Abstract
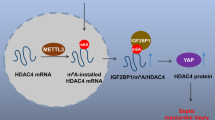
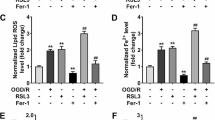
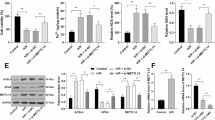
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent and phospholipid peroxidation-mediated cell death, which has been identified to be involved in sepsis-induced injury. However, the in-depth molecular mechanisms of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and ferroptosis on sepsis-induced myocardial injury are still unclear. Here, in the septic myocardial injury, m6A methyltransferase METTL3 level and methylation level high-expressed in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cardiomyocytes (H9C2). Functionally, METTL3 silencing repressed the ferroptosis phenotype induced by LPS. Mechanistically, METTL3-mediated m6A methylation on solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) empowered its mRNA with high methylation level. Moreover, YTHDF2 directly bound to the m6A modification sites of SLC7A11 to mediate the mRNA degradation. The m6A modified SLC7A11 mRNA was recognized by YTHDF2, which promoted the decay of SLC7A11 mRNA, consequently up-regulating ferroptosis in sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Together, these findings establish a role of METTL3 in the ferroptosis of LPS-induced cardiomyocytes, and provide potential therapeutic target to treat the sepsis-induced myocardial injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No research data shared.
References
Boehm D, Menke H (2021) Sepsis in burns-lessons learnt from developments in the management of septic shock. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 58(1):26
Gandhirajan A, Roychowdhury S, Vachharajani V (2021) Sirtuins and sepsis: cross talk between redox and epigenetic pathways. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 11(1):3
Li Y, Zhao H, Guo Y, Duan Y, Guo Y, Ding X (2021) Association of preadmission metformin use and prognosis in patients with sepsis and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol 12:811776
Lin J, Tan B, Li Y, Feng H, Chen Y (2021) Sepsis-exacerbated brain dysfunction after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Cell Neurosci 15:819182
Lopes-Pires ME, Frade-Guanaes JO, Quinlan GJ (2021) Clotting dysfunction in sepsis: a role for ROS and potential for therapeutic intervention. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 11(1):88
Guo L, Yang H, Zhou C, Shi Y, Huang L, Zhang J (2021) N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in the tumor immune microenvironment: novel implications for immunotherapy. Front Immunol 12:773570
Lu S, Ding X, Wang Y, Hu X, Sun T, Wei M et al (2021) The relationship between the network of non-coding RNAs-molecular targets and N6-methyladenosine modification in colorectal cancer. Front cell Dev Biol 9:772542
Liu Y, Song R, Zhao L, Lu Z, Li Y, Zhan X et al (2022) M(6)a demethylase ALKBH5 is required for antibacterial innate defense by intrinsic motivation of neutrophil migration. Signal Transduct Target therapy 7(1):194
Shen H, Xie K, Li M, Yang Q, Wang X (2022) N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) methyltransferase METTL3 regulates sepsis-induced myocardial injury through IGF2BP1/HDAC4 dependent manner. Cell death discovery 8(1):322
Zhang S, Guan X, Liu W, Zhu Z, Jin H, Zhu Y et al (2022) YTHDF1 alleviates sepsis by upregulating WWP1 to induce NLRP3 ubiquitination and inhibit caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov 8(1):244
Wang N, Yao F, Liu D, Jiang H, Xia X, Xiong S (2022) RNA N6-methyladenosine in nonocular and ocular disease. J Cell Physiol 237(3):1686–1710
Xu Y, Zhang M, Zhang Q, Yu X, Sun Z, He Y et al (2021) Role of main RNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma: N6-methyladenosine, 5-methylcytosine, and N1-methyladenosine. Front cell Dev Biol 9:767668
Li D, Pi W, Sun Z, Liu X, Jiang J (2022) Ferroptosis and its role in cardiomyopathy. Biomed Pharmacother 153:113279
Chen Z, Cao Z, Gui F, Zhang M, Wu X, Peng H et al (2022) TMEM43 protects against sepsis-induced cardiac injury via inhibiting ferroptosis in mice. Cells 11:19
Wu J, Minikes AM, Gao M, Bian H, Li Y, Stockwell BR et al (2019) Intercellular interaction dictates cancer cell ferroptosis via NF2-YAP signalling. Nature 572(7769):402–406
Ji FH, Fu XH, Li GQ, He Q, Qiu XG (2022) FTO prevents thyroid cancer progression by SLC7A11 m6A methylation in a ferroptosis-dependent manner. Front Endocrinol 13:857765
Li XC, Jin F, Wang BY, Yin XJ, Hong W, Tian FJ (2019) The m6A demethylase ALKBH5 controls trophoblast invasion at the maternal-fetal interface by regulating the stability of CYR61 mRNA. Theranostics 9(13):3853–3865
Song H, Feng X, Zhang H, Luo Y, Huang J, Lin M et al (2019) METTL3 and ALKBH5 oppositely regulate m(6)a modification of TFEB mRNA, which dictates the fate of hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated cardiomyocytes. Autophagy 15(8):1419–1437
Li B, Zhu L, Lu C, Wang C, Wang H, Jin H et al (2021) circNDUFB2 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression via destabilizing IGF2BPs and activating anti-tumor immunity. Nat Commun 12(1):295
Liu Y, Tan S, Wu Y, Tan S (2022) The emerging role of ferroptosis in Sepsis. DNA Cell Biol 41(4):368–380
Zhang MM, Lin YL, Zeng WF, Li Y, Yang Y, Liu M et al (2021) N6-methyladenosine regulator-mediated immune genes identify breast cancer immune subtypes and predict immunotherapy efficacy. Front Genet 12:790888
Zhang N, Zuo Y, Peng Y, Zuo L (2021) Function of N6-methyladenosine modification in tumors. J Oncol 2021:6461552
Li J, Xie H, Ying Y, Chen H, Yan H, He L et al (2020) YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer 19(1):152
Su J, Bian C, Zheng Z, Wang H, Meng L, Xin Y et al (2022) Cooperation effects of radiation and ferroptosis on tumor suppression and radiation injury. Front cell Dev biology 10:951116
Wang X, Wang Y, Huang D, Shi S, Pei C, Wu Y et al (2022) Astragaloside IV regulates the ferroptosis signaling pathway via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis to inhibit PM2.5-mediated lung injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 112:109186
Acknowledgements
No.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81870207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS, KX and XW wrote the main manuscript text and prepared Figures 1–7. YT help improve the language. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Xie, K., Tian, Y. et al. N6-methyladenosine writer METTL3 accelerates the sepsis-induced myocardial injury by regulating m6A-dependent ferroptosis. Apoptosis 28, 514–524 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01808-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01808-y