Abstract
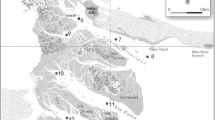
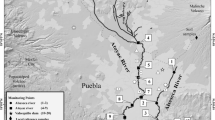
Chromium and lead concentrations and distribution have been fully studied within Bahía Blanca estuary inner area, which is strongly influenced by urban and industrial stress. Not only metals dissolved in estuarine water but also those included in sediments and suspended particulate matters (SPM) were measured. In all cases, internationally standardized protocols were applied to metal measurements, including analytical quality check test through analysis of certified reference materials. Total metal contents from surface sediments and SPM were compared with those from a historical database of the area, as well as with values representing the natural geochemical baseline within the system. Results showed that heavy metal pollution is mainly localized in the areas close to both industrial effluents discharge system and urban sewage outfall discharge. Data from sequential extractions indicate that metals from anthropogenic sources (i.e., Pb) are potentially more mobile than those inherited from geological parent material (i.e., Cr). The influences of other potential sources of metals (i.e., streams, runoff) were also considered. SPM was clearly identified as the main carrier of the studied heavy metals within the system, and its significance to metals input into sediments and/or biota was verified. Finally, the normalization of measured metal concentrations against background reference elements (i.e., Al or Fe) has allowed to identify that most of the measured Cr was lithogenic, while a significant percentage of Pb was from anthropogenic origin within Bahía Blanca estuary.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo-Figueroa D, Jimenez BD, Rodriguez-Sierra CJ (2006) Trace metals in sediments of two estuarine lagoons from Puerto Rico. Environ Pollut 141:336–342
Adamo P, Arienzo M, Imperato M, Naimo D, Nardi G, Stanzione D (2005) Distribution and partition of heavy metals in surface and sub-surface sediments of Naples city port. Chemosphere 61:800–809
Alquezar R, Markich JS, Twining JR (2007) Uptake and loss of dissolved 109Cd and 75Se in estuarine macroinvertebrates. Chemosphere 67:1202–1210
Andrade JS (2001) Metales pesados en el agua de la zona interna de Bahía Blanca y su toxicidad sobre algunas especies fitoplanctónicas. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur (UNS), Bahía Blanca
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In: Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (eds) 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Benoit G, Rozan TF (1999) The influence of size distribution on the particle concentration effect and trace metal partitioning in rivers. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:113–127
Bibby RL, Webster-Brown JG (2006) Trace metal adsorption onto urban stream suspended particulate matter (Auckland region, New Zealand). Appl Geochem 21:1135–1151
Botté SE, Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2008) Dissolved heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Cr, Ni) concentrations in surface water and porewater from Bahia Blanca estuary tidal flats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:415–421
C.de Steffens AM, C.de Ferreras AM (2004) Climatología. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) El ecosistema del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía, Bahía Blanca, pp 79–86
Censi P, Spoto SE, Saiano F, Sprovieri M, Mazzola S, Nardone G, Di Geronimo SI, Punturo R, Ottonello D (2006) Heavy metals in coastal water systems. A case study from the northwestern Gulf of Thailand. Chemosphere 64:1167–1176
Chapman PM, Wang F (2001) Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:3–22
Dauvin J-C (2008) Effects of heavy metal contamination on the macrobenthic fauna in estuaries: the case of the Seine estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 57:160–169
Doig LE, Liber K (2007) Nickel speciation in the presence of different sources and fractions of dissolved organic matter. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 66:169–177
Doong RA, Lee SH, Lee CC, Sun YC, Wu SC (2008) Characterization and composition of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants in water and estuarine sediments from Gao-Ping River, Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 57(6):846–857
Erftemeijer PLA, Lewis RRR III (2006) Environmental impacts of dredging on seagrasses: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 52:1553–1572
Fang T-H, Hwang J-S, Hsiao S-H, Chen H-Y (2006) Trace metals in seawater and copepods in the ocean outfall area off the northern Taiwan coast. Mar Environ Res 61:224–243
Ferrer LD (2001) Estudio de los diversos metales pesados en sedimentos del estuario de Bahía Blanca y sus efectos tóxicos sobre el cangrejo Chasmagnathus granulata. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur (UNS), Bahía Blanca
Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2004) Oceanografía química. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) El ecosistema del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía, Bahía Blanca, pp 69–78
Gelós EM, Marcos AO, Spagnolo JO, Schillizi RA (2004) Textura y Mineralogía de Sedimentos. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía, Bahía Blanca, pp 43–50
Gonzalez R, Araújo MF, Burdloff D, Cachão M, Cascalho J, Corredeira C, Dias JMA, Fradique C, Ferreira J, Gomes C, Machado A, Mendes I, Rocha F (2007) Sediment and pollutant transport in the Northern Gulf of Cadiz: a multi-proxy approach. J Mar Syst 68:1–23
Hansen HK, Yianatos JB, Ottosen LM (2005) Speciation and leachability of copper in mine tailings from porphyry copper mining: influence of particle size. Chemosphere 60:1497–1503
Hwang H-M, Green PG, Higashi RM, Young TM (2006) Tidal salt marsh sediment in California, USA. Part 2: occurrence and anthropogenic input of trace metals. Chemosphere 64:1899–1909
Idris AM, Eltayeb MAH, Potgieter-Vermaak SS, Van Grieken R, Potgieter JH (2007) Assessment of heavy metals pollution in Sudanese harbours along the Red Sea Coast. Microchem J 87(2):104–112
Lacerda LD, Souza CM, Pestana MHD (1988) Geochemical distribution of Cd, Cu, Cr and Pb in sediments of estuarine areas along the Southeastern Brazilian coast. In: Seelinger U, Lacerda LD, Patchineelam SR (eds) Coastal environments of Latin America. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 86–99
Limbozzi F, Leitao TE (2008) Characterization of Bahía Blanca main existing pressures and their effects on the state indicators for surface and groundwater quality. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zona management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 315–331 (ISBN:978-972-8469-74-0)
Lu Y, Allen HE (2001) Partitioning of copper onto suspended particulate matter in river waters. Sci Total Environ 277:119–132
Marcovecchio JE, Ferrer LD (2005) Distribution and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. J Coast Res 21(4):826–834
Marcovecchio J, Ferrer LD, Barral AO, Scagliola MO, Pucci AE (1998) A model for geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in the Mar del Plata coastal ecosystem, Argentina. In: Wasserman JC, Silva Filho EV, Villas-Boas R (eds) Environmental geochemistry in the tropics. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 139–149
Marcovecchio JE, Botté SE, Delucchi F, Arias AH, Fernández Severini MD, De Marco SG, Tombesi NB, Andrade SJ, Ferrer LD, Freije RH (2008). Pollution processes in Bahía Blanca estuarine environment, Chapter 28. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Scientific Publishers, Lisbon (Portugal), pp 303–316. (ISBN:978-972-8469-74-0)
Masson M, Blanc G, Schäfer J (2006) Geochemical signals and source contributions to heavy metal (Cd, Zn, Pb, Cu) fluxes into the Gironde Estuary via its major tributaries. Sci Total Environ 370:133–146
Megalatti N, Robbe O, Marchandise P, Astruk M (1983) A new chemical extraction procedure in the fractionation of heavy metals in sediments. In: Förstner U (ed) Metals in the environment. CEP Consult. Ltd, Edinburgh, pp 1090–1093
Osher LJ, Leclerc L, Wiersma GB, Hess CT, Guiseppe VE (2006) Heavy metal contamination from historic mining in upland soil and estuarine sediments of Egypt Bay, Maine, USA. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 70(1):169–179
Pasternack GB, Brown KJ (2006) Natural and anthropogenic geochemical signatures of floodplain and deltaic sedimentary strata, Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, California, USA. Environ Pollut 141:295–309
Perillo GME, Piccolo MC (1991) Tidal response in the Bahía Blanca estuary. J Coast Res 7:437–449
Perillo GME, Piccolo MC, Parodi E, Freije RH (2001) The Bahia Blanca estuary, Argentina. In: Seeliger U, Kjerfve B (eds) Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America. Springer, Berlin, pp 205–217
Piccolo MC, Perillo GME (1990) Physical characteristics of the Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 31:303–317
Piccolo MC, Perillo GME, Arango JM (1990) Hidrografía del estuario del Río Sauce Chico (Bahía Blanca). Geoacta 17:13–23
Piccolo MC, Perillo GME, Melo WD (2008) The Bahía Blanca estuary: an integrated overview of its geomorphology and dynamics. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zona management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 219–229 (ISBN: 978-972-8469-74-0)
Popovich CA, Spetter CV, Marcovecchio JE, Freije RH (2008) Dissolved nutrients availability during winter diatom bloom in a turbid and shallow estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). J Coast Res 24:95–102
Sainz A, Grande JA, de la Torre ML (2004) Characterisation of heavy metal discharge into the Ria of Huelva. Environ Int 30:557–566
Shi B, Allen HE, Grassi MT, Ma H (1998) Modeling copper partitioning in surface waters. Water Res 32:3756–3764
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1979) Biometría: Principios y métodos estadísticos en la investigación biológica. Blume Ediciones, Madrid
Sutherland TF, Petersen SA, Levings CD, Martin AJ (2007) Distinguishing between natural and aquaculture-derived sediment concentrations of heavy metals in the Broughton Archipelago, British Columbia. Mar Pollut Bull 54(9):1451–1460
Tattersall GR, Elliott AJ, Lyn NM (2003) Suspended sediment concentrations in the Tamar estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 57:679–688
Turner A (2000) Trace metal contamination in sediments from U.K. estuaries: an empirical evaluation of the role of hydrous iron and manganese oxides. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 50:355–371
Wang Z-L, Liu C-Q (2003) Distribution and partition behavior of heavy metals between dissolved and acid-soluble fractions along a salinity gradient in the Changjiang Estuary, eastern China. Chem Geol 202:383–396
Zhang C-S, Wang GS, Li GS, Dong SS, Yang J, Wang X (2002) Grain size effect on multi-element concentrations in sediments from the intertidal flats of Bohai Bay. China Appl Geochem 17:59–68
Zhou F, Guo H, Hao Z (2007) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in Hong Kong’s marine sediments and their human impacts: a GIS-based chemometric approach. Mar Pollut Bull 54(9):1372–1384
Acknowledgments
The present study was fully supported by grants from the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica—ANPCyT—(PICT No 0945/2006), and from the European Union—Latinoamerica Cooperative Program (ECOManage Project, Contract No INCO-CT-2004-003715). The authors are greatly indebted to all the staff of the Chemical Oceanography Area at IADO, who kindly collaborated with the development of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcovecchio, J., Botté, S., Severini, M.F. et al. Geochemical Control of Heavy Metal Concentrations and Distribution Within Bahia Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Aquat Geochem 16, 251–266 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-009-9076-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-009-9076-1