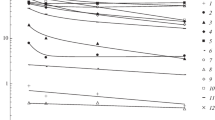
Abstract
The average composition of natural waters such as rivers, lakes, ocean, and hydrothermal vents and corresponding solids in equilibrium (e.g., river-suspended particles or shale; lake sediments; oceanic pelagic clay, organisms, and manganese nodules; and the mid-ocean ridge basalts) do not change randomly. The observed positive correlation between the electron binding energy (I z [*I z ]) and logarithms of bulk distribution coefficient (log K d ) for cations with charge of 1–4, and the negative correlation between I z [*I z ] and log K d for anions in various aquatic systems are consistent with the prediction from the surface complexation model. In other words, the bond strength between the adsorbed cation and the surface oxygen of hydrated metal oxides, and between the oxygen of adsorbed oxyanion and the surface metal of hydrated metal oxides control the partition of elements between solid and associated liquid in natural aquatic systems. For Mn, Co, Ce, Pb, and Tl, the oxidative uptake at the solid–water interface in the ocean is an additional important process. For alkali and alkaline-earth cations with large ionic radius (such as Cs, Rb, K, and Ba), their relatively small secondary solvation energy further enhances their adsorption onto solid particles. For living and non-living organic matter, the adsorbed B-type cations form extra strong bindings with hydrophilic functional groups such as –SH and –NH2 on organic matter surface.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baes CF Jr, Mesmer RE (1976) The hydrolysis of cations. Wiley, New York
Baes CF Jr, Mesmer RE (1981) The thermodynamics of cation hydrolysis. Am J Sci 281:935–962
Balistrieri L, Brewer PG, Murray JW (1981) Scavenging residence times of trace metals and surface chemistry of sinking particles in the deep ocean. Deep Sea Res 28A:101–121
Barth TW (1952) Theoretical petrology. Wiley, New York
Beasley TM, Lorz HV (1986) A review of the biological and geochemical behavior of technetium in the marine environment. In: Desmt G, Myttenaere C (eds) Technetium in the environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Berner EK, Berner RA (1987) The global water cycle: geochemistry and environment. Prentice-Hall, Englewood
Bertram MA, Cowen JP (1997) Morphological and compositional evidence for biotic precipitation of marine barite. J Mar Res 55:577–593
Broecker WS, Peng TH (1982) Tacers in the sea. Columbia University Press, New York
Buffle J (1988) Complexation reactions in aquatic systems. Ellis Horwood Limited, England
Byrne RH (2002) Inorganic speciation of dissolved elements in seawater: the influence of pH on concentration ratios. Geochem Trans 3:11–16
Chen JH, Wasserburg GJ, Von Damm KL, Edmond JM (1986) The U-Th-Pb systematics in hot springs on the East Pacific Rise at 21°N and Guaymas Basin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:2467–2480
Choppin GR, Liljenzin JO, Rydberg J (2001) Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd, Boston
Cochran JK, Livingston HD, Hirschberg DJ, Surprenant LD (1987) Natural and anthropogenic radionuclide distributions in the northwest Atlantic Ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 84:135–152
Cotton S (1991) Lanthanides and actinides. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dehairs F, Chesselet R, Jedwab J (1980) Discrete suspended particles of barite and the barium cycle in the open ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 49:528–550
Doucet FJ, Lead JR, Santschi PH (2007) Colloid-trace element interactions in aquatic systems. In: Wilkinson K, Lead J (eds) Environmental colloids and particles: behavior, separation and characterization. IUPAC Series on Analytical and Physical Chemistry of Environmental Systems. Wiley, New York, pp 95–158
Dugger DL, Stanton J, Irby BN, McConnell L, Maatman RW (1964) The exchange of twenty metal ions with the weakly acidic silanol group of silica gel. J Phys Chem 68:757–760
Firdaus ML, Norisuye K, Nakagawa Y, Nakatsuka S, Sohrin Y (2008) Dissolved and labile particulate Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Mo, and W in the western north Pacific Ocean. J Oceanogr 64:247–257
Fujinaga T, Sohrin Y, Ishiki K (eds) (2005) Chemistry of the oceans and lakes: studies using trace elements. Kyoto University Press, Kyoto, 560 p (in Japanese)
Gaillardet J, Viers J, Dupre B (2003) Trace elements in river water. In: Drever JI (ed) Water, weathering, and soils, vol 5, Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 225–272
Goldberg S (1985) Chemical modeling of anion competition on goethite using the constant capacitance model. Soil Sci Soc Am 49:851–856
Goldberg S (1986) Chemical modeling of arsenate adsorption on aluminum and iron oxide minerals. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1154–1157
Goldberg ED, Arrhenius GOS (1958) Chemistry of Pacific pelagic sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 13:153–212
Haraguchi H, Itoh A, Kimata C, Miwa H (1998) Speciation of yttrium and lanthanides in natural water by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after preconcentration by ultrafiltration and with a chelating resin. Analyst 123:773–778
Holm E (1981) Release of 237-Np to the environment. In: Impacts of radionuclide release into the marine environment. IAEA
Honeyman BD, Santschi PH (1989) A Brownian-pumping model for oceanic trace metal scavenging: evidence from thorium isotopes. J Mar Res 47:951–992
Honeyman BD, Santschi PH (1991) Coupling adsorption and particle aggregation: laboratory studies of “colloidal pumping” using 56Fe-labled hematite. Environ Sci Technol 25:1739–1747
IAEA (1985) Sediment Kd’s and concentration factors for radionuclides in the marine environment. Technical report series #110, IAEA
James RO, Healy TW (1972) Adsorption of hydrolysable metal ions at the oxide-water interface III. A thermodynamic model of adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 40:65–81
Kishida K, Sohrina Y, Okamuraa K, Ishibashi J (2004) Tungsten enriched in submarine hydrothermal fluids. Earth Planet Sci Lett 222:819–827
Klein EM (2004) Geochemistry of the igneous oceanic crust. In: Rudnick RL (ed) Crust, vol 3, Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier, Oxford
Koschinsky A, Hein JR (2003) Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation. Mar Geol 198:331–351
Li YH (1981) Ultimate removal mechanisms of elements from the ocean. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:1659–1664
Li YH (1982) Ultimate removal mechanisms of elements from the ocean (Reply to a comment by Whitfield and Turner). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:1993–1995
Li YH (1984) Why are the chemical compositions of living organisms so similar? Schweiz Z Hydrol 46(2):176–184
Li YH (1991) Distribution patterns of the elements in the ocean: a synthesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:3223–3240
Li YH (2000) A Compendium of geochemistry: from solar nebula to the human brain. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Li YH (2006) Are all creatures created equal? (Geochemistry of biosphere). Trans Res Institute Oceanochem 19:106–112
Li YH, Schoonmaker J (2003) Chemical composition and mineralogy of marine sediments. In: Mackenzie FT (ed) Sediments, diagenesis, dedimentary rocks, vol 7, Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 1–35
Li YH, Takamatsu T, Sohrin Y (2007) Geochemistry of Lake Biwa sediments revisited. Limnology 8:321–330
Li YH, Sohrin Y, Takamatsu T (2010) Lake Biwa and the ocean: geochemical similarity and difference. Limnology (in press)
Lide DR (ed) (2008) CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Michard A, Albarebe F (1986) The REE content of some hydrothermal fluids. Chem Geol 55:51–60
Mito S, Sohrin Y, Norisuye K, Matsui M, Hasegawa H, Maruo M, Tsuchiya M, Kawashima M (2004) The budget of dissolved trace metals in Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnology 5:7–16
Orians KJ, Merrin CL (2001) Refractory metals. In: Steele JH, Thorpe SA, Turekian KK (eds) Encyclopedia of ocean sciences vol. 4. Academic Press, NY, pp 2387–2398
Peucker-Ehrenbrink B, Jahn BM (2001) Rhenium-osmium isotope systematics and platinum group element concentrations: loess and the upper continental crust. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 2: 2001GC000172
Ravizza GE (2001) Platinum group elements and their isotopes in the ocean. In: Steele JH, Thorpe SA, Turekian KK (eds) Encyclopedia of ocean sciences vol. 4. Academic Press, NY, pp 2208–2216
Santschi PH, Amdurer M, Adler D, O’Hara P, Li YH, Doering P (1987) Relative mobility of radioactive trace elements across the sediment-water interface in the MERL model ecosystems of Narragansett Bay. J Mar Res 45:1007–1048
Santschi PH, Bollhalder S, Farrenkothen K, Lueck A, Zing S, Sturm M (1988) Chernobyl radionuclides in the environment: tracers for the tight coupling of atmospheric, terrestrial and aquatic geochemical processes. Environ Sci Technol 22:510–516
Schindler PW (1975) Removal of trace metals from the oceans: a zero order model. Thalassia Jugosl 11:101–111
Schindler PW, Stumm W (1987) The surface chemistry of oxides, hydroxides, and oxide minerals. In: Stumm W (ed) Aquatic surface chemistry. Wiley, New York, pp 83–110
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1981) Aquatic chemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Stumm W, Huang CP, Jenkins SR (1970) Specific chemical interaction affecting the stability of dispersed system. Croat Chem Acta 42:223–245
Takamatsu T (ed) (1985) Limnological and environmental studies of elements in the sediment of Lake Biwa. Research Report #75, National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan, 129 pp
Takamatsu T, Kawashima M, Koyama M (1985a) The role of Mn+2 - rich hydrous manganese oxide in the accumulation of arsenic in Lake sediments. Water Res 20:471–475
Takamatsu T, Kawashima M, Matsushita R, Koyama M (1985b) General distribution profiles of thirty-six elements in sediments and manganese concretions of Lake Biwa. Jpn J Limnol 46:115–127
Takamatsu T, Kawashima M, Takada J, Matsushita R (1993) Characteristics in elemental composition of ferromanganese concretions from Lake Biwa. Jpn J Limnol 54:281–291
Takebe M (2005) Carriers of rare earth elements in Pacific deep-sea sediments. J Geol 113:201–215
Taylor SR, McLennan SM, McCulloch MT (1983) Geochemistry of loess, continental crust composition and crustal model ages. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:1897–1906
Teraoka H, Kobayashi J (1980) Concentrations of 21 metals in the suspended solids collected from the principal 166 rivers and 3 lakes in Japan. Geochemical J 14:203–226
Tseng CM, Lamborg C, Fitzgerald WF, Engstrom DR (2004) Cycling of dissolved mercury in Arctic Alaskan lakes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1173–1184
Viers J, Dupre B, Polve M, Schott J, Dandurand JL, Braun JJ (1997) Chemical weathering in the drainage basin of a tropical watershed (Nsimi-Zoetele site, Cameroon) comparison between organic-poor and organic-rich waters. Chem Geol 140:181–206
Viers J, Dupré B, Gaillardet J (2009) Chemical composition of suspended sediments in world rivers: new insights from a new database. Sci Total Environ 407:853–868
Von Damm KL (1995) Controls on the chemistry and temporal variability of seafloor hydrothermal fluids. In: Humphris SF, Zierenberg RA, Mullineaux LS, Thomson RE (eds) Seafloor hydrothermal systems
Von Damm K, Edmond JM, Grant B, Measures CI, Walden B, Weiss RF (1985) Chemistry of submarine hydrothermal solutions at 21°N, East Pacific Rise. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:2197–2220
Wen LS, Santschi PH, Gill G, Lehman R, Paternostro C (1997) Colloidal and particulate silver in river and estuarine waters of Texas. Environ Sci Technol 31:723–731
Wen LS, Santschi P, Gill G, Tang D (2002) Silver concentrations in Colorado USA watersheds using improved methodology. Environ Toxico Chem 21(1):2040–2051
Zhu Y, Hattori R, Rahmi D, Okuda S, Itoh A, Fujimori E, Umemura T, Haraguchi H (2005) Fractional distribution of trace metals in surface water of Lake Biwa as studied by ultrafiltration and ICP-MS. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 78:1970–1976
Acknowledgments
The Foundation of the Research Institute for Oceanochemistry (Kyoto, Japan) sponsored this work. Support from the Hanse Institute for Advanced Study, Delmenthorst, Geremany, during my sabbatical year there was essential. Comments from Professors Y Sohrin, F Mackenzie, J Gaillardet, and P Santschi were most helpful. Editorial assistance by May Izumi is acknowledged. This work is in part supported by NOAA/OAR/OGP Grant GC02-386. SOEST contribution # 8068.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YH. Partition of Elements Between Solid and Liquid Phases in Aquatic Environments. Aquat Geochem 17, 697–725 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-011-9121-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-011-9121-8