Abstract
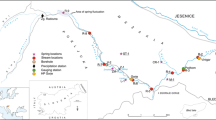
Once or twice weekly, water sampling was undertaken for a two and a half year period in the Kalix River, northern Sweden. Soil water, groundwater, water in tributaries and mire water were also sampled at several occasions. Samples were filtered and analysed for major dissolved elements and TOC. Although only 5 of the bedrock in the Kalix River drainage basin is situated in the Caledonian mountains (mostly schist, with some outcrops of dolomite and limestone), the chemical composition of the river, at the river mouth, is clearly influenced by water from the mountain areas. High dissolved Ca/Mg ratios in June and July indicate a large influence of water from the mountain areas during summer. The dissolved Si/Mg ratio increases when water from the woodland (bedrock consisting of Precambrian granitoids) predominates during snowmelt in May, but the ratio is low during summer when water from the mountains is increased. However, the low Si concentrations in the mountain areas are probably not primarily the result of the different rocks but more a reflection of the less intense weathering of silicate minerals in the mountains. High Si/Mg ratios are closely related to high TOC. All the major dissolved elements, except TOC, are diluted by snowmelt in May. However, the dilution varies for different elements. Based on the interpretations of major element ratios the melt water discharge in May reflects two major compartments in the woodland; peatland areas and the upper section of the soil. During summer and autumn storm events in the woodland most of the storm water originated from peatland. High K/Mg ratios in the river in May are related to water discharge from the upper section of the till. Low S/Mg ratios in the river indicate an influence of mire water from the woodland both during melt water discharge in May and during increased water discharge in autumn. The Ca/Mg ratios in tributaries in the woodland are consistently lower during melt water discharge compared with values in August. The lower Ca/Mg ratio in May probably reflects water that has been in contact with the B-horizon in the till during spring flood. Data show that the TOC discharged during spring flood originates from two major compartments in the landscape, the upper soil profile and peatland. Storm discharge of TOC during the rest of the year originates mostly from peatland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. S. Andersson D. Porcelli G. J. Wasserburg J. Ingri (1998) ArticleTitleParticle transport of 234U-238U in the Kalix River and the Baltic Sea Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 62 385–392 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00342-6
P. S. Andersson R. Dahlqvist J. Ingri Ö. Gustafsson (2001) The isotopic composition of Nd in a boreal river: a reflection of selective weathering and colloidal transport Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 65–521
D. E. Bazemore K. N. Eshleman K. J. Hollenbeck (1994) ArticleTitleThe role of soilwater in stormflow generation in a forested headwater catchment: synthesis of natural tracer and hydrometric evidence J. Hydrol. 162 47–75 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(94)90004-3
E. K. Berner R. A. Berner (1987) The global water cycle Prentice-Hall New Jersey
T. S. Bianchi T. Filley K. Dria P. G. Hatcher (2004) ArticleTitleTemporal variability in sources of dissolved organic carbon in the lower Mississippi River Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 68 959–967 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.gca.2003.07.011
K.H. Bishop H. Grip A. O’Neill (1990) ArticleTitleThe origins of acid runoff in a hillslope during storm events J. Hydrol. 116 35–61 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(90)90114-D
N. Christophersen C. Neal R. P. Hooper R. D. Vogt S. Andersen (1990) ArticleTitleModelling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members—A step towards second-generation acidification models J. Hydrol. 116 307–320
Dahlqvist R., Benedetti M., Andersson K., Turner D., Larsson T., Stolpe B. and Ingri J. (2004) Association of calcium with colloidal particles and speciation of calcium in the Kalix and Amazon rivers. Accepted in Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta.
M.-H. Dai J.-M. Martin (1995) ArticleTitleFirst data on trace metal level and behavior in two major arctic river-estuarine systems (OB and Yenisey) and in the adjacent Kara Sea, Russia Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 131 127–141 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0012-821X(95)00021-4
K. B. Easthouse J. Mulder N. Christophersen H. M. Seip (1992) ArticleTitleDissolved organic carbon fractions in soil and stream water during variable hydrological conditions at Birkenes, southern Norway Water Resour. Res. 28 1585–1596 Occurrence Handle10.1029/92WR00056
H. Elsenbeer A. Lack K. Cassel (1995) ArticleTitleChemical fingerprints of hydrological compartments and flow paths at La Cuenca, western Amazonia Water Resour. Res. 31 3051–3058
E. Fromm (1965) ArticleTitleBeskrivning till jordartskartan över norrbottens län, nedanför lappmarksgränsen. SGU ser. Ca 41 1–151
G. Gaal R. Gorbatschev (1987) ArticleTitleAn outline of the Precambrian evolution of the Baltic Shield Precambrian Res. 35 15–52
L. Giusti C. Neal (1993) ArticleTitleHydrological pathways and solute chemistry of storm runoff at Dargall Lane, southwest Scotland J. Hydrol. 142 1–27 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(93)90002-Q
V. V. Gordeev J. M. Martin I. S. Sidorov M. V. Sidorova (1996) ArticleTitleA reassessment of the Eurasian input of water, sediment, major elements, and nutrients to the Arctic Ocean. Am. J. Sci. 296 664–691 Occurrence Handle10.2475/ajs.296.6.664
E. Gorham (1955) ArticleTitleOn some factors affecting the chemical composition of Swedish fresh waters Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 7 129–150
Ö. Gustafsson A. Widerlund P.S Andersson J. Ingri P. Roos A. Ledin (2000) ArticleTitleColloid dynamics and transport of major elements through a boreal river-brackish bay mixing zone Mar. Chem. 71 1–21 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-4203(00)00035-9
F. K. Hare (1980) ArticleTitleLong-term annual surface heat and water balances over Canada and the United States south of 60°N; Reconciliation of precipitation runoff and temperature fields. Atmos. Ocean 18 127–153
J. I. Hedges R. G. Keil R. Benner (1997) ArticleTitleWhat happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem. 27 195–212
M. J. Hinton S. L. Schiff M. C. English (1994) ArticleTitleExamining the contributions of glacial till water to storm runoff using two-and three-component hydrograph separations Water Res. Res. 30 983–993 Occurrence Handle10.1029/93WR03246
S. Hjort (1971) Torne och Kalix älvar, del 1 Allmän beskrivning. University of Uppsala UNGI
R. P. Hooper N. Christophersen N. E. Peters (1990) ArticleTitleModelling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members—An application to the Panola Mountain catchment, Georgia, USA. J. Hydrol. 116 321–343 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(90)90131-G
C. Humborg S. Blomqvist E. Avsan Y. Bergensund E. Smedberg (2002) ArticleTitleHydrological alterations with river damming in northern Sweden: Implications for weathering and river biogeochemistry Global Biogeochem. Cycles 16 12–1–12–13 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2000GB001369
J. Ingri A. Widerlund (1994) ArticleTitleUptake of alkali and alkaline-earth elements on suspended iron and manganese in the Kalix River, northern Sweden. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58 5433–5442 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(94)90240-2
J. Ingri P. Torssander P. S. Andersson C-M. Mörth M. Kusakabe (1997) ArticleTitleHydrogeochemistry of sulfur isotopes in the Kalix River catchment, northern Sweden Appl. Geochem. 12 483–496 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0883-2927(97)00026-7
J. Ingri A. Widerlund M. Land Ö. Gustafsson P. S Andersson B Öhlander (2000) ArticleTitleTemporal variations in the fractionation of the rare earth elements in a boreal river; the role of colloidal particles Chem. Geol. 166 23–45 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00178-3
J. W. Kirchner X. Feng C. Neal (2000) ArticleTitleFractal stream chemistry and its implications for contaminant transport in catchments Nature 403 524–527 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35000537 Occurrence Handle000085227300044
M. Land B. Öhlander (1997) ArticleTitleSeasonal variations in the geochemistry of shallow groundwater hosted in granitic till Chem.Geol. 143 205–216 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00116-2
M. Land J. Ingri B. Öhlander (1999) ArticleTitlePast and present weathering rates in northern Sweden Appl. Geochem. 14 761–774 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0883-2927(98)00098-5
M. Land B. Öhlander (2000) ArticleTitleChemical weathering rates, erosion rates and mobility of major and trace elements in a boreal granitic till Aquat. Geochem. 6 435–460 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009644317427
M. Land J. Ingri P. S Andersson B. Öhlander (2000) ArticleTitleBa/Sr, Ca/Sr and 87Sr/86Sr ratios in soil water and groundwater: implications for relative contributions to stream water discharge Appl. Geochem. 15 311–325 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00054-2
G. B. Lawrence C. T. Driscoll R. D. Fuller (1988) ArticleTitleHydrologic control of aluminium chemistry in an acidic headwater stream Water Resour. Res. 24 659–669
U. S. Lundström et al. (2000) ArticleTitleAdvances in understanding the podzolization process resulting from a multidisciplinary study of three coniferous forest soils in the Nordic Countries Geoderma 94 335–353
Meybeck M. (1980) Pathways of major elements from land to ocean through rivers. In Proceedings of the review and workshop on river inputs to ocean systems, (eds. J. M. Meybeck, J. D. Burton and D. Eisma). pp. 18–30 Rome:FAO.
H. Ming-hui R. F. Stallard J. M. Edmond (1982) ArticleTitleMajor ion chemistry of some large Chinese rivers Nature 289 550–553
J. Mulder N. Christophersen M. Hauhs R. D. Vogt S. Andersen D. O. Andersen (1990) ArticleTitleWater flow paths and hydrochemical controls in the Birkenes catchment as inferred from a rainstorm high in seasalts Water Res. Res. 26 611–622 Occurrence Handle10.1029/89WR02975
P. J. Mulholland (1993) ArticleTitleHydrometric and stream chemistry evidence of three storm flowpaths in Walker Branch Watershed J. Hydrol. 151 291–316 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(93)90240-A
C. Neal T. Hill S. Hill B. Reynolds (1997) ArticleTitleAcid neutralization capacity measurements in surface and ground waters in the Upper River Severn, Plynlimon: from hydrograph splitting to water flow pathways Hydrol. Earth System Sci. 3 687–696 Occurrence Handle10.5194/hess-1-687-1997
L. Nyberg A. Rodhe K. Bishop (1999) ArticleTitleWater transit times and flow paths from two line injections of 3H and 36Cl in a microcatchment at Gårdsjön, Sweden Hydrol. Process. 13 1557–1575 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-1085(19990815)13:11<1557::AID-HYP835>3.0.CO;2-S
Öhlander B., Ingri J. and Pontér C. (1991) Geochemistry of till weathering in the Kalix River watershed, northern Sweden. Reports from a Nordic Seminar, Uppsala 1990. Rep. 63. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
B. Öhlander M. Land J. Ingri A. Widerlund (1996) ArticleTitleMobility of rare earth elements during weathering of till in northern Sweden Appl. Geochem. 11 93–99
B. Öhlander J. Ingri M. Land H. Schöberg (2000) ArticleTitleChange of Sm-Nd isotope composition during weathering of till Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 64 813–820
G. F. Pinder J. F. Jones (1969) ArticleTitleDetermination of the groundwater component of peak discharge from the chemistry of total runoff Water. Resour. Res. 5 438–445 Occurrence Handle10.1029/WR005i002p00438
C. Pontér J. Ingri J.-O. Burman K. Boström (1990) ArticleTitleTemporal variations in dissolved and suspended iron and manganese i the Kalix River, northern Sweden Chem. Geol. 81 121–131
C. Pontér J. Ingri K. Boström (1992) ArticleTitleGeochemistry of manganese in the Kalix River northern Sweden. Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 56 1485–1494
D. Porcelli P. S. Andersson G. J. Wasserburg J. Ingri M. Barskaran (1997) ArticleTitleThe importance of colloids and mires for the transport of uranium isotopes through the Kalix River watershed and Baltic Sea Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 61 4095–4113 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00235-4
P. A. Raymond J. E. Bauer (2001) ArticleTitleUse of 14C and 13C natural abundances for evaluating riverine, estuarine, and coastal DOC and POC sources and cycling: A review and synthesis. Org. Geochem. 32 469–485 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00190-X
R. D. Rember J. H. Trefry (2004) ArticleTitleIncreased concentrations of dissolved trace metals and organic carbon during snowmelt in rivers of the Alaskan Arctic Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 68 477–489 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00458-7
S. A. Sanudo-Wilhelmy G. T. Taylor (1999) ArticleTitleBacterioplankton dynamics and organic carbon partitioning in the lower Hudson River estuary Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 182 17–27
R. Sherrell J. M. Ross (1999) ArticleTitleTemporal variability of trace metals in new Jersey Pinelands streams: Relationships to discharge and pH Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 63 3321–3336
E. R. Sholkovitz E. A. Boyle N. B. Price (1978) ArticleTitleThe removal of dissolved humic acids and iron during estuarine mixing Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 40 130–136 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0012-821X(78)90082-1
M. Sjörs (1950) ArticleTitleOn the relation between vegetation and electrolytes in north Swedish mire waters Oikos 2 241–258
W. Shotyk (1988) ArticleTitleReview of the inorganic geochemistry of peats and peatland waters Earth Sci. Rev. 25 95–176 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0012-8252(88)90067-0
C. Soulsby J. Petry M. J. Brewer S. M. Dunn B. Ott I. A. Malcolm (2003) ArticleTitleIdentifying and assessing uncertainty in hydrological pathways: a novel approach to end member mixing in a Scottish agricultural catchment J. Hydrol. 274 109–128 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00398-0
E. M. Thurman (1985) Organic geochemistry of natural waters Martinus Nijhoff/ DR W. Junk Publishers Dordrecht
A. J Wade C. Neal C. Soulsby R. P. Smart S. J. Langan M. S. Cresser (1999) ArticleTitleModelling streamwater quality under varying hydrological conditions at different spatial scales J. Hydrol. 217 266–283 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00295-9
P. A. W. Hees Particlevan U. S. Lundström R. Giesler (2000) ArticleTitleLow molecular weight organic acids and their Al-complexes in soil solution-composition, distribution and seasonal variations in three podzolized soils. Geoderma 94 173–200
C. Wels R. J. Cornett B. D. Lazerte (1991) ArticleTitleHydrograph separation: A comparison of geochemical and isotopic tracers J. Hydrol. 122 253–274 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-1694(91)90181-G
R. F. Yuretich D. A. Crerar D. J. J. Kinsman J. L. Means M. P. Borcsik (1981) ArticleTitleHydrogeochemistry of the New Jersey coastal plain, 1: major element cycles in precipitation and river water Chem. Geol. 33 1–21 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0009-2541(81)90082-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingri, J., Widerlund, A. & Land, M. Geochemistry of Major Elements in a Pristine Boreal River System; Hydrological Compartments and Flow Paths. Aquat Geochem 11, 57–88 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-004-2248-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-004-2248-0