Abstract
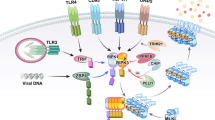
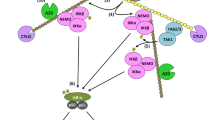
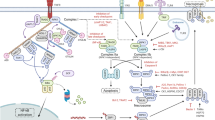
Necroptosis is a programmed necrosis that is mediated by receptor-interacting protein kinases RIPK1, RIPK3 and the mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein, MLKL. Necroptosis must be strictly regulated to maintain normal tissue homeostasis, and dysregulation of necroptosis leads to the development of various inflammatory, infectious, and degenerative diseases. Ubiquitylation is a widespread post-translational modification that is essential for balancing numerous physiological processes. Over the past decade, considerable progress has been made in the understanding of the role of ubiquitylation in regulating necroptosis. Here, we will discuss the regulatory functions of ubiquitylation in necroptosis signaling pathway. An enhanced understanding of the ubiquitylation enzymes and regulatory proteins in necroptotic signaling pathway will be exploited for the development of new therapeutic strategies for necroptosis-related diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- DAMPs:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- Ub:
-
Ubiquitin
- RIPK1:
-
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1
- RIPK3:
-
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 3
- MLKL:
-
Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNFR1:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor type I
- TRADD:
-
TNFR1-associated death domain protein
- TRAF2:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor 2
- cIAP:
-
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated protein with death domain
- CYLD:
-
Cylindromatosis
- RHIMs:
-
RIP homotypic interaction motifs
- ZBP1/DAI/DLM-1:
-
Z-DNA binding protein 1
- ORAS:
-
OTULIN-related autoinflammatory syndrome
References
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G (2010) Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(10):700–714. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2970
Cai Z, Liu ZG (2014) Execution of RIPK3-regulated necrosis. Mol Cell Oncol 1(2):e960759. https://doi.org/10.4161/23723548.2014.960759
Wallach D, Kang TB, Dillon CP, Green DR (2016) Programmed necrosis in inflammation: toward identification of the effector molecules. Science (New York, NY) 352(6281):aaf2154. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf2154
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Chan FK, Kroemer G (2017) Necroptosis: mechanisms and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol 12:103–130. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-052016-100247
He S, Liang Y, Shao F, Wang X (2011) Toll-like receptors activate programmed necrosis in macrophages through a receptor-interacting kinase-3-mediated pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(50):20054–20059. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116302108
Kaiser WJ, Sridharan H, Huang C, Mandal P, Upton JW, Gough PJ, Sehon CA, Marquis RW, Bertin J, Mocarski ES (2013) Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. J Biol Chem 288(43):31268–31279. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.462341
McComb S, Cessford E, Alturki NA, Joseph J, Shutinoski B, Startek JB, Gamero AM, Mossman KL, Sad S (2014) Type-I interferon signaling through ISGF3 complex is required for sustained Rip3 activation and necroptosis in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(31):E3206-3213. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1407068111
Van Herreweghe F, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst, that’s the question. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(10):1567–1579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0283-0
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M, Chan FK (2009) Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 137(6):1112–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.037
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L, Wang X (2009) Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 137(6):1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.021
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X, Wang X (2012) Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell 148(1–2):213–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.031
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC, Dong MQ, Han J (2009) RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science (New York, NY) 325(5938):332–336. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1172308
Zhao J, Jitkaew S, Cai Z, Choksi S, Li Q, Luo J, Liu ZG (2012) Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(14):5322–5327. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200012109
Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M, Attinger A, Valitutti S, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Seed B, Tschopp J (2000) Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat Immunol 1(6):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/82732
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM, Green DR (2017) Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(2):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.149
Yuan J, Amin P, Ofengeim D (2019) Necroptosis and RIPK1-mediated neuroinflammation in CNS diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 20(1):19–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0093-1
Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P (2015) Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 517(7534):311–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14191
Meng Y, Sandow JJ, Czabotar PE, Murphy JM (2021) The regulation of necroptosis by post-translational modifications. Cell Death Differ 28(3):861–883. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00722-7
Komander D, Rape M (2012) The ubiquitin code. Annu Rev Biochem 81:203–229. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060310-170328
Shmueli A, Oren M (2005) Life, death, and ubiquitin: taming the mule. Cell 121(7):963–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.018
Mevissen TET, Komander D (2017) Mechanisms of deubiquitinase specificity and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 86:159–192. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-044916
Swatek KN, Komander D (2016) Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res 26(4):399–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.39
Feltham R, Silke J (2017) The small molecule that packs a punch: ubiquitin-mediated regulation of RIPK1/FADD/caspase-8 complexes. Cell Death Differ 24(7):1196–1204. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.67
Yau R, Rape M (2016) The increasing complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat Cell Biol 18(6):579–586. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3358
Gerlach B, Cordier SM, Schmukle AC, Emmerich CH, Rieser E, Haas TL, Webb AI, Rickard JA, Anderton H, Wong WW, Nachbur U, Gangoda L, Warnken U, Purcell AW, Silke J, Walczak H (2011) Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling. Nature 471(7340):591–596. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09816
Chen G, Goeddel DV (2002) TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science (New York, NY) 296(5573):1634–1635. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071924
Micheau O, Tschopp J (2003) Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114(2):181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00521-x
Moquin DM, McQuade T, Chan FK (2013) CYLD deubiquitinates RIP1 in the TNFα-induced necrosome to facilitate kinase activation and programmed necrosis. PLoS ONE 8(10):e76841. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076841
Newton K, Wickliffe KE, Dugger DL, Maltzman A, Roose-Girma M, Dohse M, Kőműves L, Webster JD, Dixit VM (2019) Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8 is crucial for limiting apoptosis and necroptosis. Nature 574(7778):428–431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1548-x
Feng S, Yang Y, Mei Y, Ma L, Zhu DE, Hoti N, Castanares M, Wu M (2007) Cleavage of RIP3 inactivates its caspase-independent apoptosis pathway by removal of kinase domain. Cell Signal 19(10):2056–2067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.016
Cai Z, Jitkaew S, Zhao J, Chiang HC, Choksi S, Liu J, Ward Y, Wu LG, Liu ZG (2014) Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol 16(1):55–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2883
Chen X, Li W, Ren J, Huang D, He WT, Song Y, Yang C, Li W, Zheng X, Chen P, Han J (2014) Translocation of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein to plasma membrane leads to necrotic cell death. Cell Res 24(1):105–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.171
Dondelinger Y, Declercq W, Montessuit S, Roelandt R, Goncalves A, Bruggeman I, Hulpiau P, Weber K, Sehon CA, Marquis RW, Bertin J, Gough PJ, Savvides S, Martinou JC, Bertrand MJ, Vandenabeele P (2014) MLKL compromises plasma membrane integrity by binding to phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Cell Rep 7(4):971–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.026
Hildebrand JM, Tanzer MC, Lucet IS, Young SN, Spall SK, Sharma P, Pierotti C, Garnier JM, Dobson RC, Webb AI, Tripaydonis A, Babon JJ, Mulcair MD, Scanlon MJ, Alexander WS, Wilks AF, Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Murphy JM, Silke J (2014) Activation of the pseudokinase MLKL unleashes the four-helix bundle domain to induce membrane localization and necroptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(42):15072–15077. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408987111
Wang H, Sun L, Su L, Rizo J, Liu L, Wang LF, Wang FS, Wang X (2014) Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol Cell 54(1):133–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.003
Geserick P, Hupe M, Moulin M, Wong WW, Feoktistova M, Kellert B, Gollnick H, Silke J, Leverkus M (2009) Cellular IAPs inhibit a cryptic CD95-induced cell death by limiting RIP1 kinase recruitment. J Cell Biol 187(7):1037–1054. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200904158
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, Martin-Chouly C, Le Moigne-Muller G, Van Herreweghe F, Takahashi N, Sergent O, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Vandenabeele P, Samson M, Dimanche-Boitrel MT (2012) TRAIL induces necroptosis involving RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent PARP-1 activation. Cell Death Differ 19(12):2003–2014. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.90
Meurette O, Huc L, Rebillard A, Le Moigne G, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Dimanche-Boitrel MT (2005) TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) induces necrosis-like cell death in tumor cells at acidic extracellular pH. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1056:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1352.018
Meurette O, Rebillard A, Huc L, Le Moigne G, Merino D, Micheau O, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Dimanche-Boitrel MT (2007) TRAIL induces receptor-interacting protein 1-dependent and caspase-dependent necrosis-like cell death under acidic extracellular conditions. Cancer Res 67(1):218–226. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-1610
Kuriakose T, Kanneganti TD (2018) ZBP1: innate sensor regulating cell death and inflammation. Trends Immunol 39(2):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2017.11.002
Malireddi RKS, Kesavardhana S, Kanneganti TD (2019) ZBP1 and TAK1: master regulators of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PAN-optosis). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:406. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00406
Jiao H, Wachsmuth L, Kumari S, Schwarzer R, Lin J, Eren RO, Fisher A, Lane R, Young GR, Kassiotis G, Kaiser WJ, Pasparakis M (2020) Z-nucleic-acid sensing triggers ZBP1-dependent necroptosis and inflammation. Nature 580(7803):391–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2129-8
Zheng M, Karki R, Vogel P, Kanneganti TD (2020) Caspase-6 is a key regulator of innate immunity, inflammasome activation, and host defense. Cell 181(3):674–687.e613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.040
Zhang T, Yin C, Boyd DF, Quarato G, Ingram JP, Shubina M, Ragan KB, Ishizuka T, Crawford JC, Tummers B, Rodriguez DA, Xue J, Peri S, Kaiser WJ, Lopez CB, Xu Y, Upton JW, Thomas PG, Green DR, Balachandran S (2020) Influenza virus Z-RNAs induce ZBP1-mediated necroptosis. Cell 180(6):1115–1129.e1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.050
Lin J, Kumari S, Kim C, Van TM, Wachsmuth L, Polykratis A, Pasparakis M (2016) RIPK1 counteracts ZBP1-mediated necroptosis to inhibit inflammation. Nature 540(7631):124–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20558
Newton K, Wickliffe KE, Maltzman A, Dugger DL, Strasser A, Pham VC, Lill JR, Roose-Girma M, Warming S, Solon M, Ngu H, Webster JD, Dixit VM (2016) RIPK1 inhibits ZBP1-driven necroptosis during development. Nature 540(7631):129–133. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20559
Peltzer N, Darding M, Walczak H (2016) Holding RIPK1 on the ubiquitin leash in TNFR1 signaling. Trends Cell Biol 26(6):445–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.01.006
Haas TL, Emmerich CH, Gerlach B, Schmukle AC, Cordier SM, Rieser E, Feltham R, Vince J, Warnken U, Wenger T, Koschny R, Komander D, Silke J, Walczak H (2009) Recruitment of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex stabilizes the TNF-R1 signaling complex and is required for TNF-mediated gene induction. Mol Cell 36(5):831–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.10.013
Li H, Kobayashi M, Blonska M, You Y, Lin X (2006) Ubiquitination of RIP is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 281(19):13636–13643. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600620200
Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ (2006) Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol Cell 22(2):245–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.026
Bertrand MJ, Milutinovic S, Dickson KM, Ho WC, Boudreault A, Durkin J, Gillard JW, Jaquith JB, Morris SJ, Barker PA (2008) cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol Cell 30(6):689–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.014
O’Donnell MA, Legarda-Addison D, Skountzos P, Yeh WC, Ting AT (2007) Ubiquitination of RIP1 regulates an NF-kappaB-independent cell-death switch in TNF signaling. Curr Biol 17(5):418–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.01.027
Kist M, Kőműves LG, Goncharov T, Dugger DL, Yu C, Roose-Girma M, Newton K, Webster JD, Vucic D (2021) Impaired RIPK1 ubiquitination sensitizes mice to TNF toxicity and inflammatory cell death. Cell Death Differ 28(3):985–1000. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00629-3
Tang Y, Tu H, Zhang J, Zhao X, Wang Y, Qin J, Lin X (2019) K63-linked ubiquitination regulates RIPK1 kinase activity to prevent cell death during embryogenesis and inflammation. Nat Commun 10(1):4157. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12033-8
Zhang X, Zhang H, Xu C, Li X, Li M, Wu X, Pu W, Zhou B, Wang H, Li D, Ding Q, Ying H, Wang H, Zhang H (2019) Ubiquitination of RIPK1 suppresses programmed cell death by regulating RIPK1 kinase activation during embryogenesis. Nat Commun 10(1):4158. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11839-w
Dynek JN, Goncharov T, Dueber EC, Fedorova AV, Izrael-Tomasevic A, Phu L, Helgason E, Fairbrother WJ, Deshayes K, Kirkpatrick DS, Vucic D (2010) c-IAP1 and UbcH5 promote K11-linked polyubiquitination of RIP1 in TNF signalling. EMBO J 29(24):4198–4209. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.300
Paul A, Wang B (2017) RNF8- and Ube2S-dependent ubiquitin lysine 11-linkage modification in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell 66(4):458-472.e455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.013
Seo J, Lee EW, Sung H, Seong D, Dondelinger Y, Shin J, Jeong M, Lee HK, Kim JH, Han SY, Lee C, Seong JK, Vandenabeele P, Song J (2016) CHIP controls necroptosis through ubiquitylation- and lysosome-dependent degradation of RIPK3. Nat Cell Biol 18(3):291–302. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3314
Seo J, Lee EW, Song J (2016) New role of E3 ubiquitin ligase in the regulation of necroptosis. BMB Rep 49(5):247–248. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.5.067
Mollah S, Wertz IE, Phung Q, Arnott D, Dixit VM, Lill JR (2007) Targeted mass spectrometric strategy for global mapping of ubiquitination on proteins. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21(20):3357–3364. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.3227
Kim W, Bennett EJ, Huttlin EL, Guo A, Li J, Possemato A, Sowa ME, Rad R, Rush J, Comb MJ, Harper JW, Gygi SP (2011) Systematic and quantitative assessment of the ubiquitin-modified proteome. Mol Cell 44(2):325–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.025
Sahara N, Murayama M, Mizoroki T, Urushitani M, Imai Y, Takahashi R, Murata S, Tanaka K, Takashima A (2005) In vivo evidence of CHIP up-regulation attenuating tau aggregation. J Neurochem 94(5):1254–1263. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03272.x
Tokunaga F, Sakata S, Saeki Y, Satomi Y, Kirisako T, Kamei K, Nakagawa T, Kato M, Murata S, Yamaoka S, Yamamoto M, Akira S, Takao T, Tanaka K, Iwai K (2009) Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-kappaB activation. Nat Cell Biol 11(2):123–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1821
Tokunaga F, Nakagawa T, Nakahara M, Saeki Y, Taniguchi M, Sakata S, Tanaka K, Nakano H, Iwai K (2011) SHARPIN is a component of the NF-κB-activating linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex. Nature 471(7340):633–636. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09815
Ikeda F, Deribe YL, Skånland SS, Stieglitz B, Grabbe C, Franz-Wachtel M, van Wijk SJ, Goswami P, Nagy V, Terzic J, Tokunaga F, Androulidaki A, Nakagawa T, Pasparakis M, Iwai K, Sundberg JP, Schaefer L, Rittinger K, Macek B, Dikic I (2011) SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis. Nature 471(7340):637–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09814
Damgaard RB, Nachbur U, Yabal M, Wong WW, Fiil BK, Kastirr M, Rieser E, Rickard JA, Bankovacki A, Peschel C, Ruland J, Bekker-Jensen S, Mailand N, Kaufmann T, Strasser A, Walczak H, Silke J, Jost PJ, Gyrd-Hansen M (2012) The ubiquitin ligase XIAP recruits LUBAC for NOD2 signaling in inflammation and innate immunity. Mol Cell 46(6):746–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.04.014
Peltzer N, Rieser E, Taraborrelli L, Draber P, Darding M, Pernaute B, Shimizu Y, Sarr A, Draberova H, Montinaro A, Martinez-Barbera JP, Silke J, Rodriguez TA, Walczak H (2014) HOIP deficiency causes embryonic lethality by aberrant TNFR1-mediated endothelial cell death. Cell Rep 9(1):153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.066
Peltzer N, Darding M, Montinaro A, Draber P, Draberova H, Kupka S, Rieser E, Fisher A, Hutchinson C, Taraborrelli L, Hartwig T, Lafont E, Haas TL, Shimizu Y, Böiers C, Sarr A, Rickard J, Alvarez-Diaz S, Ashworth MT, Beal A, Enver T, Bertin J, Kaiser W, Strasser A, Silke J, Bouillet P, Walczak H (2018) LUBAC is essential for embryogenesis by preventing cell death and enabling haematopoiesis. Nature 557(7703):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0064-8
Kumari S, Redouane Y, Lopez-Mosqueda J, Shiraishi R, Romanowska M, Lutzmayer S, Kuiper J, Martinez C, Dikic I, Pasparakis M, Ikeda F (2014) Sharpin prevents skin inflammation by inhibiting TNFR1-induced keratinocyte apoptosis. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03422
Rickard JA, Anderton H, Etemadi N, Nachbur U, Darding M, Peltzer N, Lalaoui N, Lawlor KE, Vanyai H, Hall C, Bankovacki A, Gangoda L, Wong WW, Corbin J, Huang C, Mocarski ES, Murphy JM, Alexander WS, Voss AK, Vaux DL, Kaiser WJ, Walczak H, Silke J (2014) TNFR1-dependent cell death drives inflammation in Sharpin-deficient mice. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03464
Aksentijevich I, Zhou Q (2017) NF-κB pathway in autoinflammatory diseases: dysregulation of protein modifications by ubiquitin defines a new category of autoinflammatory diseases. Front Immunol 8:399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00399
Wang H, Meng H, Li X, Zhu K, Dong K, Mookhtiar AK, Wei H, Li Y, Sun SC, Yuan J (2017) PELI1 functions as a dual modulator of necroptosis and apoptosis by regulating ubiquitination of RIPK1 and mRNA levels of c-FLIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(45):11944–11949. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1715742114
de Almagro MC, Goncharov T, Izrael-Tomasevic A, Duttler S, Kist M, Varfolomeev E, Wu X, Lee WP, Murray J, Webster JD, Yu K, Kirkpatrick DS, Newton K, Vucic D (2017) Coordinated ubiquitination and phosphorylation of RIP1 regulates necroptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 24(1):26–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.78
Choi SW, Park HH, Kim S, Chung JM, Noh HJ, Kim SK, Song HK, Lee CW, Morgan MJ, Kang HC, Kim YS (2018) PELI1 selectively targets kinase-active RIP3 for ubiquitylation-dependent proteasomal degradation. Mol Cell 70(5):920-935.e927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.016
Li X, Zhang M, Huang X, Liang W, Li G, Lu X, Li Y, Pan H, Shi L, Zhu H, Qian L, Shan B, Yuan J (2020) Ubiquitination of RIPK1 regulates its activation mediated by TNFR1 and TLRs signaling in distinct manners. Nat Commun 11(1):6364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19935-y
Draber P, Kupka S, Reichert M, Draberova H, Lafont E, de Miguel D, Spilgies L, Surinova S, Taraborrelli L, Hartwig T, Rieser E, Martino L, Rittinger K, Walczak H (2015) LUBAC-recruited CYLD and A20 regulate gene activation and cell death by exerting opposing effects on linear ubiquitin in signaling complexes. Cell Rep 13(10):2258–2272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.009
Takiuchi T, Nakagawa T, Tamiya H, Fujita H, Sasaki Y, Saeki Y, Takeda H, Sawasaki T, Buchberger A, Kimura T, Iwai K (2014) Suppression of LUBAC-mediated linear ubiquitination by a specific interaction between LUBAC and the deubiquitinases CYLD and OTULIN. Genes Cells 19(3):254–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12128
Legarda D, Justus SJ, Ang RL, Rikhi N, Li W, Moran TM, Zhang J, Mizoguchi E, Zelic M, Kelliher MA, Blander JM, Ting AT (2016) CYLD proteolysis protects macrophages from TNF-mediated auto-necroptosis induced by LPS and licensed by type I IFN. Cell Rep 15(11):2449–2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.032
Ganjam GK, Terpolilli NA, Diemert S, Eisenbach I, Hoffmann L, Reuther C, Herden C, Roth J, Plesnila N, Culmsee C (2018) Cylindromatosis mediates neuronal cell death in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Differ 25(8):1394–1407. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-017-0046-7
Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R (2003) Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature 424(6950):797–801. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01811
Kovalenko A, Chable-Bessia C, Cantarella G, Israël A, Wallach D, Courtois G (2003) The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-kappaB signalling by deubiquitination. Nature 424(6950):801–805. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01802
Trompouki E, Hatzivassiliou E, Tsichritzis T, Farmer H, Ashworth A, Mosialos G (2003) CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 424(6950):793–796. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01803
O’Donnell MA, Perez-Jimenez E, Oberst A, Ng A, Massoumi R, Xavier R, Green DR, Ting AT (2011) Caspase 8 inhibits programmed necrosis by processing CYLD. Nat Cell Biol 13(12):1437–1442. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2362
Schworer SA, Smirnova II, Kurbatova I, Bagina U, Churova M, Fowler T, Roy AL, Degterev A, Poltorak A (2014) Toll-like receptor-mediated down-regulation of the deubiquitinase cylindromatosis (CYLD) protects macrophages from necroptosis in wild-derived mice. J Biol Chem 289(20):14422–14433. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.547547
Keusekotten K, Elliott PR, Glockner L, Fiil BK, Damgaard RB, Kulathu Y, Wauer T, Hospenthal MK, Gyrd-Hansen M, Krappmann D, Hofmann K, Komander D (2013) OTULIN antagonizes LUBAC signaling by specifically hydrolyzing Met1-linked polyubiquitin. Cell 153(6):1312–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.014
Elliott PR, Nielsen SV, Marco-Casanova P, Fiil BK, Keusekotten K, Mailand N, Freund SM, Gyrd-Hansen M, Komander D (2014) Molecular basis and regulation of OTULIN-LUBAC interaction. Mol Cell 54(3):335–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.018
Schaeffer V, Akutsu M, Olma MH, Gomes LC, Kawasaki M, Dikic I (2014) Binding of OTULIN to the PUB domain of HOIP controls NF-κB signaling. Mol Cell 54(3):349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.016
Wagner SA, Satpathy S, Beli P, Choudhary C (2016) SPATA2 links CYLD to the TNF-α receptor signaling complex and modulates the receptor signaling outcomes. EMBO J 35(17):1868–1884. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201694300
Wiener R, Wolberger C (2013) A new DUB makes linear ubiquitin a party to its own destruction. Cell 153(6):1189–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.018
Rivkin E, Almeida SM, Ceccarelli DF, Juang YC, MacLean TA, Srikumar T, Huang H, Dunham WH, Fukumura R, Xie G, Gondo Y, Raught B, Gingras AC, Sicheri F, Cordes SP (2013) The linear ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinase gumby regulates angiogenesis. Nature 498(7454):318–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12296
Verboom L, Martens A, Priem D, Hoste E, Sze M, Vikkula H, Van Hove L, Voet S, Roels J, Maelfait J, Bongiovanni L, de Bruin A, Scott CL, Saeys Y, Pasparakis M, Bertrand MJM, van Loo G (2020) OTULIN prevents liver inflammation and hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting FADD- and RIPK1 kinase-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis. Cell Rep 30(7):2237-2247.e2236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.028
Schünke H, Göbel U, Dikic I, Pasparakis M (2021) OTULIN inhibits RIPK1-mediated keratinocyte necroptosis to prevent skin inflammation in mice. Nat Commun 12(1):5912. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25945-1
Hoste E, Lecomte K, Annusver K, Vandamme N, Roels J, Maschalidi S, Verboom L, Vikkula HK, Sze M, Van Hove L, Verstaen K, Martens A, Hochepied T, Saeys Y, Ravichandran K, Kasper M, van Loo G (2021) OTULIN maintains skin homeostasis by controlling keratinocyte death and stem cell identity. Nat Commun 12(1):5913. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25944-2
Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H, Eby M, Aravind L, Seshagiri S, Wu P, Wiesmann C, Baker R, Boone DL, Ma A, Koonin EV, Dixit VM (2004) De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 430(7000):694–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02794
Priem D, van Loo G, Bertrand MJM (2020) A20 and cell death-driven inflammation. Trends Immunol 41(5):421–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2020.03.001
Tokunaga F, Nishimasu H, Ishitani R, Goto E, Noguchi T, Mio K, Kamei K, Ma A, Iwai K, Nureki O (2012) Specific recognition of linear polyubiquitin by A20 zinc finger 7 is involved in NF-κB regulation. EMBO J 31(19):3856–3870. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.241
Verhelst K, Carpentier I, Kreike M, Meloni L, Verstrepen L, Kensche T, Dikic I, Beyaert R (2012) A20 inhibits LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation by binding linear polyubiquitin chains via its zinc finger 7. EMBO J 31(19):3845–3855. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.240
Polykratis A, Martens A, Eren RO, Shirasaki Y, Yamagishi M, Yamaguchi Y, Uemura S, Miura M, Holzmann B, Kollias G, Armaka M, van Loo G, Pasparakis M (2019) A20 prevents inflammasome-dependent arthritis by inhibiting macrophage necroptosis through its ZnF7 ubiquitin-binding domain. Nat Cell Biol 21(6):731–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0324-3
Lee EG, Boone DL, Chai S, Libby SL, Chien M, Lodolce JP, Ma A (2000) Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science (New York, NY) 289(5488):2350–2354. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5488.2350
Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, McNally E, Pickart C, Ma A (2004) The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol 5(10):1052–1060. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1110
Zhou Q, Wang H, Schwartz DM, Stoffels M, Park YH, Zhang Y, Yang D, Demirkaya E, Takeuchi M, Tsai WL, Lyons JJ, Yu X, Ouyang C, Chen C, Chin DT, Zaal K, Chandrasekharappa SC, Hanson EP, Yu Z, Mullikin JC, Hasni SA, Wertz IE, Ombrello AK, Stone DL, Hoffmann P, Jones A, Barham BK, Leavis HL, van Royen-Kerkof A, Sibley C, Batu ED, Gül A, Siegel RM, Boehm M, Milner JD, Ozen S, Gadina M, Chae J, Laxer RM, Kastner DL, Aksentijevich I (2016) Loss-of-function mutations in TNFAIP3 leading to A20 haploinsufficiency cause an early-onset autoinflammatory disease. Nat Genet 48(1):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3459
Dziedzic SA, Su Z, Jean Barrett V, Najafov A, Mookhtiar AK, Amin P, Pan H, Sun L, Zhu H, Ma A, Abbott DW, Yuan J (2018) ABIN-1 regulates RIPK1 activation by linking Met1 ubiquitylation with Lys63 deubiquitylation in TNF-RSC. Nat Cell Biol 20(1):58–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-017-0003-1
Li M, Liu Y, Xu C, Zhao Q, Liu J, Xing M, Li X, Zhang H, Wu X, Wang L, Ou Y, Wu X, Zhao X, Liu H, Qiu L, Li F, Li J, Rong W, Luo Y, Deng J, Wang X, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Lv A, Li Q, Zhang H (2022) Ubiquitin-binding domain in ABIN1 is critical for regulating cell death and inflammation during development. Cell Death Differ. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-022-00994-1
Liu X, Li Y, Peng S, Yu X, Li W, Shi F, Luo X, Tang M, Tan Z, Bode AM, Cao Y (2018) Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 suppresses necroptosis through targeting RIPK1/3 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis 9(2):53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0081-9
Mei P, Xie F, Pan J, Wang S, Gao W, Ge R, Gao B, Gao S, Chen X, Wang Y, Wu J, Ding C, Li J (2021) E3 ligase TRIM25 ubiquitinates RIP3 to inhibit TNF induced cell necrosis. Cell Death Differ 28(10):2888–2899. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00790-3
Xie Y, Zhao Y, Shi L, Li W, Chen K, Li M, Chen X, Zhang H, Li T, Matsuzawa-Ishimoto Y, Yao X, Shao D, Ke Z, Li J, Chen Y, Zhang X, Cui J, Cui S, Leng Q, Cadwell K, Li X, Wei H, Zhang H, Li H, Xiao H (2020) Gut epithelial TSC1/mTOR controls RIPK3-dependent necroptosis in intestinal inflammation and cancer. J Clin Investig 130(4):2111–2128. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci133264
Lee SB, Kim JJ, Han SA, Fan Y, Guo LS, Aziz K, Nowsheen S, Kim SS, Park SY, Luo Q, Chung JO, Choi SI, Aziz A, Yin P, Tong SY, Fiesel FC, Springer W, Zhang JS, Lou Z (2019) The AMPK-Parkin axis negatively regulates necroptosis and tumorigenesis by inhibiting the necrosome. Nat Cell Biol 21(8):940–951. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0356-8
Liu Z, Nailwal H, Rector J, Rahman MM, Sam R, McFadden G, Chan FK (2021) A class of viral inducer of degradation of the necroptosis adaptor RIPK3 regulates virus-induced inflammation. Immunity 54(2):247-258.e247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.11.020
Onizawa M, Oshima S, Schulze-Topphoff U, Oses-Prieto JA, Lu T, Tavares R, Prodhomme T, Duong B, Whang MI, Advincula R, Agelidis A, Barrera J, Wu H, Burlingame A, Malynn BA, Zamvil SS, Ma A (2015) The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 restricts ubiquitination of the kinase RIPK3 and protects cells from necroptosis. Nat Immunol 16(6):618–627. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3172
Roedig J, Kowald L, Juretschke T, Karlowitz R, Ahangarian Abhari B, Roedig H, Fulda S, Beli P, van Wijk SJ (2021) USP22 controls necroptosis by regulating receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 ubiquitination. EMBO Rep 22(2):e50163. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202050163
Garcia LR, Tenev T, Newman R, Haich RO, Liccardi G, John SW, Annibaldi A, Yu L, Pardo M, Young SN, Fitzgibbon C, Fernando W, Guppy N, Kim H, Liang LY, Lucet IS, Kueh A, Roxanis I, Gazinska P, Sims M, Smyth T, Ward G, Bertin J, Beal AM, Geddes B, Choudhary JS, Murphy JM, Aurelia Ball K, Upton JW, Meier P (2021) Ubiquitylation of MLKL at lysine 219 positively regulates necroptosis-induced tissue injury and pathogen clearance. Nat Commun 12(1):3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23474-5
Liu Z, Dagley LF, Shield-Artin K, Young SN, Bankovacki A, Wang X, Tang M, Howitt J, Stafford CA, Nachbur U, Fitzgibbon C, Garnish SE, Webb AI, Komander D, Murphy JM, Hildebrand JM, Silke J (2021) Oligomerization-driven MLKL ubiquitylation antagonizes necroptosis. EMBO J 40(23):e103718. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019103718
Yoon S, Bogdanov K, Wallach D (2022) Site-specific ubiquitination of MLKL targets it to endosomes and targets Listeria and Yersinia to the lysosomes. Cell Death Differ 29(2):306–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00924-7
Murphy JM, Czabotar PE, Hildebrand JM, Lucet IS, Zhang JG, Alvarez-Diaz S, Lewis R, Lalaoui N, Metcalf D, Webb AI, Young SN, Varghese LN, Tannahill GM, Hatchell EC, Majewski IJ, Okamoto T, Dobson RC, Hilton DJ, Babon JJ, Nicola NA, Strasser A, Silke J, Alexander WS (2013) The pseudokinase MLKL mediates necroptosis via a molecular switch mechanism. Immunity 39(3):443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.06.018
Kesavardhana S, Kuriakose T, Guy CS, Samir P, Malireddi RKS, Mishra A, Kanneganti TD (2017) ZBP1/DAI ubiquitination and sensing of influenza vRNPs activate programmed cell death. J Exp Med 214(8):2217–2229. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20170550
Wang X, Xiong J, Zhou D, Zhang S, Wang L, Tian Q, Li C, Liu J, Wu Y, Li J, Wang J (2022) TRIM34 modulates influenza virus-activated programmed cell death by targeting Z-DNA-binding protein 1 for K63-linked polyubiquitination. J Biol Chem 298(3):101611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101611
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA1302200); National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.32170748 and No.81773075); the Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia (No.2022BFH02012); Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (No. 21490714300 and No.18410720600) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 22ZR1448000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZC had the idea for the review article; YC, WR, and QW performed the literature search; ZC, YC and WR drafted the manuscript; YH and DM critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Ren, W., Wang, Q. et al. The regulation of necroptosis by ubiquitylation. Apoptosis 27, 668–684 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01755-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01755-8