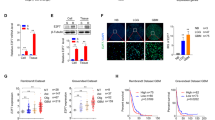
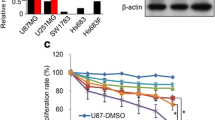
Abstract
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) has been characterized by the high incidence, therapy tolerance and relapse. The molecular events controlling GBM resistant to chemotherapy temozolomide (TMZ) remain to be elusive. Here, we identified WNT signaling was amplified by TMZ and mediated drug response in GBM. We found O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) was redundant to WNT-mediated chemoresistance, which was highly associated with p53 mutation status. In GBM with p53 mutation, loss of function of p53 downregulated miR-34a expression, which represses transcription of WNT ligand 6 (WNT6) by directly binding to 3′ UTR of WNT6 mRNA, leading to activation of WNT signaling, and the eventual WNT-mediated chemoresistance to TMZ. Combined treatment of TMZ with WNT inhibitor or miR34a mimic induced drug sensitivity of p53-mutant GBM cells and extended survival in xenograft mice in vivo. Our findings provide insight into understanding the molecular mechanism of GBM chemoresistance to TMZ and facilitating to develop novel treatment strategy to combat p53-mutant GBM by targeting miR-34a/WNT6 axis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alexander BM, Cloughesy TF (2017) Adult glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 35(21):2402–2409
Anjum K et al (2017) Current status and future therapeutic perspectives of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) therapy: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 92:681–689
Zhang J, Stevens MF, Bradshaw TD (2012) Temozolomide: mechanisms of action, repair and resistance. Curr Mol Pharmacol 5(1):102–114
Yang SH et al (2016) Metformin treatment reduces temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 7(48):78787–78803
Aldape K et al (2015) Glioblastoma: pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol 129(6):829–848
Alonso MM et al (2007) Adenovirus-based strategies overcome temozolomide resistance by silencing the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter. Cancer Res 67(24):11499–11504
Bocangel DB et al (2002) Multifaceted resistance of gliomas to temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 8(8):2725–2734
Yin J et al (2019) Exosomal transfer of miR-1238 contributes to temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma. EBioMedicine 42:238–251
Lee Y et al (2016) WNT signaling in glioblastoma and therapeutic opportunities. Lab Invest 96(2):137–150
McCord M et al (2017) Targeting WNT signaling for multifaceted glioblastoma therapy. Front Cell Neurosci 11:318
Kim Y et al (2012) Wnt activation is implicated in glioblastoma radioresistance. Lab Invest 92(3):466–473
Tomar VS, Patil V, Somasundaram K (2020) Temozolomide induces activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in glioma cells via PI3K/Akt pathway: implications in glioma therapy. Cell Biol Toxicol 36(3):273–278
Miao W et al (2015) p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis sensitizes drug-resistant U251 glioblastoma stem cells to temozolomide through enhanced apoptosis. Mol Med Rep 11(6):4165–4173
Lin J et al (2018) Characterizing the molecular mechanisms of acquired temozolomide resistance in the U251 glioblastoma cell line by protein microarray. Oncol Rep 39(5):2333–2341
Yun EJ et al (2020) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway induces autophagy-mediated temozolomide-resistance in human glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis 11(9):771
Zhan T, Rindtorff N, Boutros M (2017) Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36(11):1461–1473
Erasimus H et al (2016) DNA repair mechanisms and their clinical impact in glioblastoma. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 769:19–35
Wellenstein MD et al (2019) Loss of p53 triggers WNT-dependent systemic inflammation to drive breast cancer metastasis. Nature 572(7770):538–542
Cho YH et al (2020) 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/beta-catenin pathway activation. Nat Commun 11(1):5321
Borges KS et al (2020) Wnt/beta-catenin activation cooperates with loss of p53 to cause adrenocortical carcinoma in mice. Oncogene 39(30):5282–5291
Kim NH et al (2011) p53 and microRNA-34 are suppressors of canonical Wnt signaling. Sci Signal 4(197):ra71
Lee SY (2016) Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Dis 3(3):198–210
Ahmad A et al (2019) Thymoquinone (2-Isoprpyl-5-methyl-1, 4-benzoquinone) as a chemopreventive/anticancer agent: chemistry and biological effects. Saudi Pharm J 27(8):1113–1126
Yi GZ et al (2019) Acquired temozolomide resistance in MGMT-deficient glioblastoma cells is associated with regulation of DNA repair by DHC2. Brain 142(8):2352–2366
Ham SW et al (2019) TP53 gain-of-function mutation promotes inflammation in glioblastoma. Cell Death Differ 26(3):409–425
Zhang Y et al (2018) The p53 pathway in glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10090297
Wang Y et al (2004) p53 disruption profoundly alters the response of human glioblastoma cells to DNA topoisomerase I inhibition. Oncogene 23(6):1283–1290
Koul D et al (2012) Antitumor activity of NVP-BKM120–a selective pan class I PI3 kinase inhibitor showed differential forms of cell death based on p53 status of glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res 18(1):184–195
Saadatpour L et al (2016) Glioblastoma: exosome and microRNA as novel diagnosis biomarkers. Cancer Gene Ther 23(12):415–418
Qiu S et al (2013) Interactions of miR-323/miR-326/miR-329 and miR-130a/miR-155/miR-210 as prognostic indicators for clinical outcome of glioblastoma patients. J Transl Med 11:10
Funding
This work was supported by the Suzhou Science and Technology Development Plan (SYS2020161 to Z.R. Ma, SYS2020151 to Z.H. Zhu and SYS2018072 to Q. Wang), Gusu Health personnel Training program of Suzhou city (GSWS2020050 to S.Z. Cai and GSWS2019017 to X.M. Yan), Clinical key diseases diagnosis and treatment technology projects (LCZX201908 to X.M. Yan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZM, SC, QX, WL, HX, and ZH, performed the experiments; ZM, SC, ZH and XY, performed data analysis; QW, ZM and SC designed the studies and wrote the manuscript; QW, ZH and XY revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Cai, S., Xiong, Q. et al. WNT signaling modulates chemoresistance to temozolomide in p53-mutant glioblastoma multiforme. Apoptosis 27, 80–89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-021-01704-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-021-01704-x