Abstract
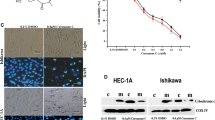
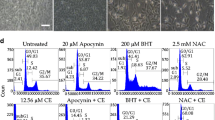
Centchroman (CC) or Ormeloxifene has been shown to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in various types of cancer cells. This has, however, not been addressed for endometrial cancer cells where its (CC) mechanism of action remains unclear. This study focuses on the basis of antineoplasticity of CC by blocking the targets involved in the cell cycle, survival and apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. Ishikawa Human Endometrial Cancer Cells were cultured under estrogen deprived medium, exposed to CC and analyzed for proliferation and apoptosis. Additionally, we also analyzed oxidative stress induced by CC. Cell viability studies confirmed the IC50 of CC in Ishikawa cells to be 20 µM after 48 h treatment. CC arrests the cells in G0/G1 phase through cyclin D1 and cyclin E mediated pathways. Phosphatidylserine externalization, nuclear morphology changes, DNA fragmentation, PARP cleavage, and alteration of Bcl-2 family protein expression clearly suggest ongoing apoptosis in the CC treated cells. Activation of caspase 3 & 9, up-regulation of AIF and inhibition of apoptosis by z-VAD-fmk clearly explains the participation of the intrinsic pathway of programmed cell death. Further, the increase of ROS, loss of MMP, inhibition of antioxidant (MnSOD, Cu/Zn-SOD and GST) and inhibition of apoptosis with L-NAC suggests CC induced oxidative stress leading to apoptosis via mitochondria mediated pathway. Therefore, CC could be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of Endometrial Cancer adjunct to its utility as a contraceptive and an anti-breast cancer agent.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jordan VC (1988) Tamoxifen and endometrial cancer. Lancet 2:1019
Anand N, Ray S (1977) Centchroman–a post-coital contraceptive agent. Indian J Exp Biol 15:1130–1142
Kamboj VP, Setty BS, Chandra H, Roy SK, Kar AB (1977) Biological profile of centchroman-a new post-coital contraceptive. Indian J Exp Biol 15:1144–1150
Srivastava S, Sharma R, Balapure AK (2004) Morphological and biochemical basis of centchroman as a novel antineoplastic agent in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Indian J Pharmacol 36:238–243
Nigam M, Ranjan V, Srivastava S, Sharma R, Balapure AK (2008) Centchroman induces G0/G1 arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis involving mitochondrial membrane depolarization in MCF-7 and MDA MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Life Sci 82:577–590
Nigam M, Singh N, Ranjan V et al (2010) Centchroman mediated apoptosis involves cross-talk between extrinsic/intrinsic pathways and oxidative regulation. Life Sci 87:750–758
Singh N, Zaidi D, Shyam H, Sharma R, Balapure AK (2012) Polyphenols sensitization potentiates susceptibility of MCF-7 and MDA MB-231 cells to centchroman. PLoS ONE 7:e37736
Gara RK, Sundram V, Chauhan SC, Jaggi M (2013) Anti-cancer potential of a novel SERM ormeloxifene. Curr Med Chem 20:4177–4184
Srivastava VK, Gara RK, Bhatt ML, Sahu DP, Mishra DP (2011) Centchroman inhibits proliferation of head and neck cancer cells through the modulation of PI3K/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:40–45
Maher DM, Khan S, Nordquist JL et al (2015) Ormeloxifene efficiently inhibits ovarian cancer growth. Cancer Lett 356:606–612
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E et al (2005) Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 55:10–30
Bokhman JV (1983) Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 15:10–17
Smita A, Amita D, Anila D (2007) Modulation of AP-1 mediated estrogenic response by ormeloxifene in rat uterus. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 104:208–214
Daverey A, Saxena R, Tewari S, Goel SK, Dwivedi A (2009) Expression of estrogen receptor co-regulators SRC-1, RIP140 and NCoR and their interaction with estrogen receptor in rat uterus, under the influence of ormeloxifene. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 116:93–101
Shang Y, Brown M (2002) Molecular determinants for the tissue specificity of SERMs. Science 295:2465–2468
Soto AM, Sonnenschein C (1985) The role of estrogens on the proliferation of human breast tumor cells (MCF-7). J Steroid Biochem 23:87–94
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D et al (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1107–1112
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Arbab IA, Abdul AB, Sukari MA et al (2013) Dentatin isolated from Clausena excavata induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through the intrinsic pathway with involvement of NF-kappaB signalling and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest: a bioassay-guided approach. J Ethnopharmacol 145:343–354
Wilkins HR, Doucet K, Duke V, Morra A, Johnson N (2010) Estrogen prevents sustained COLO-205 human colon cancer cell growth by inducing apoptosis, decreasing c-myb protein, and decreasing transcription of the anti-apoptotic protein bcl-2. Tumour Biol 31:16–22
Olsson M, Zhivotovsky B (2011) Caspases and cancer. Cell Death Differ 18:1441–1449
Lal J (2010) Clinical pharmacokinetics and interaction of centchroman–a mini review. Contraception 81:275–280
Pal P, Kanaujiya JK, Lochab S et al (2011) 2-D gel electrophoresis-based proteomic analysis reveals that ormeloxifen induces G0-G1 growth arrest and ERK-mediated apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells K562. Proteomics 11:1517–1529
Dulic V, Lees E, Reed SI (1992) Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science 257:1958–1961
Ohtsubo M, Theodoras AM, Schumacher J, Roberts JM, Pagano M (1995) Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 15:2612–2624
Gartel AL, Tyner AL (1999) Transcriptional regulation of the p21[(WAF1/CIP1)] gene. Exp Cell Res 246:280–289
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Haas K, Johannes C, Geisen C et al (1997) Malignant transformation by cyclin E and Ha-Ras correlates with lower sensitivity towards induction of cell death but requires functional Myc and CDK4. Oncogene 15:2615–2623
Hubalek MM, Widschwendter A, Erdel M et al (2004) Cyclin E dysregulation and chromosomal instability in endometrial cancer. Oncogene 23:4187–4192
Spruck CH, Won KA, Reed SI (1999) Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature 401:297–300
Castagnetta L, Granata OM, Lo Casto M, Miserendino V, Calo M, Carruba G (1986) Estrone conversion rates by human endometrial cancer cell lines. J Steroid Biochem 25:803–809
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, CSIR-CDRI for permitting to carry out the work. Mr. A. L. Vishwakarma, SAIF is thanked for the experiments with flow cytometry. Hari Shyam and Shweta Kaushik gratefully acknowledge the fellowship received from ICMR and UGC New Delhi, respectively. This is the CSIR-CDRI communication no. 9428.
Author Contributions
Conception and design: Hari Shyam, Neetu Singh and Anil K. Balapure. Development of methodology: Hari Shyam, Neetu Singh and Anil K.Balapure. Acquisition of data: Hari Shyam, Shweta Kaushik and Ramesh Sharma. Shyam, Neetu Singh, Ramesh Sharma and Anil K. Balapure. Writing, review and/or revision of the manuscript: Hari Shyam, Neetu Singh and Anil K. Balapure. Study supervision: Anil K. Balapure.
Funding
This study was supported by Project code BSC0001, CSIR-Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow, India and Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of Interest.
Additional information
Hari Shyam is the recipient of a research fellowship from the Indian Council of Medical Research, and this work constitutes a part of his PhD thesis.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shyam, H., Singh, N., Kaushik, S. et al. Centchroman induces redox-dependent apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in human endometrial cancer cells. Apoptosis 22, 570–584 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1346-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1346-6