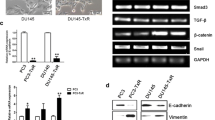
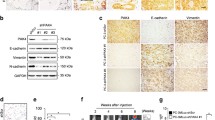
Abstract
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is implicated in the metastasis of human prostate cancer (PCa). Notch signaling has been established as a regulator of EMT. Notch-4 has emerged as a mammary proto-oncogene and a target in several cancers. However, the role and the mechanism of action of Notch-4 in PCa are still unclear. In the present study, we first observed a marked increase in Notch-4 expression in the PCa cell lines DU145, PC3 and LnCAP compared with the non-malignant prostate epithelial cell line RWPE1. Knocking down the expression of Notch-4 suppressed the viability and proliferation in the PCa cell lines DU145 and PC3. Also, further study showed that a decline in Notch-4 significantly promoted apoptosis in PC3 cells. Notch-4 silencing also resulted in decreased cell migration and invasion and affected the expression of EMT markers. We hypothesized that Notch-4 ablation suppresses the activity of NF-κB, so we used PMA to stimulate NF-κB p50 and p65 activation in PC3 cells. The results indicate that PMA treatment impaired the action of Notch-4 ablation in the biology of PC3 cells including cell growth, apoptosis, migration, invasion and EMT. The results of the present study show that RNAi targeting against Notch-4 expression suppresses PCa progression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao W, Guo W, Zhou Q, Ma SN, Wang R, Qiu Y, Jin M, Duan HQ, Kong D (2013) In vitro antimetastatic effect of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor ZSTK474 on prostate cancer PC3 cells. Int J Mol Sci 14(7):13577–13591
Andreoiu M, Cheng L (2010) Multifocal prostate cancer: biologic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications. Hum Pathol 41(6):781–793
Crawford ED, Higano CS, Shore ND, Hussain M, Petrylak DP (2015) Treating patients with metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer: a comprehensive review of available therapies. J Urol 194(6):1537–1547
Shi J, Xia Y, Song Q, Zhou X, Mizokami A, Keller E, Zhang J, Lu Y (2014) Interaction of prostate cancer cells with tumor microenvironment promotes EMT and DTCs activation. Cancer Res 74(19 Supplement):1–1
Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, Hynes PG, Casey OM, Fang L, Yi M, Stephens RM, Seng V, Sheppard-Tillman H, Martin P, Kelly K (2013) MiR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms. Oncogene 32(3):296–306
Prasad CP, Rath G, Mathur S, Bhatnagar D, Parshad R, Ralhan R (2009) Expression analysis of E-cadherin, Slug and GSK3beta in invasive ductal carcinoma of breast. BMC Cancer 9(325):1471–2407
Voulgari A, Pintzas A (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta 2:75–90
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J, Lander ES, Weinberg RA (2008) Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res 68(10):3645–3654
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D, zur Hausen A, Brunton VG, Morton J, Sansom O, Schuler J, Stemmler MP, Herzberger C, Hopt U, Keck T, Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2009) The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 11(12):1487–1495
Byles V, Zhu L, Lovaas JD, Chmilewski LK, Wang J, Faller DV, Dai Y (2012) SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell migration and metastasis. Oncogene 31(43):4619–4629
Sahlgren C, Gustafsson MV, Jin S, Poellinger L, Lendahl U (2008) Notch signaling mediates hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(17):6392–6397
Bui Q, Kang K (2016) Abstract P1-05-06: Essential role of notch-4/STAT3 signaling in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer. Cancer Res 76(4 Supplement):P1-05-06–P01-05-06
Speiser J, Foreman K, Drinka E, Godellas C, Perez C, Salhadar A, Ersahin C, Rajan P (2012) Notch-1 and Notch-4 biomarker expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Surg Pathol 20(2):139–145
Ntziachristos P, Lim JS, Sage J, Aifantis I (2014) From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: a centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell 25(3):318–334
Haines N, Irvine KD (2003) Glycosylation regulates Notch signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(10):786–797
Okajima T, Irvine KD (2002) Regulation of notch signaling by o-linked fucose. Cell 111(6):893–904
Delury C, Hart C, Brown M, Clarke N, Parkin E (2016) Stroma-induced Jagged1 expression drives PC3 prostate cancer cell migration; disparate effects of RIP-generated proteolytic fragments on cell behaviour and Notch signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 472(1):255–261
Yin L, Velazquez OC, Liu ZJ (2010) Notch signaling: emerging molecular targets for cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol 80(5):690–701
Naik S, MacFarlane M, Sarin A (2015) Notch4 signaling confers susceptibility to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 116(7):1371–1380
Chan GK, Kleinheinz TL, Peterson D, Moffat JG (2013) A simple high-content cell cycle assay reveals frequent discrepancies between cell number and ATP and MTS proliferation assays. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63583
Fan X, Chen X, Deng W, Zhong G, Cai Q, Lin T (2013) Up-regulated microRNA-143 in cancer stem cells differentiation promotes prostate cancer cells metastasis by modulating FNDC3B expression. BMC Cancer 13(61):1471–2407
Chen W, Zhang H, Wang J, Cao G, Dong Z, Su H, Zhou X, Zhang S (2013) Lentiviral-mediated gene silencing of Notch-4 inhibits in vitro proliferation and perineural invasion of ACC-M cells. Oncol Rep 29(5):1797–1804
Saini S, Majid S, Shahryari V, Tabatabai ZL, Arora S, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Dahiya R, Deng G (2014) Regulation of SRC kinases by microRNA-3607 located in a frequently deleted locus in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 13(7):1952–1963
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T, Kawakami Y (2009) Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell 15(3):195–206
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D, Ahmad A, Nogueira V, Hay N, Sarkar FH (2010) Down-regulation of Notch-1 and Jagged-1 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis via inactivation of Akt, mTOR, and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem 109(4):726–736
Bolos V, Mira E, Martinez-Poveda B, Luxan G, Canamero M, Martinez AC, Manes S, de la Pompa JL (2013) Notch activation stimulates migration of breast cancer cells and promotes tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res 15(4):R54 doi:10.1186/bcr3447
Wan X, Cheng C, Shao Q, Lin Z, Lu S, Chen Y (2016) CD24 promotes HCC progression via triggering Notch-related EMT and modulation of tumor microenvironment. Tumour Biol 37(5):6073–6084. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4442-7
Carvalho FL, Simons BW, Eberhart CG, Berman DM (2014) Notch signaling in prostate cancer: a moving target. Prostate 74(9):933–945. doi:10.1002/pros.22811
Clementz AG, Rogowski A, Pandya K, Miele L, Osipo C (2011) NOTCH-1 and NOTCH-4 are novel gene targets of PEA3 in breast cancer: novel therapeutic implications. Breast Cancer Res 13(3):R63
Reedijk M, Odorcic S, Chang L, Zhang H, Miller N, McCready DR, Lockwood G, Egan SE (2005) High-level coexpression of JAG1 and NOTCH1 is observed in human breast cancer and is associated with poor overall survival. Cancer Res 65(18):8530–8537
Bell D, Hanna EY, Miele L, Roberts D, Weber RS, El-Naggar AK (2014) Expression and significance of notch signaling pathway in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Ann Diagn Pathol 18(1):10–13
Li Y, Chen L, Yang Y et al (2014) MP31-17 NOTCH 4 REGULATED, LEF1 MEDIATED PROSTATE CANCER METASTASIS AND ANDROGEN INDEPENDENCE. J Urol 191(4):e328–e329
Yabuuchi S, Pai SG, Campbell NR, de Wilde RF, De Oliveira E, Korangath P, Streppel MM, Rasheed ZA, Hidalgo M, Maitra A, Rajeshkumar NV (2013) Notch signaling pathway targeted therapy suppresses tumor progression and metastatic spread in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 335(1):41–51
Kopan R, Ilagan MX (2009) The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 137(2):216–233
Somnay YR, Yu XM, Lloyd RV, Leverson G, Aburjania Z, Jang S, Jaskula-Sztul R, Chen H (2016) Notch3 expression correlates with thyroid cancer differentiation, induces apoptosis, and predicts disease prognosis. Cancer 2(10):30403
Yun J, Pannuti A, Espinoza I, Zhu H, Hicks C, Zhu X, Caskey M, Rizzo P, D’Souza G, Backus K, Denning MF, Coon J, Sun M, Bresnick EH, Osipo C, Wu J, Strack PR, Tonetti DA, Miele L (2013) Crosstalk between PKCalpha and Notch-4 in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 5(2):26
Ding LC, She L, Zheng DL, Huang QL, Wang JF, Zheng FF, Lu YG (2010) Notch-4 contributes to the metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oncol Rep 24(2):363–368
Sekhon K, Bucay N, Majid S, Dahiya R, Saini S (2016) MicroRNAs and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 30(10):11708
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Kuang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Notch-4 silencing inhibits prostate cancer growth and EMT via the NF-κB pathway. Apoptosis 22, 877–884 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1368-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1368-0