alfredo Olivera and Luis Vinatea are CNPq research fellows.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brito, L.O., Arana, L.A.V., Soares, R.B. et al. Water quality, phytoplankton composition and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in an integrated biofloc system with Gracilaria birdiae (Greville) and Gracilaria domingensis (Kützing). Aquacult Int 22, 1649–1664 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-014-9771-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-014-9771-9